Class는 틀이다.
class로부터 나온 산물 인스턴스를 생성
생성자: 생성해주는 역할을 하는 함수
생성자의 규칙
new 생성자();
생성자는 클래스의이름과 반드시 동일해야한다.
public class A{
// 이곳에 채워지는 것들이 '명세'가 될 것
}자료형 변수명 = new Class_name();
자료형은 class_name과 같다.
A a = new A();
Class A는 "사용자 정의 자료형"
참조변수: 주소를 가지고 있는 변수
우리가 필요한 자료형을 직접 만들어서 쓸 것이다. → 명세
자료형의 또 다른 의미는 설명
Class의 구성요소
- 변수 → field, 멤버변수: 클래스 안에 선언된 변수이므로 멤버변수라고 부른다.
- 함수 → method,멤버함수: 클래스 안에 선언된 함수이므로 멤버함수라고 하고, 메소드라고 부른다.
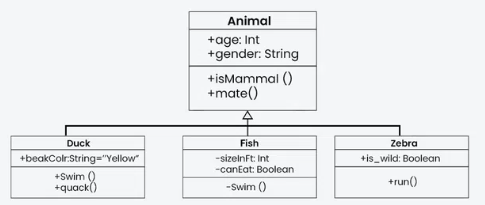
Class diagram
이름, 변수 목록, 함수 목록
class A(){
int n;
void f(int x){
p("hi");
}
}
함수의 시그니처: 이름, 매개변수/타입/개수, 결과자료(void, int등)
→ 함수마다 다르다.
예시
배열과 구조체
배열은 동일 Type, 구조체는 이형의 자료형(변수만 해당)
class는 구조체의 성격을 가지고 왔다. +함수(기능)까지 생성 가능
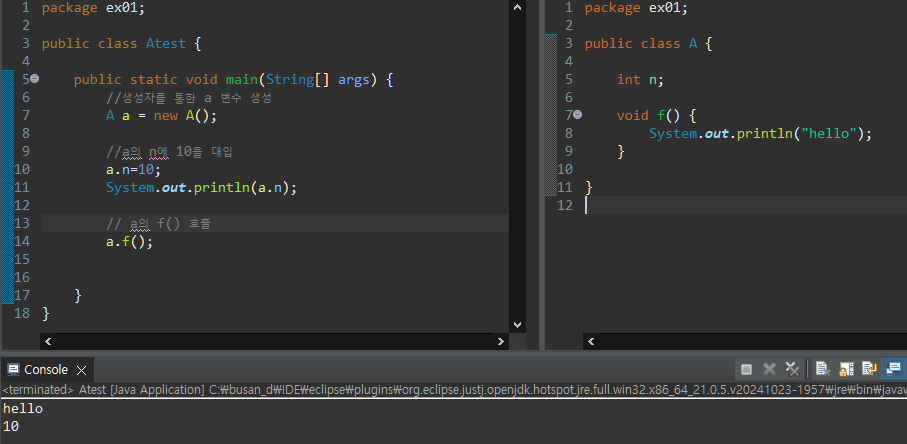
package ex01;
public class A {
int n;
double d;
char c;
long l;
float f;
boolean tf;
String s;
int[] arr;
void f() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}인스턴스가 처음 만들어지면 n = 0으로, s는 null로 초기화되어 있다.
인스턴스의 생애 주기
정리
Class는 사용자가 만들어 쓰는 자료형이다.
멤버변수, 멤버한수로 명세를 할 수 있다.
명세되어 있는 형태대로 new 생성자 함수를 써준다.
생성자 함수 이름은 class이름과 동일해야 한다.
클래스이름.변수명 → 참조변수를 반드시 이용한다.
같은 class에서 메소드를 만들 때는 참조변수가 필요하지 않다.
