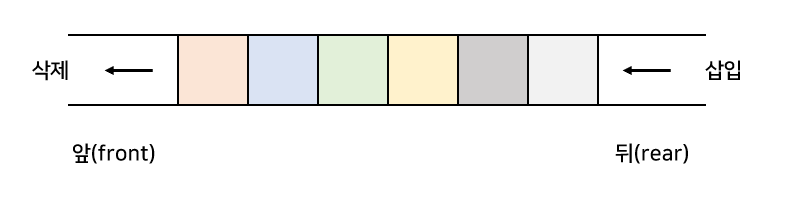
정의
큐는 FIFO(First In First Out) 원칙을 따르는 선형 자료구조다. 먼저 삽입된 요소가 가장 먼저 삭제되는 구조로, 한쪽 끝(rear)에서 삽입하고 다른 쪽 끝(front)에서 삭제가 이루어진다.
기본 개념
← dequeue enqueue →
┌─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┐
│ 1 │ 3 │ 5 │ 7 │ 9 │
└─────┴─────┴─────┴─────┴─────┘
↑ ↑
front rear
(삭제) (삽입)
주요 연산
- enqueue: 큐의 뒤쪽(rear)에 요소 삽입
- dequeue: 큐의 앞쪽(front)에서 요소 제거 및 반환
- front/peek: 앞쪽 요소 조회 (제거하지 않음)
- rear: 뒤쪽 요소 조회 (제거하지 않음)
- isEmpty: 큐가 비어있는지 확인
- size: 큐의 크기 반환
시간 복잡도
| 연산 | 시간 복잡도 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| enqueue | O(1) | 뒤쪽에 삽입 |
| dequeue | O(1) | 앞쪽에서 제거 |
| front/peek | O(1) | 앞쪽 요소 조회 |
| search | O(n) | 특정 요소 찾기 |
공간 복잡도
- O(n): n개의 요소를 저장하는 공간 필요
JavaScript/TypeScript 구현
배열 기반 큐 (비효율적)
class ArrayQueue<T> {
private items: T[] = [];
// 큐 뒤쪽에 요소 삽입
enqueue(item: T): void {
this.items.push(item);
}
// 큐 앞쪽에서 요소 제거 (O(n) - 비효율적!)
dequeue(): T | undefined {
return this.items.shift();
}
// 앞쪽 요소 조회
front(): T | undefined {
return this.items[0];
}
// 뒤쪽 요소 조회
rear(): T | undefined {
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
size(): number {
return this.items.length;
}
}
왜 비효율적인가?
Array.shift() 메서드는 첫 번째 요소를 제거한 후, 나머지 모든 요소들을 한 칸씩 앞으로 이동시켜야 한다:
dequeue 전: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
dequeue 후: [2, 3, 4, 5] ← 모든 요소가 한 칸씩 이동 (O(n))
따라서 dequeue 연산이 O(n) 시간이 걸려서 비효율적이다.
원형 큐 (Circular Queue) - 효율적
class CircularQueue<T> {
private items: (T | undefined)[];
private frontIndex: number = 0;
private rearIndex: number = -1;
private count: number = 0;
private capacity: number;
constructor(capacity: number) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.items = new Array(capacity);
}
enqueue(item: T): boolean {
if (this.isFull()) {
return false; // 큐가 가득 참
}
this.rearIndex = (this.rearIndex + 1) % this.capacity;
this.items[this.rearIndex] = item;
this.count++;
return true;
}
dequeue(): T | undefined {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
const item = this.items[this.frontIndex];
this.items[this.frontIndex] = undefined;
this.frontIndex = (this.frontIndex + 1) % this.capacity;
this.count--;
return item;
}
front(): T | undefined {
return this.isEmpty() ? undefined : this.items[this.frontIndex];
}
rear(): T | undefined {
return this.isEmpty() ? undefined : this.items[this.rearIndex];
}
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.count === 0;
}
isFull(): boolean {
return this.count === this.capacity;
}
size(): number {
return this.count;
}
toArray(): T[] {
const result: T[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.count; i++) {
const index = (this.frontIndex + i) % this.capacity;
result.push(this.items[index]!);
}
return result;
}
}
왜 효율적인가?
