
해당 글은 스프링 시큐리티 공식문서 중
Servlet Applications/Authentication/Authentication Architecture 부분을 번역한 글입니다.
Servlet Authentication Architecture
이 글은 스프링 시큐리티에서 사용하는 인증 컴포넌트를 설명하기 위한 “아키텍서블릿 시큐리티 큰 그림”의 확장판입니다.
이러한 요소들이 어떻게 결합하는지 구체적인 흐름이 필요하시면 인증메커니즘 섹션을 살펴보세요.
- SecurityContextHolder -
SecurityContextHolder는 스프링이 인증된 유저의 디테일을 저장해놓는 저장소입니다. - SecurityContext - SecurityContextHolder에서 가져오며 현재 인증된 유저의 인증객체(
Authentication)을 포함합니다. - Authentication - 인증(authenticate)을 위해 제공한 사용자 자격증명(the credentials a user) 또는 SecurityContext에서 꺼재온 현재 유저를 제공하기 위해
AuthenticationManager의 인풋이 될 수 있습니다. - GrantedAuthority -
Authentication의 주체(principal)에게 부여되는 권한입니다. - AuthenticationManager - 스프링 시큐리티 필터가 인증을 수행하는 방법을 정의한 API 입니다.
- ProviderManager -
AuthenticationManager의 가장 일반적인 구현체입니다. - AuthenticationProvider - 특정 유형의 인증을 수행하기 위해 ProviderManager에 의해 사용됩니다.
- Request Credentials with
AuthenticationEntryPoint- 클라이언트에게 자격증명을 요청할 때 사용됩니다. (i.e 로그인 페이지로 이동시켜준다거나 WWW-Authenticate 응답을 보내는 등의 행위가 있을 수 있습니다.) - AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter - 인증을 위한 기본
Filter로 사용됩니다. 이 필터는 인증에 대한 높은 수준의 흐름과 그 조각들이 어떻게 함께 동작하는지에 대한 좋은 아이디어를 주기도 합니다.
SecurityContextHolder
스프링 시큐리티 인증모델의 심장(heart)은 SecurityContextHolder 입니다. 이 친구는 SecurityContext도 포함해요.

SecurityContextHolder는 스프링이 인증된 유저의 디테일을 저장해놓는 저장소입니다. 스프링 시큐리티는 SecurityContextHolder가 어떻게 채워지는지 전혀 신경쓰지 않아요. 만약 홀더가 값을 갖고 있다면 그 값은 현재 인증된 유저로 사용됩니다.
인증된 유저임을 가리키는 가장 간단한 방법은 SecurityContextHolder에 값을 채워넣는 것입니다.
Example 1. Setting SecurityContextHolder
val context: SecurityContext = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext() // 1
val authentication: Authentication = TestingAuthenticationToken("username", "password", "ROLE_USER") // 2
context.authentication = authentication
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context) // 3
- 빈 SecurityContext를 만드는 것을 시작합니다. 반드시 새로운 SecurityContext을 만들어야 해요. SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication)를 사용하게 된다면 멀티스레드 환경에서 race condition이 발생할 수 있기 때문입니다.
- 그 다음 새로운 Authentication 객체를 만듭니다. 스프링 시큐리티는 SecurityContext에 어떤 유형의 인증 구현이 설정되어 있는지 신경 쓰지 않습니다. 여기 예시에서는 TestAuthenticationToken을 만들었습니다. 매우 심플하죠? 더 많은 일반적인 운영 시나리오는 UsernamePasswordAuthentication(userDetails, password, authorities)입니다.
- 마지막으로 SecurityContextHolder에 SecurityContext를 설정해줍니다. 스프링 시큐리티는 context안에 있는 authorization의 정보를 사용할 겁니다.
인증된 주체에 대한 정보를 얻기 위해서는 SecurityContextHolder에 접근하면 됩니다.
Access Currently Authenticated User
val context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
val authentication = context.authentication
val username = authentication.name
val principal = authentication.principal
val authorities = authentication.authorities디폴트로 SecurityContextHolder는 이러한 세부 정보들을 저장하기 위해 ThreadLocal을 사용하는데요. 이것은 SecurityContext가 동일한 스레드에서는 항상 같은 메서드를 사용한다는 것을 의미합니다. 비록 명시적으로 SecurityContext를 메서드의 파라미터로 전달하지 않더라도 말이죠.
ThreadLocal을 이러한 방법으로 사용하는 것은 매우 안전합니다. 현재 주체의 요청이 처리 된후 스레드를 지우도록 주의만 한다면요. 스프링 시큐리티의 FilterChainProxy는 SecurityContext가 항상 초기화 되도록 보장합니다!
