LLM: Finetuned Language Models Are Zero-shot Learners (FLAN)
FLAN
2021.09
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2109.01652
github: https://github.com/google-research/FLAN
abstract
FLAN은 [in-context learning을 적용한 few-shot learning] 대신 [instruction tuning을 사용한 zero-shot learning]의 성능을 향상시킨다. unseen task에 대한 모델의 zero-shot 성능 향상에 집중했다.
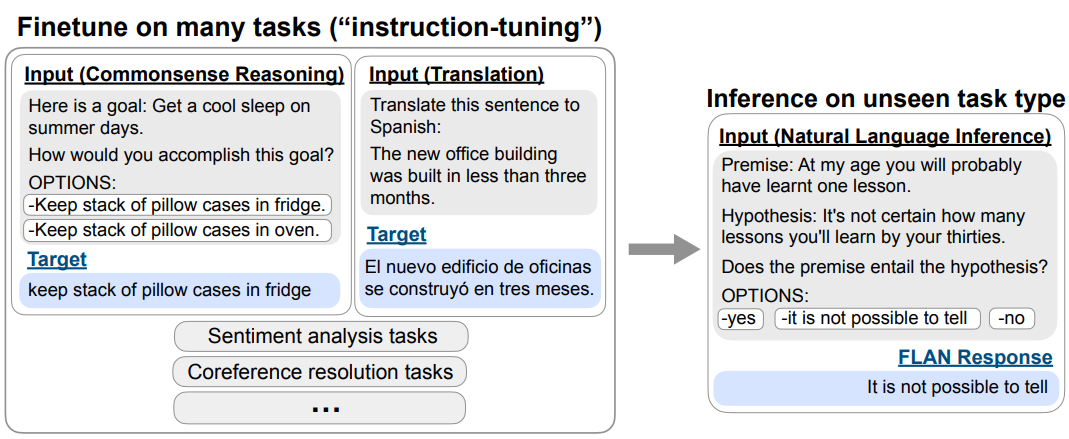
GPT-3는 zero-shot성능이 few-shot 성능보다 현저히 떨어졌는데, FLAN은 이를 개선시켰다고 볼 수 있다. 137B zero-shot FLAN은 unseen task에 대해 zero-shot 175B GPT-3을 25개 중 20개의 데이터셋에서 능가했다. ANLI, RTE, BoolQ, AI2-ARC 등의 데이터셋에 대해서는 few-shot GPT-3보다 성능이 좋았다고 한다.
Ablation studies reveal that number of finetuning datasets, model scale, and natural language instructions are key to the success of instruction tuning.
instruction tuning에 중요한 것은 fine-tuning에 사용된 데이터셋의 수, 모델의 크기, 자연어로 된 지시문이다.
+) ablation -> 머신러닝이나 딥러닝 모델의 특정 요소를 제거해서 그것이 모델 성능에 미치는 영향을 분석하는 연구 기법
추가로, unseen task는 nlp dataset들을 태스크 유형별로 클러스터로 나누고 테스트해보고 싶은 task 클러스터를 제외한 나머지를 학습시키는 방식으로 실험이 진행되었는데, 이때 number of task clusters이 많을수록 모델 성능이 개선된다는 것을 발견했다.
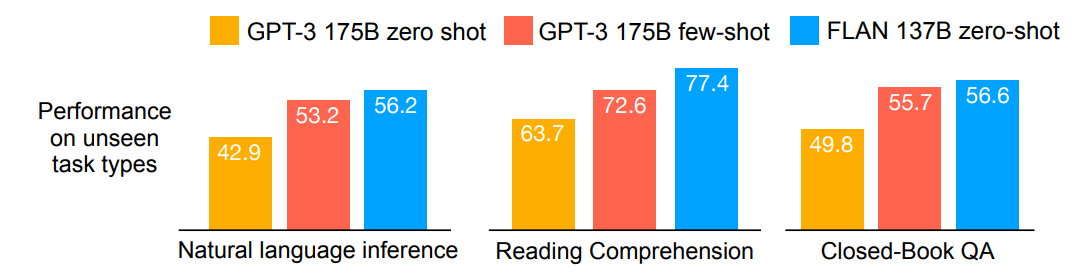
위의 그래프를 보면 NLI 등 세 개의 unseen task type에 대해 zero-shot FLAN이 GPT-3를, 심지어는 few-shot learned 모델을 능가하고 있다는 것을 알 수 있다.
