코어 자바스크립트 책을 읽고 배운 내용을 바탕으로 작성되었다.
📌 클래스
class: 객체 지향 프로그래밍에서 구체적인instance를 생성하기 위해 변수와 메소드를 정의하는 일종의 틀이다.instance: 클래스를 통해 만든 객체, 클래스의 속성을 지니는 실존하는 개체 (구체적인 예시)superclass: 상위 클래스,subclass: 하위 클래스- 하위 클래스는 상위 클래스의 속성을 상속하면서 더 구체적인 요건이 추가 또는 변경된다.
📌 자바스크립트의 클래스 (ES5 기준)
- 자바스크립트는 프로토타입 기반 언어이고 ES5에서는 생성자 함수와 프로토타입, 클로저를 사용하여 객체 지향 프로그래밍을 구현했다.
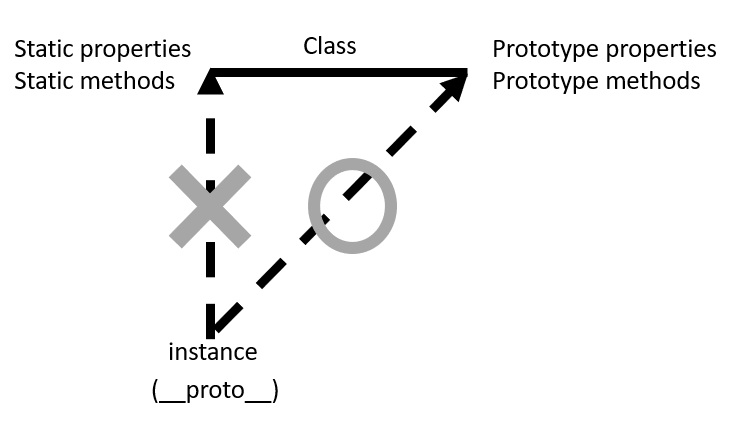
class의 멤버 (프로퍼티, 메서드) 중instance가 상속하는지 (참조하는지)에 대한 여부에 따라static member와prototype member로 나뉜다.
// Constructor (Class)
const Retangle = function (width, height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
// prototype method
Rectangle.prototype.getArea = function () {
return this.width * this.height;
}
// static method
Rectangle.isRectangle = function (instance) {
return instance instanceof Rectangle && instance.width > 0 && instance.height> 0;
}
const rect1 = Rectangle(3, 4);
console.log(rect1.getArea()); // 12
console.log(rect1.isRectangle(rect1)); // Error
console.log(Rectangle.isRectangle(rect1)); // trueprototype method
getArea메서드는Constructor의prototype프로퍼티 내부에 있는 메서드이므로prototype프로퍼티는 참조하고 있는instance의__proto__프로퍼티를 통해getArea메서드를 호출할 수 있다.- 이때
__proto__프로퍼티는 생략 가능하므로instance에서 직접 호출할 수 있다. getArea메서드처럼Constructor의prototype프로퍼티 내부에 있어instance에서 직접 호출할 수 있는 메서드를prototype method라고 한다.
static method
- 반면,
isRectangle메서드는Constructor의prototype프로퍼티 내부에 있지 않는static method이므로instance에서 직접 호출할 수 없다. - 실제로
rect1인스턴스에서isRectangle메서드를 검색할 때 우선rect1에 해당 메서드가 있는지 검색하고, 없으니rect1.__proto__를 검색하고 없으니까,rect1.__proto__.__proto__(= Object.prototype)를 검색한다. (Prototype Chain을 통해 검색) static method는 생성자 함수를 통해서만 호출할 수 있다.
📌 클래스 상속
Prototype Chain을 활용해 클래스 상속을 구현할 수 있다.