스레드가 동작하는 세부방식 때문에 ThreadLocal이 적합하지 않은 애플리케이션이 있을수도 있습니다. 예를 들어 스윙 클라이언트가 Java Virtual Machine 내부의 모든 스레드가 동일한 security context를 사용하길 바랄 수가 있습니다. 이럴 때 context가 어떻게 저장될 것인가 전략을 시작시에 특정해서, SecurityContextHolder를 설정할 수도 있습니다. 독립형 애플리케이션인 경우에는 SecurityContextHolder.MODE_GLOBAL 전략을 사용할 수 있습니다.
다른 애플리케이션의 경우에는 보안 스레드에서 만들어진 스레드를 동일한 보안 아이디를 가정하도록 원할 수도 있습니다. 이럴 땐 SecurityContextHolder.MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 설정을 사용할 수 있습니다.
디폴트 모드인 SecurityContextHolder.MODE_THREADLOCAL에서 위모드처럼 변경을 하는 방법이 두 가지 있습니다. 첫 번째는 system property를 설정하는 것이고, 두 번째는 SecurityContextHolder에서 정적 메서드로 호출하는 것입니다. 대부분의 경우에는 디폴트 모드를 변경할 필요가 없고 만약 필요하다면 SecurityContextHolder의 javaDoc을 유심히 살펴보시길 바랄게요.
SecurityContext
SecurityContext는 SecurityContextHolder에서 가져옵니다. SecurityContext는 Authentication객체를 포함하고 있어요.
Authentication
Authentication인터페이스는 스프링 시큐리티에서 두 가지 주요 목적을 전달합니다.
AuthenciationManager에 입력하여 사용자가 인증하기 위해 제공한 자격증명을 제공합니다. 이 시나리오에서는isAuthenticated()는 false를 반환합니다.- 현시점에서 인증된 유저를 나타냅니다. SecurityContext에서 현재
Authentication을 얻을 수 있어요.
Authentication 은 아래 항목들을 포함합니다.
principal: 유저의 id입니다. username/password로 인증할 때UserDetails의 인스턴스인 경우가 많아요.credentials: password인 경우가 많습니다. 대부분 상황에서 유저가 인증된 이후 유출되지 않게 지워집니다.authorities:GrantedAuthority의 인스턴스는 유저에게 부여된 상위 수준의 권한입니다. 두 개의 예시로는 roles, scopes가 있어요.
GrantedAuthority
GrantedAuthority의 인스턴스는 유저에게 부여된 상위 수준의 권한입니다. 두 개의 예시로는 roles, scopes가 있습니다.
GrantedAuthority 인스턴스는 Authentication.getAuthorities() 메서드를 통해 얻을 수 있습니다. 이 메서드는 GrantedAuthority의 Colllection을 제공해요. 놀랍지 않게, GrantedAuthority는 principal에 부여된 권한입니다. 이러한 권한들은 보통 “roles”입니다. ROLE_ADMINISTRATOR 또는 ROLE_HR_SUPERVISOR 같이 말이죠. web authorization, method authorization, domain object authorization을 위해서 이 롤들은 나중에 설정됩니다. 스프링 시큐리티의 다른 부분들은 이런 권한들을 해석하고 또 권한이 있을 것이라고 기대합니다. username/password 기반의 인증을 사용할 때는 GrantedAuthority 인스턴스는 보통 UserDetailsService에 의해 로드됩니다.
보통, GrantedAuthority 객체 같은 경우는 애플리케이션의 전체 권한입니다. 이런 권한은 특정 도메인 객체에 대해서는 특정지어지지 않아요. 그러므로 54번 직원에 대한 권한을 나타내는 GrantedAuthority 는 가질수 없을 겁니다. 왜냐하면 이러한 권한이 수천개 존재한다면 아마도 메모리가 빠르게 바닥날것이기 때문이죠.(또는, 최소한 애플리케이션이 사용자를 인증하는데 오래걸릴 것입니다.) 물론, 스프링시큐리티는 명시적으로 이런 공통요구사항을 처리하도록 디자인 되어있어요. 하지만 이런 목적을 위해서라면 도메인 보안객체를 대신 사용해야합니다.
AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager는 시큐리티 필터가 인증을 수행하는 방식을 정의한 API 입니다. 반환되는 Authentication은 SecurityContextHolder에 세팅되는데요, 세팅하는 주체는 AuthenticationManager를 호출한 컨트롤러입니다.(즉, Spring Security의 Filter인스턴스)
만약 스프링시큐리티의 Filter인스턴스와 통합하고 싶지 않다면 SecurityContextHolder에 직접 바로 설정을 하면 되고 AuthenticationManager의 사용은 불필요해 집니다.
AuthenticationManager의 구현은 무엇이든 가능하지만 가장 일반적인 구현은 ProviderManager입니다.