원형 큐는 배열을 원형으로 취급하여 인덱스 포인터만 이동시킨다:
배열: [_, _, _, _, _] (capacity: 5)
↑
front=0, rear=-1
enqueue(1): [1, _, _, _, _] front=0, rear=0
enqueue(2): [1, 2, _, _, _] front=0, rear=1
enqueue(3): [1, 2, 3, _, _] front=0, rear=2
dequeue(): [_, 2, 3, _, _] front=1, rear=2 ← 요소 이동 없음!
dequeue(): [_, _, 3, _, _] front=2, rear=2
enqueue(4): [_, _, 3, 4, _] front=2, rear=3
enqueue(5): [_, _, 3, 4, 5] front=2, rear=4
enqueue(6): [6, _, 3, 4, 5] front=2, rear=0 ← 원형으로 순환!
핵심 차이점:
- 배열 기반:
dequeue시 모든 요소를 이동 → O(n) - 원형 큐:
dequeue시 인덱스만 이동 → O(1)
모든 연산이 O(1) 시간에 수행되어 효율적이다.
연결 리스트 기반 큐
class QueueNode<T> {
data: T;
next: QueueNode<T> | null;
constructor(data: T) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedQueue<T> {
private frontNode: QueueNode<T> | null = null;
private rearNode: QueueNode<T> | null = null;
private count: number = 0;
enqueue(data: T): void {
const newNode = new QueueNode(data);
if (!this.rearNode) {
// 첫 번째 요소
this.frontNode = this.rearNode = newNode;
} else {
this.rearNode.next = newNode;
this.rearNode = newNode;
}
this.count++;
}
dequeue(): T | undefined {
if (!this.frontNode) {
return undefined;
}
const data = this.frontNode.data;
this.frontNode = this.frontNode.next;
if (!this.frontNode) {
// 마지막 요소였다면
this.rearNode = null;
}
this.count--;
return data;
}
front(): T | undefined {
return this.frontNode?.data;
}
rear(): T | undefined {
return this.rearNode?.data;
}
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.frontNode === null;
}
size(): number {
return this.count;
}
toArray(): T[] {
const result: T[] = [];
let current = this.frontNode;
while (current) {
result.push(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
return result;
}
}
실생활 비유
은행 대기줄
- 고객이 도착: 줄의 맨 뒤에 선다 (enqueue)
- 고객 서비스: 줄의 맨 앞 고객부터 처리 (dequeue)
- 먼저 온 고객이 먼저 서비스를 받는다
프린터 대기열
- 문서 출력 요청: 대기열 맨 뒤에 추가
- 프린터 동작: 대기열 맨 앞 문서부터 출력
- 먼저 요청한 문서가 먼저 인쇄된다
버퍼/스트리밍
- 데이터 수신: 버퍼 뒤쪽에 저장
- 데이터 처리: 버퍼 앞쪽부터 순서대로 처리
- 데이터의 순서가 보장된다
프론트엔드에서의 활용
이벤트 큐 (Event Queue)
interface QueuedEvent {
id: string;
type: string;
data: any;
timestamp: number;
}
class EventQueue {
private queue: LinkedQueue<QueuedEvent> = new LinkedQueue();
private processing: boolean = false;
// 이벤트 추가
addEvent(type: string, data: any): void {
const event: QueuedEvent = {
id: Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 9),
type,
data,
timestamp: Date.now()
};
this.queue.enqueue(event);
this.processEvents();
}
// 이벤트 처리
private async processEvents(): Promise<void> {
if (this.processing) return;
this.processing = true;
while (!this.queue.isEmpty()) {
const event = this.queue.dequeue();
if (event) {
await this.handleEvent(event);
}
}
this.processing = false;
}
private async handleEvent(event: QueuedEvent): Promise<void> {
console.log(`Processing event: ${event.type}`, event.data);
// 실제 이벤트 처리 로직
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 100));
}
getQueueSize(): number {
return this.queue.size();
}
}
// 사용 예시
const eventQueue = new EventQueue();
eventQueue.addEvent('USER_CLICK', { buttonId: 'submit' });
eventQueue.addEvent('API_CALL', { endpoint: '/users' });
API 요청 큐
interface ApiRequest {
url: string;
method: 'GET' | 'POST' | 'PUT' | 'DELETE';
data?: any;
resolve: (value: any) => void;
reject: (error: any) => void;
}
class ApiRequestQueue {
private queue: LinkedQueue<ApiRequest> = new LinkedQueue();
private processing: boolean = false;