introduction
In this paper, we explore a simple method to improve the zero-shot performance of large language models, which would expand their reach to a broader audience. We leverage the intuition that NLP tasks can be described via natural language instructions, such as “Is the sentiment of this movie review positive or negative?” or “Translate ‘how are you’ into Chinese.” We take a pretrained language model of 137B parameters and perform instruction tuning—finetuning the model on a mixture of more than 60 NLP datasets expressed via natural language instructions. We refer to this resulting model as FLAN, for Finetuned Language Net.

단순히 지시문 만으로 작업을 수행하는 데에 있어 높은 성능
task & templates
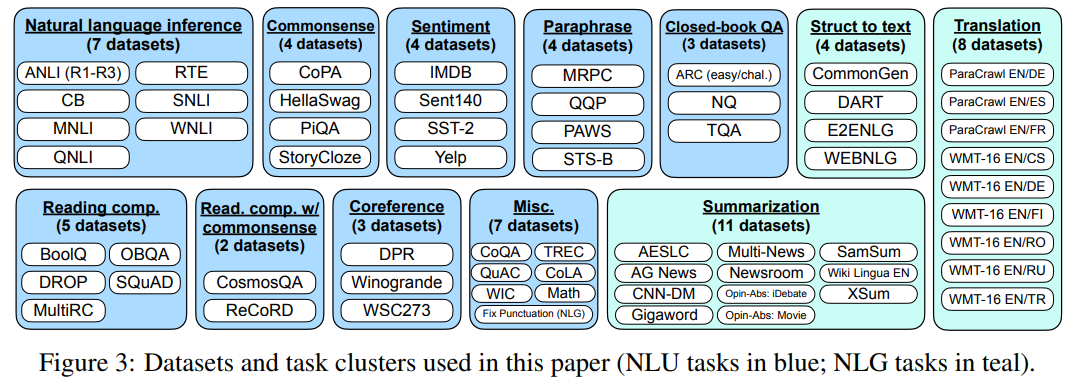
연구 커뮤니티의 데이터셋을 instruction form으로 변형해서 사용했다고 함
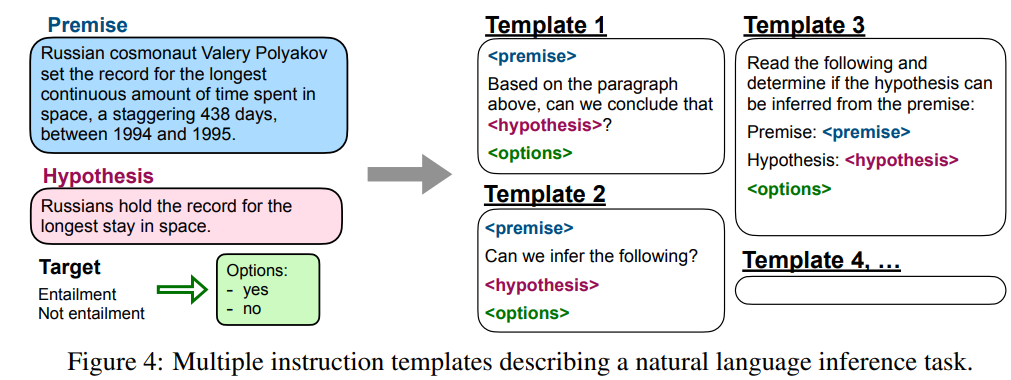
각 데이터셋에 대해 10개의 다른 탬플릿을 구성함
그중 최대 3개까지 데이터셋과 상관없는 (turned the task around) 탬플릿을 구성함
-> 과적합 방지, 일반화 키움
ex. sentiment(감정) 데이터셋을 가지고 영화 리뷰 생성하라는 instruction
supervised learning이라고 한다.