예시
const Retangle = function (width, height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
Rectangle.prototype.getArea = function () {
return this.width * this.height;
}
const rect1 = Rectangle(3, 4);
console.log(rect1.getArea()); // 12
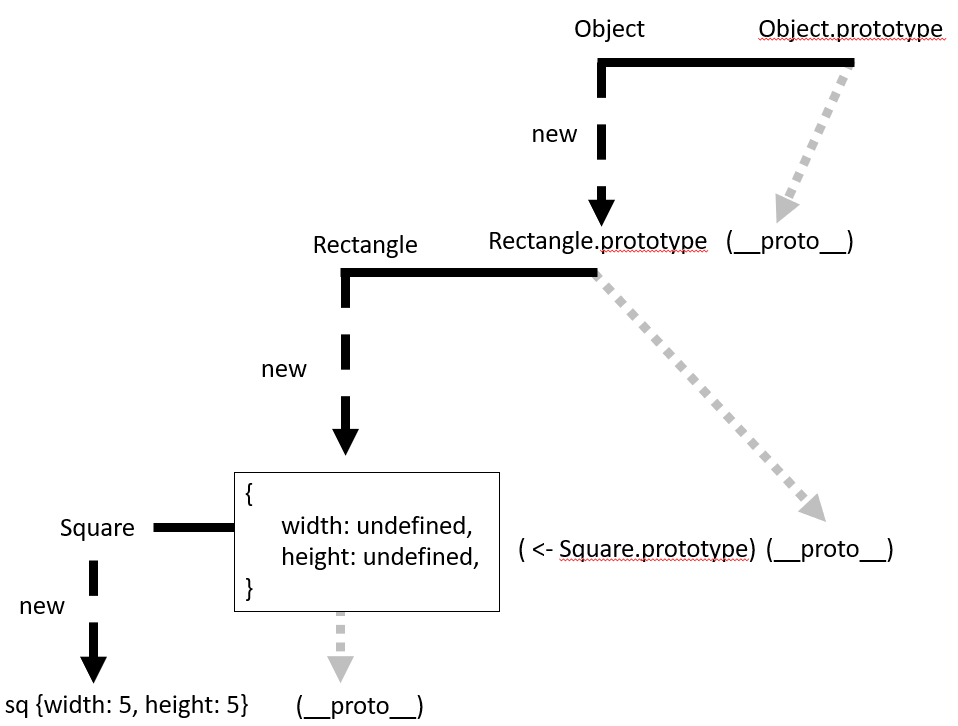
const Square = function (width) {
Rectangle.call(this, width, width);
}
Square.prototype = new Rectange();
const sq = new Square(5);Rectangle.prototype내부의 메서드를 상속받기 위해Square.prototype객체에Rectangle instance부여sq.__proto__=Square.prototype=Rectangle's instance
- 문제 1 :
Square.prototype에 값이 들어있다.- 먄약 이후에 임의로
Square.prototype.width (또는 height)에 값을 부여하고sq.width (또는 height)를 삭제한다면Prototype Chaining에 의해 엉뚱한 값이 나올 수 있다.
- 먄약 이후에 임의로
- 문제 2:
sq.constructor==Rectanglesq.__proto__.constructor=Square.prototype.constructor=Rectangle
💡 하위 클래스를 삼을 생성자 함수의 prototype에 상위 클래스의 instance를 부여하는 것만으로 기본적인 클래스 상속을 구현할 수 있지만 구조적으로 안전성이 떨어진다.
📙 클래스에 구체적인 데이터를 지니지 않게 하기
1) 첫번째 방법: 하위 클래스를 삼을 생성자 함수의 prototype에 상위 클래스의 instance를 부여하고 나서 하위 클래스의 prototype 내부에 존재하는 프로퍼티들을 전부 지우고 하위 클래스의 prototype를 freeze하는 방법
const extendClass1 = function (SuperClass, SubClass, subMethods){
SubClass.prototype = new SuperClass();
for (let prop in SubClass.prototype){
if (SubClass.prototype[prop].hasOwnProperty(prop)){
delete SubClass.prototype[prop];
}
}
if (subMethods){
for (let method in subMethods){
SubClass.prototype[method] = subMethods[method];
}
}
Object.freeze(SubClass.prototype);
return SubClass;
}2) 두번째 방법: 좀 더 대중적인 방법으로 하위 클래스의 prototype에 직접 상위 클래스의 instance를 부여하는 대신 아무런 프로퍼티를 생성하지 않는 빈 생성자 함수(Bridge)를 하나 더 만들어서 빈 생성자 함수의 prototype에 상위 클래스의 prototype를 부여하고, 하위 클래스의 prototype에는 Bridge의 instance를 할당한다.
const extendClass2 = (function (SuperClass, SubClass, subMethods){
const Bridge = function () {};
return function (){
Bridge.prototype = SuperClass.prototype;
SubClass.prototype = new Bridge ();
if (subMethods){
for (let method in subMethods){
SubClass.prototype[method] = subMethods[method];
}
}
Object.freeze(SubClass.prototype);
return SubClass;
};
})();- 즉시실행함수 내부에서 빈 생성자 함수
Bridge를 만들고 클로저를 활용하여Bridge를 기억하는 함수를 리턴함으로써 불필요한 메모리에 불필요한 함수 선언을 줄였다.