private maxConcurrent: number = 3;
private currentRequests: number = 0;
async request(url: string, method: 'GET' | 'POST' | 'PUT' | 'DELETE', data?: any): Promise<any> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const apiRequest: ApiRequest = {
url,
method,
data,
resolve,
reject
};
this.queue.enqueue(apiRequest);
this.processQueue();
});
}
private async processQueue(): Promise<void> {
if (this.processing || this.currentRequests >= this.maxConcurrent) {
return;
}
this.processing = true;
while (!this.queue.isEmpty() && this.currentRequests < this.maxConcurrent) {
const request = this.queue.dequeue();
if (request) {
this.executeRequest(request);
}
}
this.processing = false;
}
private async executeRequest(request: ApiRequest): Promise<void> {
this.currentRequests++;
try {
const response = await fetch(request.url, {
method: request.method,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: request.data ? JSON.stringify(request.data) : undefined,
});
const result = await response.json();
request.resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
request.reject(error);
} finally {
this.currentRequests--;
// 큐에 남은 요청이 있다면 계속 처리
if (!this.queue.isEmpty()) {
this.processQueue();
}
}
}
}
// 사용 예시
const apiQueue = new ApiRequestQueue();
async function fetchUserData() {
try {
const user = await apiQueue.request('/api/users/1', 'GET');
const posts = await apiQueue.request('/api/users/1/posts', 'GET');
console.log('User data:', user, posts);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to fetch user data:', error);
}
}
애니메이션 큐
interface Animation {
element: HTMLElement;
property: string;
from: string;
to: string;
duration: number;
easing?: string;
}
class AnimationQueue {
private queue: LinkedQueue<Animation> = new LinkedQueue();
private isRunning: boolean = false;
addAnimation(animation: Animation): void {
this.queue.enqueue(animation);
if (!this.isRunning) {
this.processAnimations();
}
}
private async processAnimations(): Promise<void> {
this.isRunning = true;
while (!this.queue.isEmpty()) {
const animation = this.queue.dequeue();
if (animation) {
await this.runAnimation(animation);
}
}
this.isRunning = false;
}
private runAnimation(animation: Animation): Promise<void> {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
const { element, property, from, to, duration, easing = 'ease' } = animation;
element.style.setProperty(property, from);
element.style.transition = `${property} ${duration}ms ${easing}`;
// 다음 프레임에서 애니메이션 시작
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
element.style.setProperty(property, to);
setTimeout(() => {
element.style.transition = '';
resolve();
}, duration);
});
});
}
}
// React 컴포넌트에서 사용
const AnimatedComponent: React.FC = () => {
const animationQueue = useRef(new AnimationQueue());
const elementRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
const handleClick = () => {
if (elementRef.current) {
// 순차적으로 애니메이션 실행
animationQueue.current.addAnimation({
element: elementRef.current,
property: 'transform',
from: 'translateX(0px)',
to: 'translateX(100px)',
duration: 500
});
animationQueue.current.addAnimation({
element: elementRef.current,
property: 'background-color',
from: 'blue',
to: 'red',
duration: 300
});
}
};
return (
<div>
<div ref={elementRef} style={{ width: 100, height: 100, backgroundColor: 'blue' }} />
