What is Stack?
- Last-in-first-out (LIFO)
- push( ) : 삽입, pop( ) : 삭제
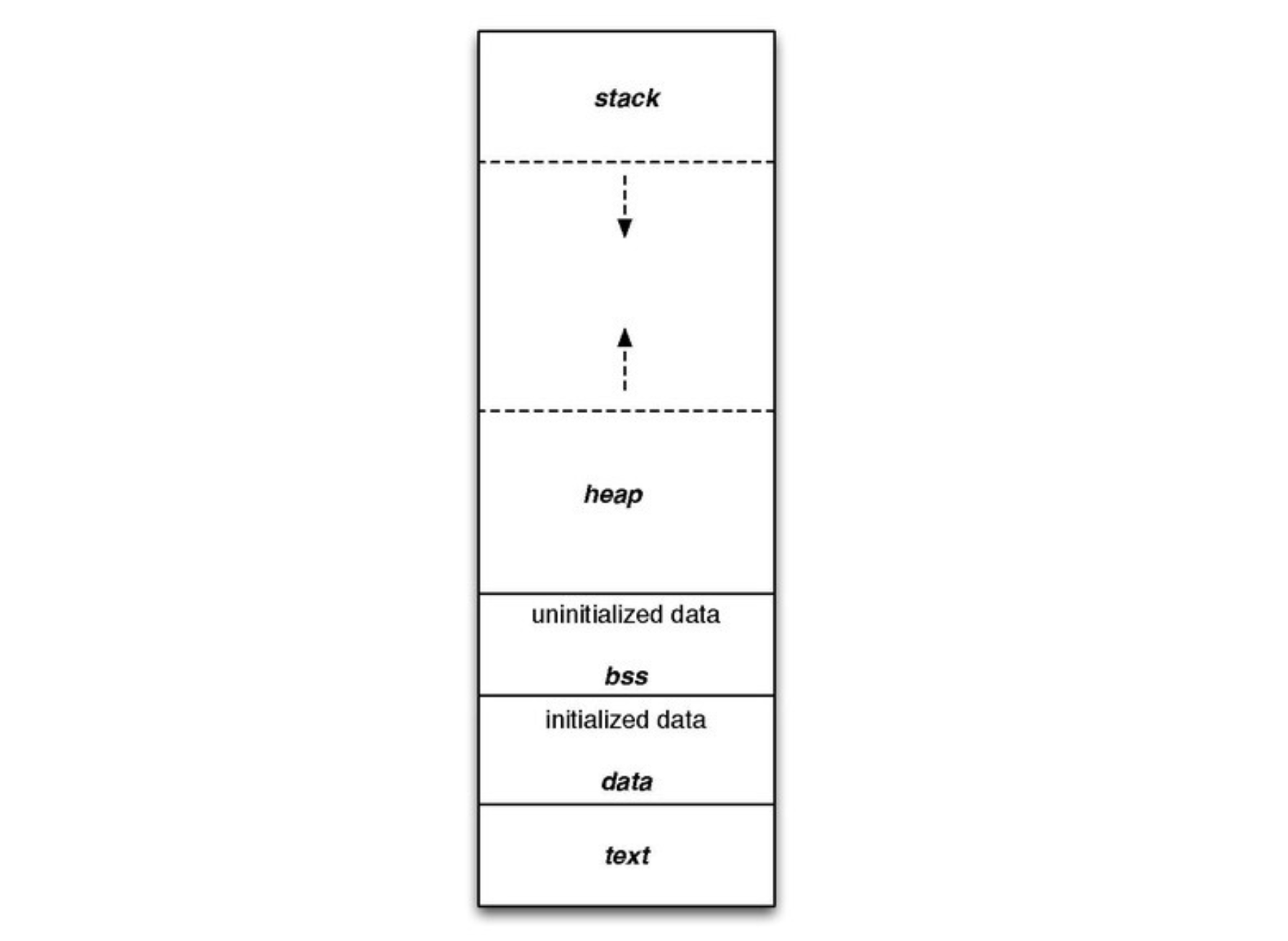
- Process의 memory 영역은 Code, Data, Heap, Stack 네 개의 segment로 이루어져있다.
이 중 stack에는 local variable, parameter, return address 등을 저장한다. word의 크기 단위로 저장한다. - Stack Pointer는 stack의 top element word의 시작 주소를 가리킨다.
- Address가 큰 부분부터 채워넣는 방식, push하고 stack pointer를 증가시키는 방식으로 생각하자.