architecture는 T5를 그대로 썼다고 한다
evaluation
62개의 데이터셋을 12개의 task 클러스터로 나눠서 학습
Zero shot: task A에 대한 테스트를 진행할 때는 나머지 11개의 task 클러스터만 학습시킴
C개의 task 클러스터에 대해 평가하고 싶을 때 c개의 모델을 instruction tuning 해야 한다
Classification
분류 task의 경우, yes-no 관련된 답변에 대해 확률분포가 분산되는걸 막기 위해 출력 분포를 측정하는 방식은 사용하지 않는다
options 토큰을 삽입하고 그 이후에 보기 입력을 줌으로써 모델이 어떤 답변을 생성해야 하는지 알려준다
result
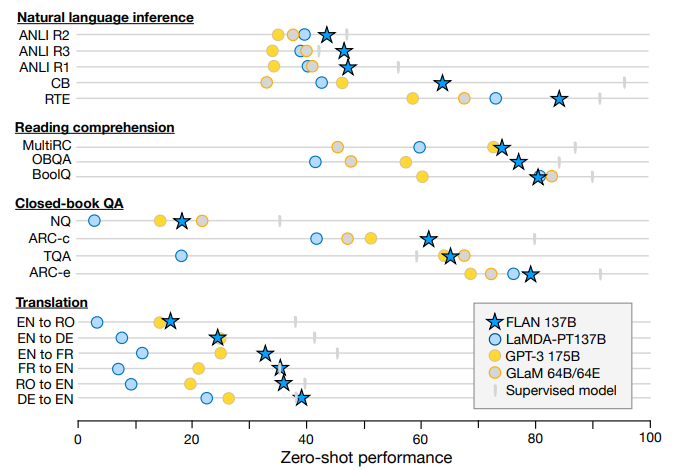
NLI task에 대해서는 대부분 가장 좋은 성능
다른 dataset들은 학습했어도 테스트하고자 하는 task+dataset 모두 학습을 하지 않은 상태이기 때문에 zero-shot 조건은 만족한다
Instruction tuning의 한계점: 성능을 크게 향상시키지는 못했다
눈여겨볼 점
Although we see strong results for the above task clusters, one limitation with instruction tuning is that it does not improve performance for many language modeling tasks (e.g., commonsense reasoning or coreference resolution tasks formulated as sentence completions). For seven commonsense reasoning and coreference resolution tasks (see Table 2 in the Appendix), FLAN only outperforms LaMDA-PT on three of the seven tasks. This negative result indicates that when the downstream task is the same as the original language modeling pre-training objective (i.e., in cases where instructions are largely redundant), instruction tuning is not useful.
FLAN 같은 모델은 기본적으로 pre-training을 거친다.
instruction tuning은 사전 학습된 모델을 fine-tuning하는 과정이다.
연구진이 특정 task에 대한 학습을 시키지 않았어도 그게 사전 학습되는 내용에 포함되어 있으면 이미 학습된거기 때문에(FLAN은 파인튜닝 없이도 그걸 잘 수행할 수 있는 상태였음) 사전학습 외의 학습(fine-tuning)이 성능을 개선시키지는 못한다
-> instruction tuning의 강점은 모델이 보지 못한 새로운 작업에 대한 generaliztion 능력을 키우는 데에 있다!
결론: instruction tuning을 통해 더 적은 파라미터 수로도 few-shot GPT-3를 능가한 zero-shot FLAN 모델~