<button onClick={handleClick}>애니메이션 시작</button>
</div>
);
};
BFS (너비 우선 탐색) 구현
interface TreeNode {
value: number;
children: TreeNode[];
}
function breadthFirstSearch(root: TreeNode, target: number): TreeNode | null {
const queue = new LinkedQueue<TreeNode>();
queue.enqueue(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
const current = queue.dequeue()!;
if (current.value === target) {
return current;
}
// 현재 노드의 모든 자식을 큐에 추가
for (const child of current.children) {
queue.enqueue(child);
}
}
return null; // 찾지 못함
}
// 사용 예시
const tree: TreeNode = {
value: 1,
children: [
{
value: 2,
children: [
{ value: 4, children: [] },
{ value: 5, children: [] }
]
},
{
value: 3,
children: [
{ value: 6, children: [] },
{ value: 7, children: [] }
]
}
]
};
const result = breadthFirstSearch(tree, 5);
console.log(result?.value); // 5
큐의 변형
우선순위 큐 (Priority Queue)
interface PriorityItem<T> {
data: T;
priority: number;
}
class PriorityQueue<T> {
private items: PriorityItem<T>[] = [];
enqueue(data: T, priority: number): void {
const newItem: PriorityItem<T> = { data, priority };
// 우선순위에 따라 적절한 위치에 삽입
let inserted = false;
for (let i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) {
if (newItem.priority > this.items[i].priority) {
this.items.splice(i, 0, newItem);
inserted = true;
break;
}
}
if (!inserted) {
this.items.push(newItem);
}
}
dequeue(): T | undefined {
const item = this.items.shift();
return item?.data;
}
peek(): T | undefined {
return this.items[0]?.data;
}
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
}
// 태스크 스케줄러 예시
interface Task {
id: string;
name: string;
execute: () => Promise<void>;
}
class TaskScheduler {
private taskQueue = new PriorityQueue<Task>();
addTask(task: Task, priority: number): void {
this.taskQueue.enqueue(task, priority);
}
async processTasks(): Promise<void> {
while (!this.taskQueue.isEmpty()) {
const task = this.taskQueue.dequeue();
if (task) {
console.log(`Executing task: ${task.name}`);
await task.execute();
}
}
}
}
덱 (Deque - Double Ended Queue)
class Deque<T> {
private items: T[] = [];
// 앞쪽에 삽입
addFront(item: T): void {
this.items.unshift(item);
}
// 뒤쪽에 삽입
addRear(item: T): void {
this.items.push(item);
}
// 앞쪽에서 제거
removeFront(): T | undefined {
return this.items.shift();
}
// 뒤쪽에서 제거
removeRear(): T | undefined {
return this.items.pop();
}
peekFront(): T | undefined {
return this.items[0];
}
peekRear(): T | undefined {
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
isEmpty(): boolean {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
size(): number {
return this.items.length;
}
}
장점
- 순서 보장: FIFO 원칙으로 데이터 순서가 보장된다
- 효율적 연산: enqueue, dequeue 모두 O(1) 시간
- 자연스러운 모델링: 대기열, 버퍼 등을 자연스럽게 표현
- 동시성 처리: 멀티스레딩 환경에서 작업 분배에 유용
단점
- 제한적 접근: 앞쪽과 뒤쪽 요소만 접근 가능
- 중간 요소 접근 불가: 특정 위치 요소에 바로 접근할 수 없다
- 검색 비효율: 특정 요소 찾기에 O(n) 시간 필요
- 메모리 사용: 배열 기반 구현 시 크기 제한이나 메모리 낭비 가능
활용 사례 정리
- 운영체제: 프로세스 스케줄링, 버퍼 관리
- 네트워킹: 패킷 버퍼링, 요청 대기열
- 웹 개발: 이벤트 처리, API 요청 관리, 애니메이션 시퀀싱
- 알고리즘: BFS 탐색, 레벨 순서 순회
- 시뮬레이션: 대기줄 모델링, 작업 스케줄링
스택 vs 큐 비교
| 특성 | 스택 (Stack) | 큐 (Queue) |
|---|---|---|
| 원칙 | LIFO | FIFO |
| 삽입 위치 | top | rear |
| 삭제 위치 | top | front |
| 주요 연산 | push, pop | enqueue, dequeue |
| 대표적 활용 | 함수 호출, Undo/Redo | BFS, 작업 스케줄링 |
최적화 팁
- 구현 방식 선택: 크기가 고정이면 원형 큐, 동적이면 연결 리스트
- 메모리 관리: 원형 큐로 메모리 재사용 극대화
- 배치 처리: 여러 요소를 한 번에 처리하여 오버헤드 감소
- 우선순위 고려: 단순 FIFO가 아닌 우선순위가 필요하면 우선순위 큐 사용