-
64 비트 블록 암호화를 수행하는 블록 암호화 기법
-
64 비트 평문에 대응하는 64비트 암호문을 생성한다.
-
입력되는 키는 64비트이며, 패리티 비트 8개를 drop하여 56비트가 실사용된다.
-
56비트 키로부터 48비트 서브키 16개를 만들고 이를 각 라운드에서 사용한다.
-
Tables: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DES_supplementary_material
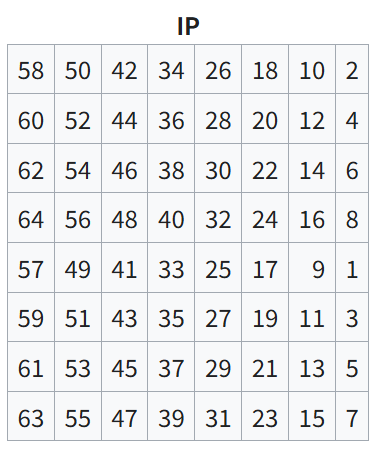
1. Initial Permutation, IP
64 비트 평문 블록은 IP를 통해서 전치된다. 비트의 순서는 IP table(Initial Permutation table)의 사전 정의된 규칙을 따라서 수행한다. IP는 첫 라운드를 시작하기 전 오직 한번만 수행된다.
(1-Based임에 유의한다.)
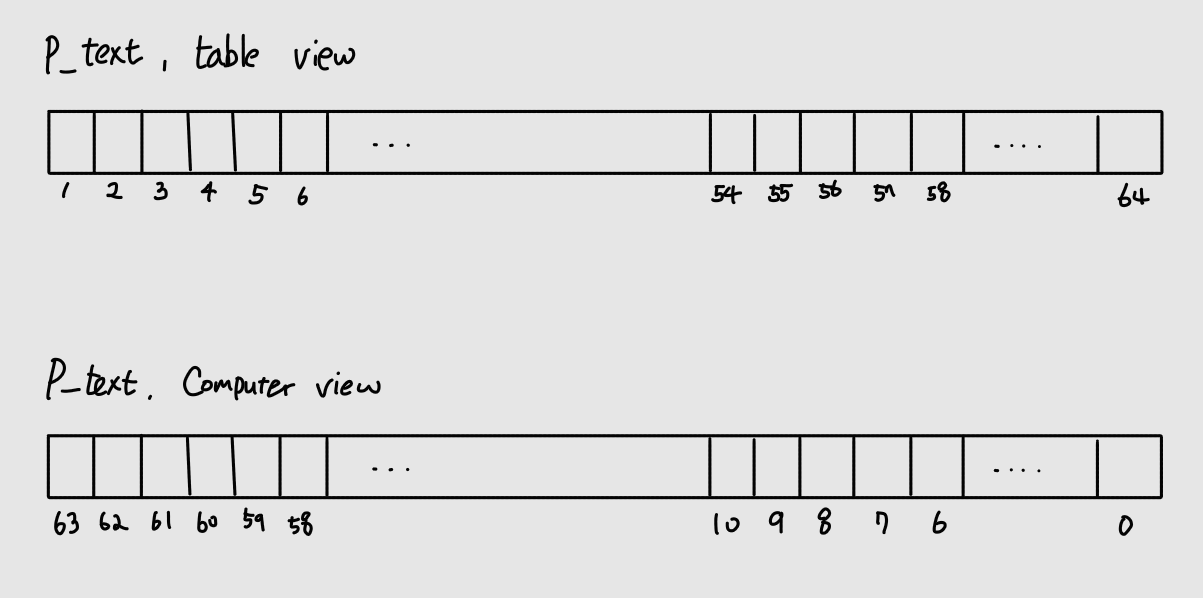
원문을 입력으로 받아서 IP 테이블에 따라 permutation을 수행한다.
테이블의 N번 비트는 사람들이 읽기 쉽게(1-Based, 왼쪽부터 1) 작성되었으므로 이를 적절하게 변경해줘야 한다.