3) 세번째 방법: Object.create() 이용
Object.create()는proto라는 인자를 반드시 필요로 한데 이 인자는 새로 만든 객체의 프로토타입이어야 할 객체이다.- 하위 클래스의
prototype의__proto__객체가 상위 클래스의prototype을 바라보되, 상위 클래스의instance가 되지 않는다.
const extendClass3 = function (SuperClass, SubClass, subMethods){
SubClass.prototype = Object.create(SuperClass.prototype);
if (subMethods){
for (let method in subMethods){
SubClass.prototype[method] = subMethods[method];
}
}
Object.freeze(SubClass.prototype);
return SubClass;
}아이디어
💡
subclass의prototype내부의__proto__객체가superclass의prototype을 참조하고,subclass의prototype에는 불필요한 인스턴스 프로퍼티가 남아 있지 않도록 상속을 구현하면 된다.
📙 constructor 복구하기
subclass의prototype객체 내부의constructor프로퍼티가 원래의subclass를 바라보도록 하면 된다.
const extendClass1 = function (SuperClass, SubClass, subMethods){
SubClass.prototype = new SuperClass();
for (let prop in SubClass.prototype){
if (SubClass.prototype[prop].hasOwnProperty(prop)){
delete SubClass.prototype[prop];
}
}
SubClass.prototype.constructor = SubClass;
if (subMethods){
for (let method in subMethods){
SubClass.prototype[method] = subMethods[method];
}
}
Object.freeze(SubClass.prototype);
return SubClass;
}const extendClass2 = (function (SuperClass, SubClass, subMethods){
const Bridge = function () {};
return function (){
Bridge.prototype = SuperClass.prototype;
SubClass.prototype = new Bridge ();
SubClass.prototype.constructor = SubClass;
if (subMethods){
for (let method in subMethods){
SubClass.prototype[method] = subMethods[method];
}
}
Object.freeze(SubClass.prototype);
return SubClass;
};
})();const extendClass3 = function (SuperClass, SubClass, subMethods){
SubClass.prototype = Object.create(SuperClass.prototype);
SubClass.prototype.constructor = SubClass;
if (subMethods){
for (let method in subMethods){
SubClass.prototype[method] = subMethods[method];
}
}
Object.freeze(SubClass.prototype);
return SubClass;
}📙 상위 클래스 접근 수단 제공
- 하위 클래스의 메서드에서 상위 클래스의 실행 결과를 바탕으로 추가적인 작업을 수행하고 싶을 때가 있다.
- 다른 객체 지향 언어들의 클래스 문법 중 하나인
super구현하기 - 상위 클래스 접근 수단인
super메서드 추가
const extendClass = function (SuperClass, SubClass, subMethods){
SubClass.prototype = Object.create(SuperClass.prototype);
SubClass.prototype.constructor = SubClass;
SubClass.prototype.super = function (propName){
const self = this;
if (!propName) return function (){
SuperClass.apply(self, arguments);
};
const prop = SuperClass.prototype[propName];
if (typeof prop !== "function") return prop;
return function () {
return prop.apply(self, arguments);
};
}
if (subMethods){
for (let method in subMethods){
SubClass.prototype[method] = subMethods[method];
}
}
Object.freeze(SubClass.prototype);
return SubClass;
}
const Rectangle = function (width, height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
Rectangle.prototype.getArea = function () {
return this.width * this.height;
}
const Square= extendClass(
Rectangle,
function (width){
this.super()(width, width);
}, {
getArea: function (){
console.log('size if :', this.super("getArea")());
}
}
);
const sq = new Square(10);
sq.getArea(); // size is : 100 (subclass의 메서드 실행)
console.log(sq.super("getArea")()); // 100 (superclass의 메서드 실행)superclass의 생성자 함수에 접근하고자 할 때는this.super(),superclass의 프로토타입 메서드에 접근하고자 할 때는this.super(propName)와 같이 사용하면 된다.
📌 ES6의 클래스 및 클래스 상속
📙 ES5와 ES6 클래스 문법 비교
const ES5 = function (name) {
this.name = name;
}
ES5.staticMethod = function () {
return this.name + 'staticMethod';
}
ES5.prototype.method = function () {
return this.name + 'method';
}
const ES6 = class {
// 생성자
constructor (name) {
this.name = name;
}
// static method : 생성자 함수(클래스)만이 호출할 수 있음.
static staticMethod () {
return this.name + 'staticMethod';
}
// prototype method
method () {
return this.name + 'method';
}
};✨ 클래스 생성
- 클래스 선언과 클래스 표현식 두가지 방식으로 클래스를 생성할 수 있다.
- 클래스 선언 및 클래스 표현식은 호이스팅되지 않으므로 클래스에 접근하기 전에 클래스를 선언하지 않으면
reference error가 발생한다.
// 클래스 선언
class Person {
}
// 클래스 표현식
const person = class Person {
};- 생성자는 하나만 존재해야 한다. 클래스에 생성자가 두 개 이상 존재하면
syntax error가 발생한다.