[예제]
Student 클래스
멤버변수: 이름 name, 번호 no, 국어점수 kor_score, 영어점수 eng_score, 수학점수 math_score
멤버함수: 학생의 정보를 보여주는 함수
참조변수: James, Ann, Bread
Test0324.java
package ex01;
public class Test0324 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student James = new Student();
Student Ann = new Student();
Student Bread = new Student();
James.name="James";
James.no=1;
James.kor_score=90;
James.eng_score=80;
James.math_score=70;
Ann.name="Ann";
Ann.no=2;
Ann.kor_score=100;
Ann.eng_score=90;
Ann.math_score=60;
Bread.name="Bread";
Bread.no=3;
Bread.kor_score=60;
Bread.eng_score=40;
Bread.math_score=100;
James.infoPrint();
Ann.infoPrint();
Bread.infoPrint();
}
}
Student.java
package ex01;
public class Student {
String name;
int no;
int kor_score;
int eng_score;
int math_score;
void infoPrint() {
System.out.println("이름: "+name);
System.out.println("번호: "+no);
System.out.println("국어점수: "+kor_score);
System.out.println("영어점수: "+eng_score);
System.out.println("수학점수: "+math_score);
System.out.println("------------------");
}
}
[예제] 계산기
calculator: 멤버변수 2개, 사칙연산하는 멤버함수(멤버변수 활용)
calcTest에서 생성자를 활용하여 결과 확인
CalcTest.java
package ex01;
public class CalcTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator cc = new Calculator();
cc.a = 9;
cc.b = 4;
System.out.println(cc.add());
System.out.println(cc.min());
System.out.println(cc.mul());
System.out.println(cc.div());
}
}Calcultator.java
package ex01;
public class Calculator {
float a;
float b;
float add() {
return a+b;
}
float min() {
return a-b;
}
float mul() {
return a*b;
}
float div() {
return a/b;
}
}
[예제] 멤버변수가 없는 계산기
Calculator에서 멤버변수를 주석처리하고
main에서 값을 넣어주어 결과값을 출력한다.
main.java
package ex01;
public class CalcTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator cc = new Calculator();
System.out.println(cc.add(9, 4));
System.out.println(cc.min(9, 4));
System.out.println(cc.mul(9, 4));
System.out.println(cc.div(9, 4));
}
}Calculator.java
package ex01;
public class Calculator {
// float a;
// float b;
float add(float a, float b) {
return a+b;
}
float min(float a, float b) {
return a-b;
}
float mul(float a, float b) {
return a*b;
}
float div(float a, float b) {
return a/b;
}
}
[예제]
학생 class 활용해서,
1. 학생 3명의 인스턴스를 생성하시오.
2. 1번을 활용해서 학생 배열을 만드시오.
→ Student[] arr = new Student[3]; 로 가능
3. 학생들의 국어점수 합계를 구한다.
student.java
package ex01;
public class Student {
String name;
int no;
int kor_score;
int eng_score;
int math_score;
void infoPrint() {
System.out.println("이름: "+name);
System.out.println("번호: "+no);
System.out.println("국어점수: "+kor_score);
System.out.println("영어점수: "+eng_score);
System.out.println("수학점수: "+math_score);
System.out.println("------------------");
}
}
Test0324.java
package ex01;
public class Test0324 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int korSum=0;
Student James = new Student();
Student Ann = new Student();
Student Bread = new Student();
James.name="James";
James.no=1;
James.kor_score=90;
James.eng_score=80;
James.math_score=70;
Ann.name="Ann";
Ann.no=2;
Ann.kor_score=100;
Ann.eng_score=90;
Ann.math_score=60;
Bread.name="Bread";
Bread.no=3;
Bread.kor_score=60;
Bread.eng_score=40;
Bread.math_score=100;
Student[] students = new Student[3];
students[0] = James;
students[1] = Ann;
students[2] = Bread;
for(int i=0; i<students.length; i++) {
korSum+=students[i].kor_score;
}
System.out.println(korSum);
}
}