// Initial Permutation (IP)
int ip_table[64] = {
58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18, 10, 2,
60, 52, 44, 36, 28, 20, 12, 4,
62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22, 14, 6,
64, 56, 48, 40, 32, 24, 16, 8,
57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17, 9, 1,
59, 51, 43, 35, 27, 19, 11, 3,
61, 53, 45, 37, 29, 21, 13, 5,
63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15, 7
};ip_tables[0], 58은 LSB(0th)로부터 6칸 떨어진 비트를 지목하는 것이며 맨 앞자리로 해당 비트가 전치되어야 한다는 것을 의미한다.
template<int N, int INW = 64>
inline u64 permute(u64 x, const int(&tab)[N]) {
u64 y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
y |= ((x >> (INW - tab[i])) & 1ULL) << (N - i - 1);
}
return y;
}위의 코드는 permutation을 수행하는 함수이다.
y |= ((x >> (INW - tab[i])) & 1ULL) << (N - i - 1);
LSB로부터 6칸 떨어진 비트(테이블 상 58번 비트)를 0번 비트 자리로 옮기고 1ULL(이진수로 000..1)과 &연산을 한 뒤 전치 위치로 옮긴다.
permutation은 앞으로도 여러번 수행되는데 동작은 똑같다.
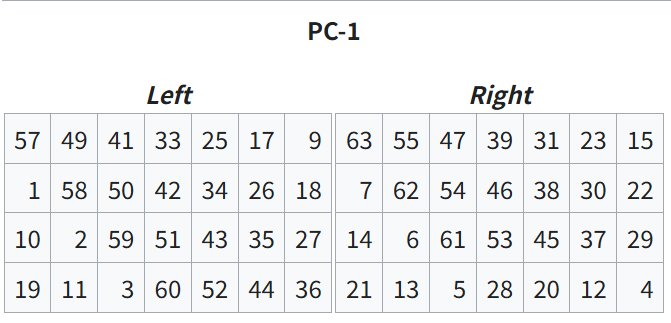
Key Transformation
PC-1 테이블을 이용하여 64비트 키를 56비트의 effective key로 만든다.
// Permuted Choice 1 (64 bits -> 56 bits), 1 Based
int pc1[56] = {
57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17, 9,
1, 58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18,
10, 2, 59, 51, 43, 35, 27,
19, 11, 3, 60, 52, 44, 36,
63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15,
7, 62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22,
14, 6, 61, 53, 45, 37, 29,
21, 13, 5, 28, 20, 12, 4
};
// Permuted Choice 2 (56 bits -> 48 bits), 1 Based
int pc2[48] = {
14, 17, 11, 24, 1, 5,
3, 28, 15, 6, 21, 10,
23, 19, 12, 4, 26, 8,
16, 7, 27, 20, 13, 2,
41, 52, 31, 37, 47, 55,
30, 40, 51, 45, 33, 48,
44, 49, 39, 56, 34, 53,
46, 42, 50, 36, 29, 32
};
64비트 키에는 패리티 비트가 포함되어있기 때문에 이를 제거하여 56비트의 키를 만들어야 한다.
패리티 비트의 위치는 8번, 16번, 24번...64번인데, PC 테이블을 보면 해당 위치는 포함되어 있지 않은 것을 알 수 있다.
// 1,2,9,16 round: 1 Bit shift. else 2 Bit shift
int rotations[16] = {
1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1
};
u32 rol28(u32 num, u32 n) {
return (((num << n) & 0x0fffffff) | (num >> (28 - n)));
}PC-1을 통해 얻은 56비트의 키를 28비트씩 분할한다. 그 후, 16개의 라운드 키를 만들기 위해서 각각 rotation을 적용한다. 이때 rotation하는 값은 라운드에 따라 다르다.
1,2,9,16 라운드는 1 비트만큼 rotation하고, 나머지 라운드는 2 비트 rotation한다.
pc-1과 pc-2는 permutation이므로 생략한다.
Feistel Rounds(1 ~ 16)
매 라운드마다 전치된(IP) 64비트 평문과 48비트 서브키가 사용된다. 전치된 64비트 평문을 LPT(Left Plain Text, 32bit)와 RPT로 분할한다.

RPT는 다음 LPT가 됨과 동시에 f(mangler function)함수에서 처리되고, 그 반환값은 LPT와 XOR 연산을 거쳐 다음 RPT가 된다.