예시
class Person {
constructor (name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
greet() {
console.log(`Hi my name is ${this.name} and I'm ${this.age} years old`);
}
farewell() {
console.log("goodbye friend");
}
}
const alberto = new Person ("Alberto", 26);
alberto.greet(); // Hi my name is Alberto and I'm 26 years old
alberto.farewell(); // goodbye friend✨ 정적 메서드
static method : 생성자 함수 (클래스) 통해서만 접근할 수 있음. 인스턴스에서 호출할 수 없는 메서드
- 메서드 앞에
static키워드를 붙여 정적 메서드 생성
class Person {
constructor (name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
static info () {
console.log("I am a Person class, nice to meet you");
}
}
const alberto = new Person ("Alberto", 26);
alberto.info(); // TypeError
Person.info(); // I am a Person class, nice to meet you✨ set과 get
setter와 getter 메서드를 사용하여 클래스 내에 값을 설정하거나 가져올 수 있다.
- 메서드 앞에
set이나get키워드를 붙여setter나getter메서드 생성
class Person {
constructor (name, surname){
this.name = name;
this.surname = surname;
this.nickname = "";
}
set nicknames(value){
this.nickname = value;
console.log(this.nickname);
}
get nicknames(){
console.log(`Your nickname is ${this.nickname}`);
}
}
const alberto = new Person("Alberto", "Montalesi");
// setter 호출
alberto.nicknames = "Albi"; // Albi
// getter 호출
alberto.nicknames; // "Your nickname is Albi"✨ 클래스 상속하기
extends키워드를 이용하여 클래스 상속을 구현할 수 있다. (모든 속성과 메서드를 상속함)
class Person {
constructor (name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
greet() {
console.log(`Hi my name is ${this.name} and I'm ${this.age} years old`);
}
}
class Adult extends Person {
constructor (name, age, work){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.work = work;
}
}
const alberto = new Adult("Alberto", 26, "softward developer"); // ReferenceErrorAdult클래스는Person으로부터 상속받는 클래스이기 때문에Adult를 만들기에 앞서Person을 만들어야 한다.- 따라서 상속받는 클래스의 생성자 내부에서
super()를 호출하여 상위 클래스를 생성해야 한다.
class Person {
constructor (name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
greet() {
console.log(`Hi my name is ${this.name} and I'm ${this.age} years old`);
}
}
class Adult extends Person {
constructor (name, age, work){
super(name, age);
this.work = work;
}
}또 다른 예시
const Rectangle = class {
constructor(width, height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
getArea() {
return this.width * this.height;
}
};
const Square = class {
constructor(width) {
super(width, width);
}
getArea() {
console.log('size is: ', super.getArea());
}
};constructor내부에서super키워드를 함수처럼 사용하여superclass의constructor실행한다.constructor를 제외한 다른 메서드에서는super키워드를 객체처럼 사용할 수 있고, 이때 객체는Superclass.prototype을 바라본다.- 이때 호출한 메서드의
this는super가 아니라 원래의this를 그대로 따른다.
📌 정리
class는 어떤 사물의 공통 속성을 모아 정의한 추상적인 개념 (구체적인instance를 생성하기 위해 변수와 메소드를 정의하는 일종의 틀)이고,instance는 클래스의 속성을 지니는 구체적인 사례이다.- 상위 클래스 (
superclass)의 조건을 충족하면서 더 구체적인 조건이 추가된 것이 하위 클래스 (subclass)이다. - 클래스 (생성자 함수)의
prototype내부에 정의된 메서드를prototype method라고 하고, 이들은instance가 마치 자신의 것처럼 호출할 수 있다. - 반면 클래스 (생성자 함수)에 직접 정의한 메서드를
static method라고, 이들은 인스턴스에서 호출할 수 없고, 클래스(생성자 함수)를 통해서만 호출할 수 있다. - 클래스 상속을 흉내내기 위한 세 가지 방법
subclass의prototype에superclass의instance를 부여한 다음,subclass의prototype내부 프로퍼티를 모두 삭제하는 방법- 빈 생성자 함수 (
Bridge) 활용 Object.create()이용- 위 세가지 방법 모두
subclass의prototype의constructor프로퍼티가subclass를 바라보도록 해야 한다. - 💡
subclass의prototype프로퍼티 내부의__proto__프로퍼티가superclass의prototype프로퍼티를 참조하도록 하고,subclass의prototype내부에는 불필요한 인스턴스 프로퍼티가 존재하지 않아야 한다.
- 상위 클래스에 접근할 수 있는 수단인
super구현 - ES6에서는 클래스 문법이 도입되어 전보다 쉽게 클래스를 생성하고 상속을 구현할 수 있다.