ProviderManager
ProviderManager는 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 AuthenticationManager의 구현체입니다. ProviderManager는 AuthenticationProvider 인스턴스의 리스트에게 위임합니다. 각각의 AuthenticationProvider는 기회가 있는데, 그 기회는 인증이 성공하는지 실패하는지 혹은 성공/실패 결정을 할 수 없어 다음차례의 AuthenticationProvider에게 결정하게 할지를 나타낼 수 있는 기회입니다.
만약에 인증을 할 수 있는 AuthenticationProvider가 없다면 ProviderNotFoundException과 함께 인증이 실패하게 됩니다. 이 예외는 전달된 인증타입을 지원하는 ProviderManager가 없다는걸 가리키는 특수한 예외입니다.
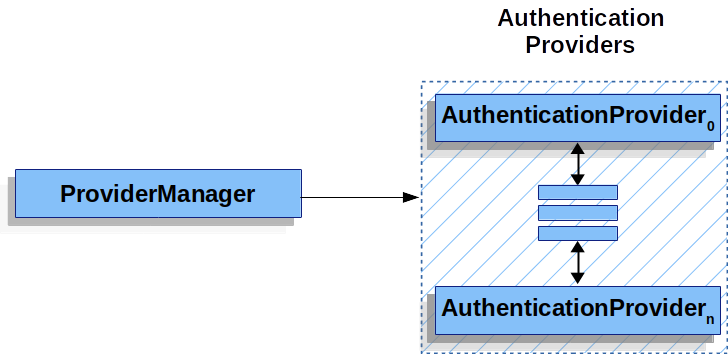
실제로 각 AuthenticationProvider들은 특정 인증방식을 어떻게 수행 할 지를 알고 있습니다. 예를 들어 한 AuthenticationProvider가 username/password에 대한 검증을 할 수 있다면 다른 것은 SAML assertion을 인증할 수 있죠. 이건 각각의 AuthenticationProvider가 매우 특정한 타입의 인증을 할 수 있고 다양한 타입을 지원하는 반면 하나의 단일 AuthenticationManager 빈만 노출할 수 있게 합니다.
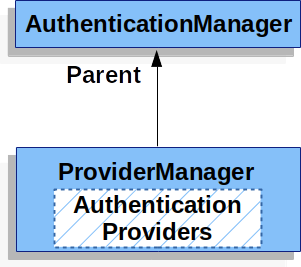
ProviderManager는 또한 인증을 수행할 수 있는 AuthenticationProvider가 없을 땐, 옵셔널한 부모 AuthenticationManager를 정의할 수도 있습니다. 그 부모는 AuthenticationManager의 어떠한 타입도 될 수 있지만 보통은 ProviderManager가 됩니다.
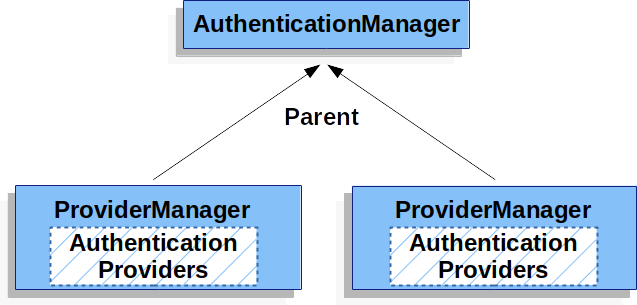
실제로 다중 ProviderManager 인스턴스는 공통 부모 AutheticationManager를 공유합니다. 이는 공통된 일부 인증(공유 상위 AuthenticationManager)이 있지만 다른 인증 메커니즘(다른 ProviderManager 인스턴스)을 갖는 여러 SecurityFilterChain 인스턴스가 있는 시나리오에서 다소 일반적입니다.
디폴트로 ProviderManger는 성공적으로 인증요청이 처리되었을때, Authentication 객체에서 나온 민감한 증명정보를 지우려고 합니다. 이건 패스워드같은 정보들이 필요이상으로 HttpSession에 유지되는 것을 방지해요.
예를 들어 무상태 애플리케이션에서 성능을 향상 시키기 위해 유저 객체등을 캐싱할 때 문제의 원인이 될 수 있습니다. 만약 Authentication이 캐시에 존재하는 객체를 참조하고(예를 들어 UserDetails 인스턴스) 이게 credentials를 지웠다면 이 객체는 캐시된 값에 대해서는 더이상 인증이 불가하게 됩니다. 캐시를 사용하는 경우 이 부분을 인지해야 해요. 확실한 해결책은 캐시구현체나 반한되는 Authentication 객체를 만드는 AuthenticationProvider에서 먼저 객체의 복사본을 만드는 것입니다. 대안책으로는 ProviderManager에 존재하는 property인 eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication를 disable처리 하는 방안도 있습니다.