해당 함수 f에서 수행되는 과정은 아래와 같다.
1. 확장(expansion): 32비트 데이터를 48비트로 확장함.
2. 키 혼합(key mixing): 48비트 라운드키와 XOR
3. 치환(substitution): S-box를 이용한 치환
4. 순열 또는 전치(permutation): P-box를 이용한 전치
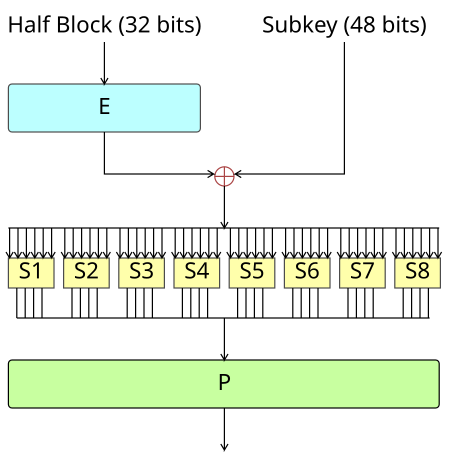
위의 복잡한 과정을 통해서 32비트 원본 데이터가 완전히 새로운 32비트의 데이터로 변형되며, 이는 비선형적인 특성을 나타낸다.
Expansion
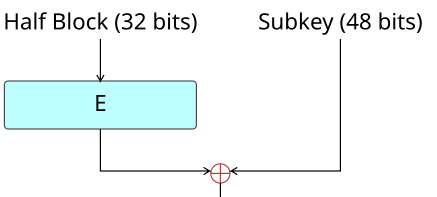
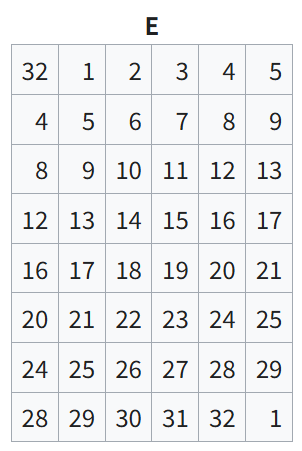
// Expansion Permutation (E-box), 32 bits -> 48 bits
int exp_table[48] = {
32, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,
16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21,
20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29,
28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 1
};
Data XOR Subkey
save = (save ^ subkey);Substitution, S-box

// DES S-boxes (S1-S8)
int s_boxes[8][4][16] = {
// S1
{
{14, 4, 13, 1, 2, 15, 11, 8, 3, 10, 6, 12, 5, 9, 0, 7},
{0, 15, 7, 4, 14, 2, 13, 1, 10, 6, 12, 11, 9, 5, 3, 8},
{4, 1, 14, 8, 13, 6, 2, 11, 15, 12, 9, 7, 3, 10, 5, 0},
{15, 12, 8, 2, 4, 9, 1, 7, 5, 11, 3, 14, 10, 0, 6, 13}
},
// S2
{
{15, 1, 8, 14, 6, 11, 3, 4, 9, 7, 2, 13, 12, 0, 5, 10},
{3, 13, 4, 7, 15, 2, 8, 14, 12, 0, 1, 10, 6, 9, 11, 5},
{0, 14, 7, 11, 10, 4, 13, 1, 5, 8, 12, 6, 9, 3, 2, 15},
{13, 8, 10, 1, 3, 15, 4, 2, 11, 6, 7, 12, 0, 5, 14, 9}
},
// S3
{
{10, 0, 9, 14, 6, 3, 15, 5, 1, 13, 12, 7, 11, 4, 2, 8},
{13, 7, 0, 9, 3, 4, 6, 10, 2, 8, 5, 14, 12, 11, 15, 1},
{13, 6, 4, 9, 8, 15, 3, 0, 11, 1, 2, 12, 5, 10, 14, 7},
{1, 10, 13, 0, 6, 9, 8, 7, 4, 15, 14, 3, 11, 5, 2, 12}
},
// S4
{
{7, 13, 14, 3, 0, 6, 9, 10, 1, 2, 8, 5, 11, 12, 4, 15},
{13, 8, 11, 5, 6, 15, 0, 3, 4, 7, 2, 12, 1, 10, 14, 9},
{10, 6, 9, 0, 12, 11, 7, 13, 15, 1, 3, 14, 5, 2, 8, 4},
{3, 15, 0, 6, 10, 1, 13, 8, 9, 4, 5, 11, 12, 7, 2, 14}
},
// S5
{
