[week17] 2021/11/22
강의 리뷰
모델최적화 1강 - 최적화 소개
- 경량화의 목적
- on device limitation:
- Power usage(battery)
- RAM Memory usage
- storage
- computing power - on cloud
: 배터리, 저장공간, 연산능력의 제약은 줄어드나, latency와 throughput의 제약이 존재 - computation as a key component of AI progress
: 모델의 연산량(크기)가 점점 증가해간다.
- on device limitation:
- 경량화,최적화의 종류
(네트워크 구조 관점)
- Efficient Architecture Design(+AutoML;Neural architecture search(NAS))
: 사람의 직관보다 상회하는 성능의 모듈들을 찾아낼수 있음
- Network Pruning(가지치기)
: 중요도가 낮은 파라미터를 제거하는 것, 좋은 중요도를 정의, 찾는것이 주요 연구 토픽중 하나.
- structured pruning
: 파라미터를 그룹단위로 pruning하는 기법들을 총칭(그룹;channel/filter,layer등), Dense computation에 최적화된 소프트웨어 또는 하드웨어에 적합한 기법
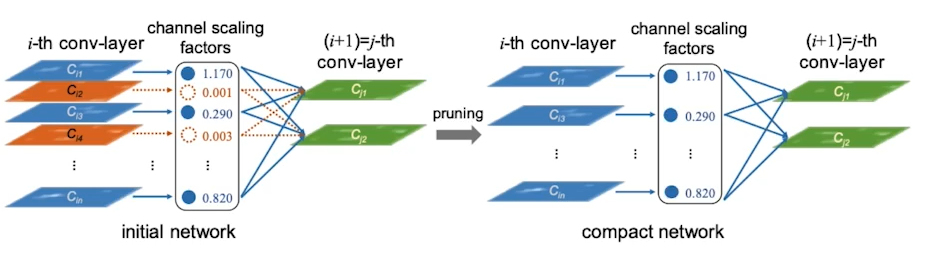
- unstructured pruning
: 파라미터를 각각 독립적으로 prunin하는 기법, pruning을 수행할수록 네트워크 내부의 행렬이 점차 희소(sparse)해짐. srtuctured pruning과 달리 sparse computation에 쵲거화된 소프트웨어 또는 하드웨어에 적합한 기법.
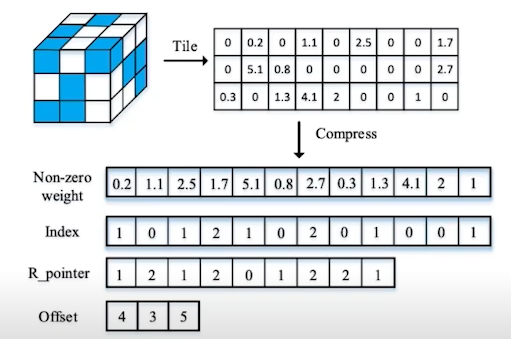
- Knowledge Distillation
: 학습된 큰 네트워크를 작은 네트워크의 학습 보조로 사용하는 방법. soft targets(soft outouts)에는 ground truth보다 더 많은 정보를 담고 있음.

- Matrix/Tensor Decomposition
: 하나의 Tensor를 작은 Tensor들의 operation들의 조합(합,곱)으로 표현하는것. Cp decomposition:rank 1 vector들의 outer product의 합으로 tensor를 approximation.
(Hardware 관점)
- Network Quantization
: 일반적인 float 32데이터타입의 Network의 연산과정을 그보다 작은 크기의 제이터 타입으로 변환하여 연산을 수행. 사이즈 감소, 성능 약간 하락, 속도 향상추세
- Network Compiling
: 학습완료된 Network를 deploy하려는 target hardware에서 inference가 가능하도록 compile하는 것. 속도 향상. ex) TensorRT,Tflite,TVM.... compile과정에서, layer fusion(graph optimization)등의 최적화가 수행됨. layer fusion의 조합에 따라 성능차이가 발생.모델 최적화 3강 - 작은 모델, 좋은 파라미터 찾기: AutoML이론
- AutoML의 문제 정의
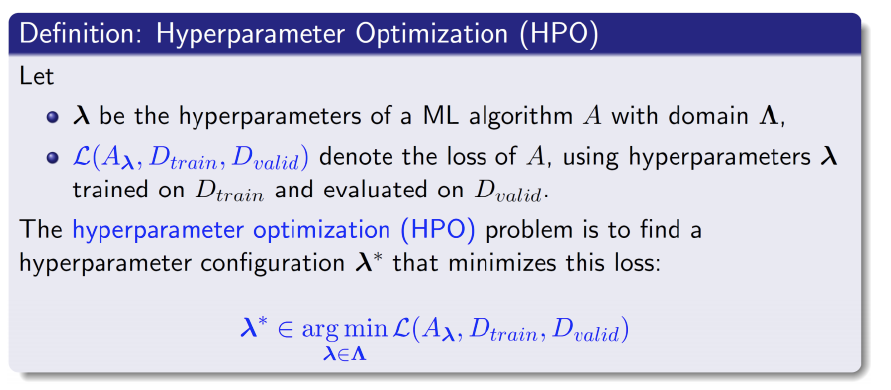
- DL model Configuration
- 주요 타입 구분
- categorical: optimizer, module(conv,bottleneck,...)
- continuous: learning rate, regularizer param,
- integer: batch_size,epochs,... - Conditional: 한 configuration에 따라 search space가 달라진다.