Dynamic Memory Allocation of Local Variables
다음 코드를 수행할 때 runtime stack을 확인해보자.
main()
{
int a = 2, b = 13;
int res;
res = add(a,b);
}
int add(int x, int y)
{
int r;
r = x + y;
return r;
}C source code를 compile했을 때 다음과 같은 assembly code를 확인할 수 있다.
main:
pushl %ebp ;push old ebp
movl %esp, %ebp ;new ebp
subl $12, %esp ;space for local variables, a,b, and res
movl $2, -4(%ebp) ;a,b initialization
movl $13, -8(%ebp)
movl -8(%ebp), %eax ;parameter y for function add
pushl %eax
movl -4(%ebp), %eax ;parameter x for function add
pushl %eax
call add
addl $8, %esp ;return space for parameters of function add
movl %eax, %eax ;return value from function add
movl %eax, -12(%ebp)
.L1:
movl %ebp, %esp ;return space for local variables
popl %ebp ;pop old ebp
ret ;pop old eip and return
add:
pushl %ebp ;push old ebp
movl %esp,%ebp ;new ebp
subl $4,%esp ;space for local variable, r
movl 8(%ebp),%eax
movl 12(%ebp),%edx
leal (%edx,%eax),%ecx ;add
movl %ecx,-4(%ebp)
movl -4(%ebp),%edx ;move it to r
movl %edx,%eax ;return value
jmp .L2
.align 4
.L2:
movl %ebp, %esp ;return space for local variable
popl %ebp ;pop old ebp
ret ;pop old eip and return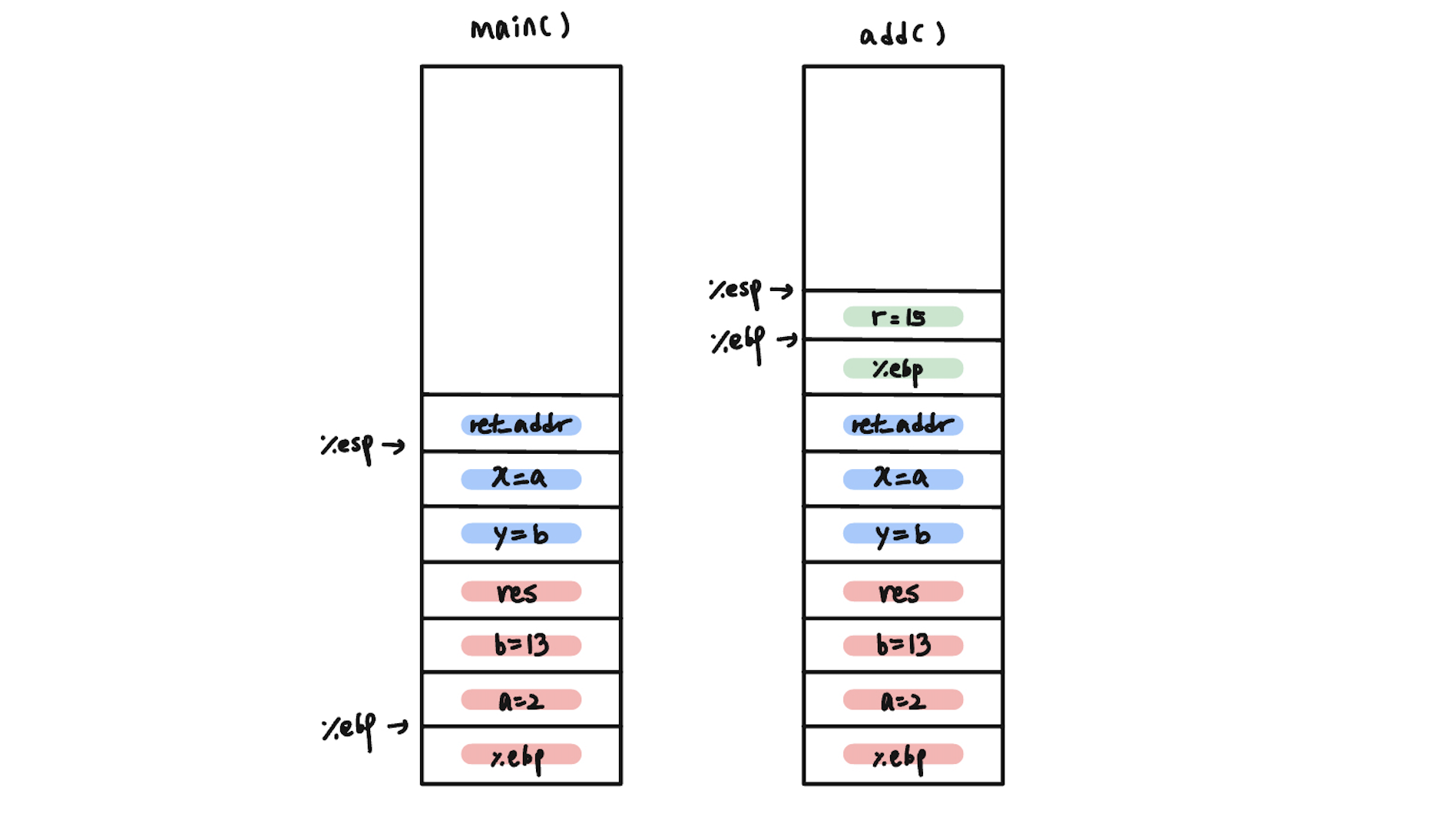
함수가 call 되었을 때
1) push old ebp
2) 현재 %esp로 %ebp를 옮긴다
3) local variable을 위한 공간확보
다른 함수 call할 때
1) 넘겨줄 parameter를 위한 공간 확보 및 assign
2) push ret_addr
3) 해당 함수로 jump
함수 return 할때
1) local variable을 위한 공간 반환
2) old ebp를 pop해서 %ebp에 저장
3) old eip를 pop해서 jump