{2, 12, 4, 1, 7, 10, 11, 6, 8, 5, 3, 15, 13, 0, 14, 9},
{14, 11, 2, 12, 4, 7, 13, 1, 5, 0, 15, 10, 3, 9, 8, 6},
{4, 2, 1, 11, 10, 13, 7, 8, 15, 9, 12, 5, 6, 3, 0, 14},
{11, 8, 12, 7, 1, 14, 2, 13, 6, 15, 0, 9, 10, 4, 5, 3}
},
// S6
{
{12, 1, 10, 15, 9, 2, 6, 8, 0, 13, 3, 4, 14, 7, 5, 11},
{10, 15, 4, 2, 7, 12, 9, 5, 6, 1, 13, 14, 0, 11, 3, 8},
{9, 14, 15, 5, 2, 8, 12, 3, 7, 0, 4, 10, 1, 13, 11, 6},
{4, 3, 2, 12, 9, 5, 15, 10, 11, 14, 1, 7, 6, 0, 8, 13}
},
// S7
{
{4, 11, 2, 14, 15, 0, 8, 13, 3, 12, 9, 7, 5, 10, 6, 1},
{13, 0, 11, 7, 4, 9, 1, 10, 14, 3, 5, 12, 2, 15, 8, 6},
{1, 4, 11, 13, 12, 3, 7, 14, 10, 15, 6, 8, 0, 5, 9, 2},
{6, 11, 13, 8, 1, 4, 10, 7, 9, 5, 0, 15, 14, 2, 3, 12}
},
// S8
{
{13, 2, 8, 4, 6, 15, 11, 1, 10, 9, 3, 14, 5, 0, 12, 7},
{1, 15, 13, 8, 10, 3, 7, 4, 12, 5, 6, 11, 0, 14, 9, 2},
{7, 11, 4, 1, 9, 12, 14, 2, 0, 6, 10, 13, 15, 3, 5, 8},
{2, 1, 14, 7, 4, 10, 8, 13, 15, 12, 9, 0, 3, 5, 6, 11}
}
};
inline u32 sb_and_pb(u64 x48) {
u32 out32 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < S_BOXES; i++) {
u8 chunk = (x48 >> (42 - 6 * i)) & 0x3Fu;
int row = ((chunk & 0x20) >> 4) | (chunk & 0x01);
int col = (chunk >> 1) & 0x0F;
out32 = (out32 << 4) | s_boxes[i][row][col];
}
u32 p = permute<32, 32>(out32, p_boxes);
return p;
}48비트를 6비트씩 순서대로 8개의 S-box에 넣어서 4비트로 치환한다.
첫 6비트 청크를 101010 이라고 할 때, 양 옆 2비트 10과 가운데 4비트 0101로 나누어 이에 대응하는 치환 값을 S-Box 테이블에서 찾아야 한다.
양 옆 2비트는 row를 나타내고, 가운데 4비트는 col을 나타내므로 두 값이 교차하는 지점의 값으로 치환된다. (0 <= row <= 3) (0 <= col <= 15)
이진수 10은 2이므로 row = 2이고, 이진수 0101은 5이므로 col = 5가 된다. s1-box의 2행 5열은 6이므로 이진수로 0110이며, 4비트 치환 결과값이 된다.
위의 방식대로 6비트 청크 8개를 모두 4비트 청크 8개로 바꾸면 48비트로 확장되었던 데이터가 다시 32비트 길이가 된다.
Permutation
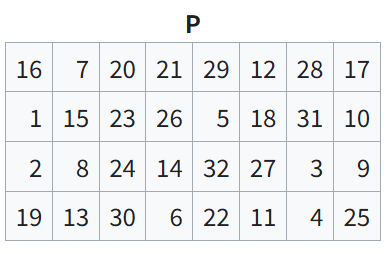
마지막으로 P 테이블을 이용하여 Permutation을 수행한다.