- 주요 타입 구분
- AutoML Pipeline
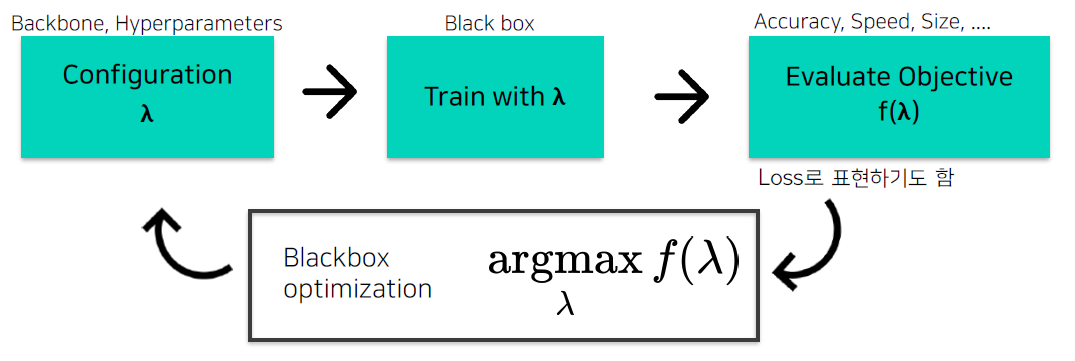
- Bayesian Optimization(BO) with Gaussian process regression
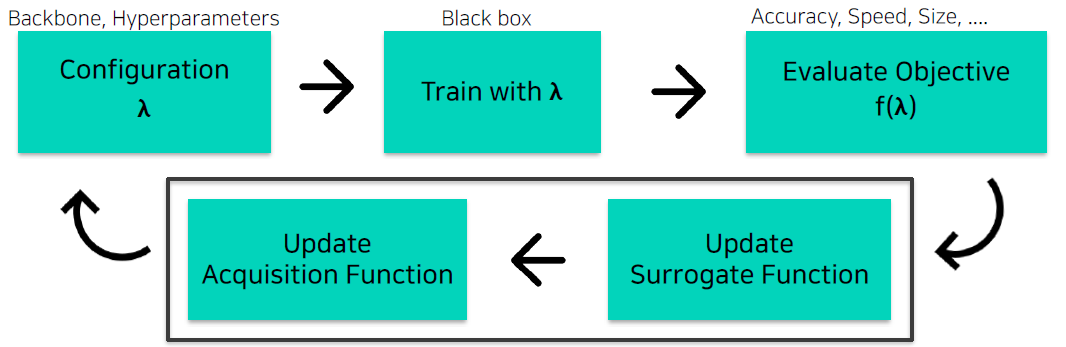
: 매 iteration마다,
1. 를 sample(observation)
2. 해당 sample(configuration)로 DL모델을 학습
3. objective를 계산
4. surrogate model 업데이트
5. Acquisition function 업데이트- Surrogate Model(function): f()의 regression model
- Objective f()값을 예측하는 모델
- objective를 estimate하는 surrogate model을 학습, 다음 좋은 를 선택하는 기준으로 사용
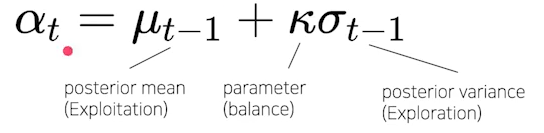
- 대표적인 surrogate model로는 gaussian process regression(GPR) Model - Acquisition Function: 다음은 어디를 trial하면 좋을지
- surrogate model의 output으로부터, 다음시도해보면 좋을 를 계산하는 함수
- Exploration(불확실한 지점) vs Exploitation(알고있는 가장 좋은 곳)
- Aquisition function의 max지점을 다음 iteration에서 trial
ex) Uper Confidence Bound(UCB)
- Surrogate Model(function): f()의 regression model
- Bayesian Optimization(BO) with Tree-structured Pasrzen Estimator
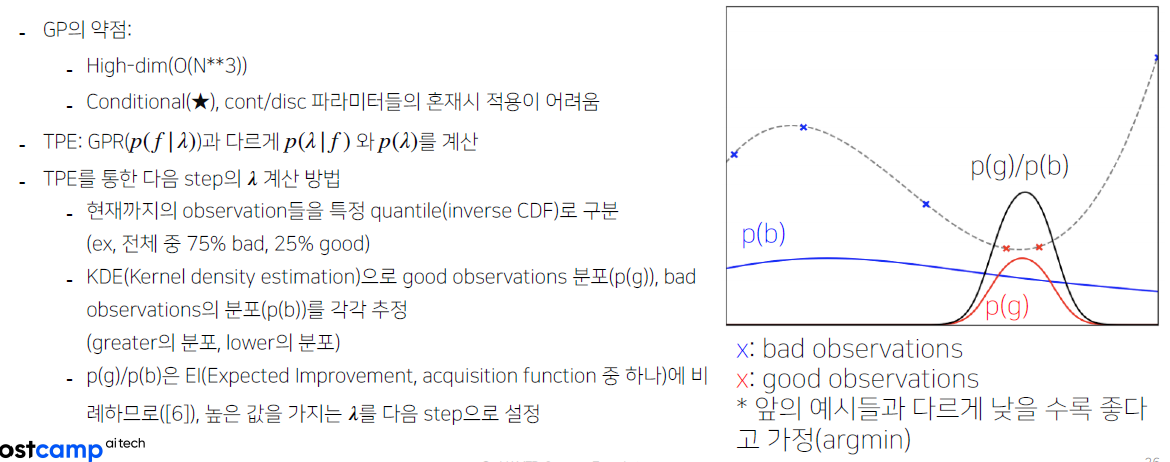
- 한계점
- 로 학습을 반복하는 과정이 오래걸린다.