AuthenticationProvider
ProviderManager에 많은 AuthenticationProvider 인스턴스를 주입할 수도 있어요. 각 AuthenticationProvider는 특정한 타입의 인증을 수행합니다. 예를 들어 DaoAuthenticationProvider는 username/password 기반의 인증을 지원하는 반면 JwtAuthenticationProvider는 JWT토큰 인증방식을 지원합니다.
Request Credential with AuthenticationEntiryPoint
AuthenticationEntiryPoint는 사용자의 자격요청에 대한 응답을 보낼때 사용됩니다.
때때로 사용자는 리소스를 요청하기 위해 자격증명(username이나 password같은)을 사전에 포함합니다. 이런 경우에는 이미 자격증명이 포함되어있기 때문에 HTTP 응답을 제공할 필요가 없게 되죠.
다른 경우에는 권한이 없는 리소스에 대해서 인증되지 않은 요청을 만들어 보낼 때도 있습니다. 이런 상황에서는 AuthenticationEntiryPoint의 구현체가 사용자에게 자격증명을 요청할 때 사용됩니다. AuthenticationEntiryPoint 구현체는 아마 로그인 페이지로 리다이렉트 시키거나 WWW-Authenticate 헤더를 응답하거나 다른 액션을 하게 돼요.
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter는 유저의 자격증명을 인증하는 기본 필터로 사용됩니다. 자격증명이 인증되기 전에는 스프링 시큐리티는 일반적으로 AuthenticationEntryPoint를 이용해 자격증명을 요청합니다.
그 다음이 되어야 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter는 제출된 모든 인증요청을 인증할 수 있어요.
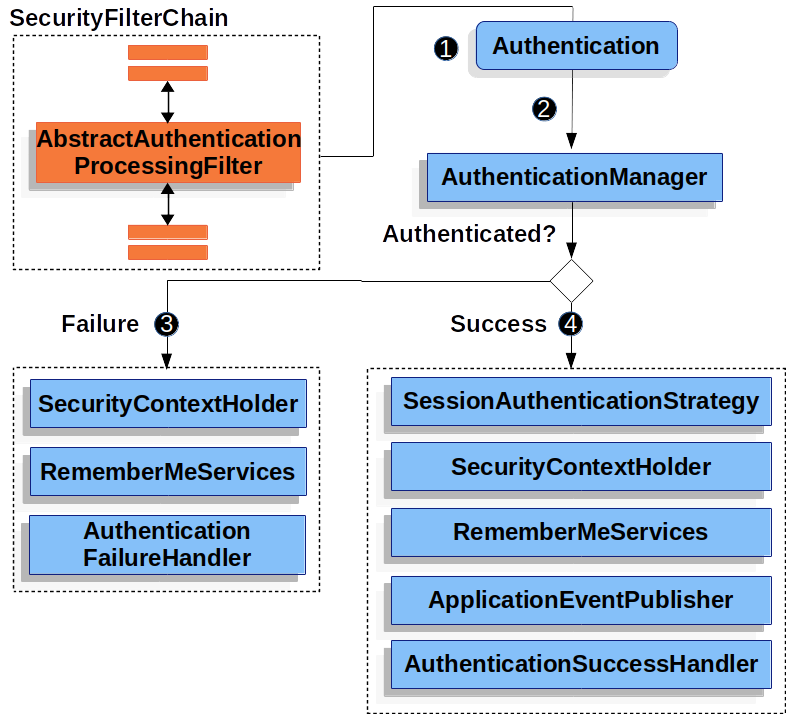
- 유저가 자격증명을 제출하면
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter는 인증을 하기위해HttpServletRequest로부터Authentication을 만듭니다.Authentication의 타입은AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter의 서브클래스에 따라 다릅니다. 예를 들면UsernamePAsswordAuthenticationFilter는UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을HttpServletRequest로부터 username과 password를 추출해 만들어내죠. - 그 다음,
Authentication은 인증절차를 거치기 위해AuthenticationManager에게 전달됩니다. - 만약 인증이 실패하면, Failure입니다.
- SecurityContextHolder가 초기화 됩니다.
RememberMeServicese.loginFail이 호출됩니다. 만약 remember me가 활성화되지 않았다면 동작하지 않습니다.AuthenticationFailureHandler가 호출됩니다.
- 만약 인증이 성공한다면, Success입니다.
SessionAuthenticationStrategy에게 새로운 로그인 알림이 갑니다.- Authentication 객체가 SecurityContextHolder에 저장됩니다. 나중에 만약 요청으로부터
SecurityContext를 저장해야할 때가 생기면SecurityContextRepository#saveContext를 명시적으로 호출해야 합니다. RememeberMeServices.loginSuccess가 호출됩니다. 만약 remember me가 활성화되지 않았다면 동작하지 않습니다.ApplicationEventPublisher가InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent를 발행합니다.AuthenticationSuccessHandler가 호출됩니다.
참고
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/reference/servlet/authentication/architecture.html