Final Permutation
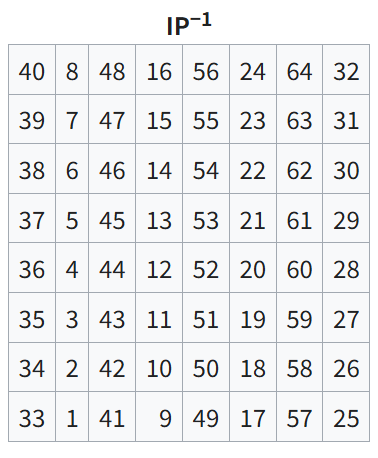
16회의 feistel rounds를 모두 완료했다면 final permutation을 수행한다. 마지막 라운드에서는 LPT와 RPT가 스왑되지 않으므로, 마지막 라운드에서 스왑했다면 스왑을 한번 더 수행하고 final permutation을 수행한다.
전체 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <math.h>
#include "DES_tables.h"
#define DES_BLOCK_BITS 64
#define DES_KEY_BITS 64
#define DES_SUBKEY_BITS 48
#define DES_HALF_BLOCK_BITS 32
#define DES_HALF_KEY_BITS 28
#define DES_ROUNDS 16
#define S_BOXES 8
typedef uint64_t u64;
typedef uint32_t u32;
typedef uint8_t u8;
template<int N, int INW = 64>
inline u64 permute(u64 x, const int(&tab)[N]) {
u64 y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
y |= ((x >> (INW - tab[i])) & 1ULL) << (N - i - 1);
}
return y;
}
u32 rol28(u32 num, u32 n) {
return (((num << n) & 0x0fffffff) | (num >> (28 - n)));
}
inline u64 expand_e(u32 r) {
u64 e = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < DES_SUBKEY_BITS; i++) {
e |= (u64)((r >> (DES_HALF_BLOCK_BITS - e_boxes[i])) & 1U) << (DES_SUBKEY_BITS - i - 1);
}
return e;
}
inline u32 sb_and_pb(u64 x48) {
u32 out32 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < S_BOXES; i++) {
u8 chunk = (x48 >> (42 - 6 * i)) & 0x3Fu;
int row = ((chunk & 0x20) >> 4) | (chunk & 0x01);
int col = (chunk >> 1) & 0x0F;
out32 = (out32 << 4) | s_boxes[i][row][col];
}
u32 p = permute<32, 32>(out32, p_boxes);
return p;
}
u32 f(u32 right, u64 subkey) {
u64 RPT_48bit = expand_e(right);
RPT_48bit = (RPT_48bit ^ subkey);
u32 res = sb_and_pb(RPT_48bit);
return res;
}
// init_round: encrypt(0), decrypt(15)
u64 feistel_rounds(u32 LPT, u32 RPT, const u64(&round_keys)[DES_ROUNDS], int init_round) {
u64 res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < DES_ROUNDS; i++) {
u32 temp_RPT = RPT;
u32 f_result = f(RPT, round_keys[abs(i - init_round)]);
RPT = f_result ^ LPT;
LPT = temp_RPT;
}
// 마지막 라운드에서는 swap하지 않음. 그러므로 한번 더 스왑
u32 temp_swap = LPT;
LPT = RPT;
RPT = temp_swap;
res = ((u64)LPT << 32) | RPT;
return res;
}
int main() {
u64 plain_text = 0x00;
u64 cipher_text = 0x00;
u64 key = 0x00; // key with parity bits
u64 round_keys[16] = { 0x00, };
printf("평문 (16진수 16자리) 입력:"); // test vector : 0x4E6F772069732074 (ASCII: "Now is the time for all ")
scanf_s("%llx", &plain_text);
printf("키 (16진수 16자리) 입력:"); // test vector : 0x0123456789ABCDEF
scanf_s("%llx", &key);
// Key schedule
u64 key_56bit = permute<56,64>(key, pc1);
u32 key_28bit_l = (u32)(key_56bit >> 28);
u32 key_28bit_r = (u32)(key_56bit & 0x0fffffff);
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
key_28bit_l = rol28(key_28bit_l, rotations[i]);
key_28bit_r = rol28(key_28bit_r, rotations[i]);
u64 subkey_48bit = 0x00;
subkey_48bit = ((u64)key_28bit_l) << 28;
subkey_48bit = (subkey_48bit | key_28bit_r);
round_keys[i] = permute<48,56>(subkey_48bit, pc2);
}
// Encryption
plain_text = permute<64, 64>(plain_text, ip_table);
u32 LPT = (u32)(plain_text >> 32);
u32 RPT = (u32)(plain_text & 0xffffffff);
//init_round: encrypt(0), decrypt(15)
u64 final_text = feistel_rounds(LPT, RPT, round_keys, 0);
cipher_text = permute<64,64>(final_text, fp_table);
// decryption
u64 permuted_cipher_text = permute<64, 64>(cipher_text, ip_table);
u32 dec_LPT = (u32)(permuted_cipher_text >> 32);
u32 dec_RPT = (u32)(permuted_cipher_text & 0xffffffff);
u64 dec_final_text = feistel_rounds(dec_LPT, dec_RPT, round_keys, 15);
u64 rec_plain_text = permute<64, 64>(dec_final_text, fp_table);
printf("암호문 (Ciphertext): 0x%016llX\n", cipher_text); // test vector : 0x3FA40E8A984D4815
printf("복호화된 평문: 0x%016llX\n", rec_plain_text);
return 0;
}tables
// Initial Permutation (IP)
int ip_table[64] = {
58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18, 10, 2,
60, 52, 44, 36, 28, 20, 12, 4,
62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22, 14, 6,
64, 56, 48, 40, 32, 24, 16, 8,
57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17, 9, 1,
59, 51, 43, 35, 27, 19, 11, 3,
61, 53, 45, 37, 29, 21, 13, 5,
63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15, 7
};
// Permuted Choice 1 (PC-1)
int pc1[56] = {
57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17, 9,
1, 58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18,
10, 2, 59, 51, 43, 35, 27,
19, 11, 3, 60, 52, 44, 36,
63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15,
7, 62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22,
14, 6, 61, 53, 45, 37, 29,
21, 13, 5, 28, 20, 12, 4
};
// Permuted Choice 2 (PC-2)
int pc2[48] = {
14, 17, 11, 24, 1, 5,
3, 28, 15, 6, 21, 10,
23, 19, 12, 4, 26, 8,
16, 7, 27, 20, 13, 2,
41, 52, 31, 37, 47, 55,
30, 40, 51, 45, 33, 48,
44, 49, 39, 56, 34, 53,
46, 42, 50, 36, 29, 32
};
// 1,2,9,16 round: 1 Bit shift. else 2 Bit shift
int rotations[16] = {
1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1
};
// Expansion Permutation (E-box), 32 bits -> 48 bits
int e_boxes[48] = {
32, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,
16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21,
20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29,
28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 1
};
// S-box (S1-S8)
int s_boxes[8][4][16] = {
// S1
{
{14, 4, 13, 1, 2, 15, 11, 8, 3, 10, 6, 12, 5, 9, 0, 7},
{0, 15, 7, 4, 14, 2, 13, 1, 10, 6, 12, 11, 9, 5, 3, 8},
{4, 1, 14, 8, 13, 6, 2, 11, 15, 12, 9, 7, 3, 10, 5, 0},
{15, 12, 8, 2, 4, 9, 1, 7, 5, 11, 3, 14, 10, 0, 6, 13}
},
// S2
{
{15, 1, 8, 14, 6, 11, 3, 4, 9, 7, 2, 13, 12, 0, 5, 10},
{3, 13, 4, 7, 15, 2, 8, 14, 12, 0, 1, 10, 6, 9, 11, 5},
{0, 14, 7, 11, 10, 4, 13, 1, 5, 8, 12, 6, 9, 3, 2, 15},
{13, 8, 10, 1, 3, 15, 4, 2, 11, 6, 7, 12, 0, 5, 14, 9}
},
// S3
{
{10, 0, 9, 14, 6, 3, 15, 5, 1, 13, 12, 7, 11, 4, 2, 8},
{13, 7, 0, 9, 3, 4, 6, 10, 2, 8, 5, 14, 12, 11, 15, 1},
{13, 6, 4, 9, 8, 15, 3, 0, 11, 1, 2, 12, 5, 10, 14, 7},
{1, 10, 13, 0, 6, 9, 8, 7, 4, 15, 14, 3, 11, 5, 2, 12}
},
// S4
{
{7, 13, 14, 3, 0, 6, 9, 10, 1, 2, 8, 5, 11, 12, 4, 15},
{13, 8, 11, 5, 6, 15, 0, 3, 4, 7, 2, 12, 1, 10, 14, 9},
{10, 6, 9, 0, 12, 11, 7, 13, 15, 1, 3, 14, 5, 2, 8, 4},
{3, 15, 0, 6, 10, 1, 13, 8, 9, 4, 5, 11, 12, 7, 2, 14}
},
// S5
{
{2, 12, 4, 1, 7, 10, 11, 6, 8, 5, 3, 15, 13, 0, 14, 9},
{14, 11, 2, 12, 4, 7, 13, 1, 5, 0, 15, 10, 3, 9, 8, 6},
{4, 2, 1, 11, 10, 13, 7, 8, 15, 9, 12, 5, 6, 3, 0, 14},
{11, 8, 12, 7, 1, 14, 2, 13, 6, 15, 0, 9, 10, 4, 5, 3}
},
// S6
{
{12, 1, 10, 15, 9, 2, 6, 8, 0, 13, 3, 4, 14, 7, 5, 11},
{10, 15, 4, 2, 7, 12, 9, 5, 6, 1, 13, 14, 0, 11, 3, 8},
{9, 14, 15, 5, 2, 8, 12, 3, 7, 0, 4, 10, 1, 13, 11, 6},
{4, 3, 2, 12, 9, 5, 15, 10, 11, 14, 1, 7, 6, 0, 8, 13}
},
// S7
{
{4, 11, 2, 14, 15, 0, 8, 13, 3, 12, 9, 7, 5, 10, 6, 1},
{13, 0, 11, 7, 4, 9, 1, 10, 14, 3, 5, 12, 2, 15, 8, 6},
{1, 4, 11, 13, 12, 3, 7, 14, 10, 15, 6, 8, 0, 5, 9, 2},
{6, 11, 13, 8, 1, 4, 10, 7, 9, 5, 0, 15, 14, 2, 3, 12}
},
// S8
{
{13, 2, 8, 4, 6, 15, 11, 1, 10, 9, 3, 14, 5, 0, 12, 7},
{1, 15, 13, 8, 10, 3, 7, 4, 12, 5, 6, 11, 0, 14, 9, 2},
{7, 11, 4, 1, 9, 12, 14, 2, 0, 6, 10, 13, 15, 3, 5, 8},
{2, 1, 14, 7, 4, 10, 8, 13, 15, 12, 9, 0, 3, 5, 6, 11}
}
};
// P-box Permutation, 32 bits -> 32 bits
int p_boxes[32] = {
16, 7, 20, 21,
29, 12, 28, 17,
1, 15, 23, 26,
5, 18, 31, 10,
2, 8, 24, 14,
32, 27, 3, 9,
19, 13, 30, 6,
22, 11, 4, 25
};
// Final Permutation (IP inverse)
int fp_table[64] = {
40, 8, 48, 16, 56, 24, 64, 32,
39, 7, 47, 15, 55, 23, 63, 31,
38, 6, 46, 14, 54, 22, 62, 30,
37, 5, 45, 13, 53, 21, 61, 29,
36, 4, 44, 12, 52, 20, 60, 28,
35, 3, 43, 11, 51, 19, 59, 27,
34, 2, 42, 10, 50, 18, 58, 26,
33, 1, 41, 9, 49, 17, 57, 25
};복호화는 암호화의 반대로 수행한다. 암호화를 수행해서 얻은 cipher_text에 대하여 Initial permutation 수행 후, 16회의 페이스텔 라운드에서 0번 ~ 15번 서브키 순서가 아닌, 15 ~ 0번 서브키 순서로 사용한다. 동일하게 final permutation 까지 수행하면 원본 plain_text를 얻을 수 있다.