-
MST(Minimun Spanning Tree)구현 시 사용되는 알고리즘
-
크루스탈 알고리즘 간선을 정렬하여 작은 간선부터 추가 해 주는 방식으로 부분적인 트리를 완성하면서 나중에 하나의 트리로 만드는 과정이라면 프림 알고리즘은 하나의 노드를 시작으로 트리를 형성하는 구조
-
조사가 끝난 노드에 대하여는 조사를 더 하지 않음으로 싸이클이 발생하는 경우는 존재하지 않음
*문제상황
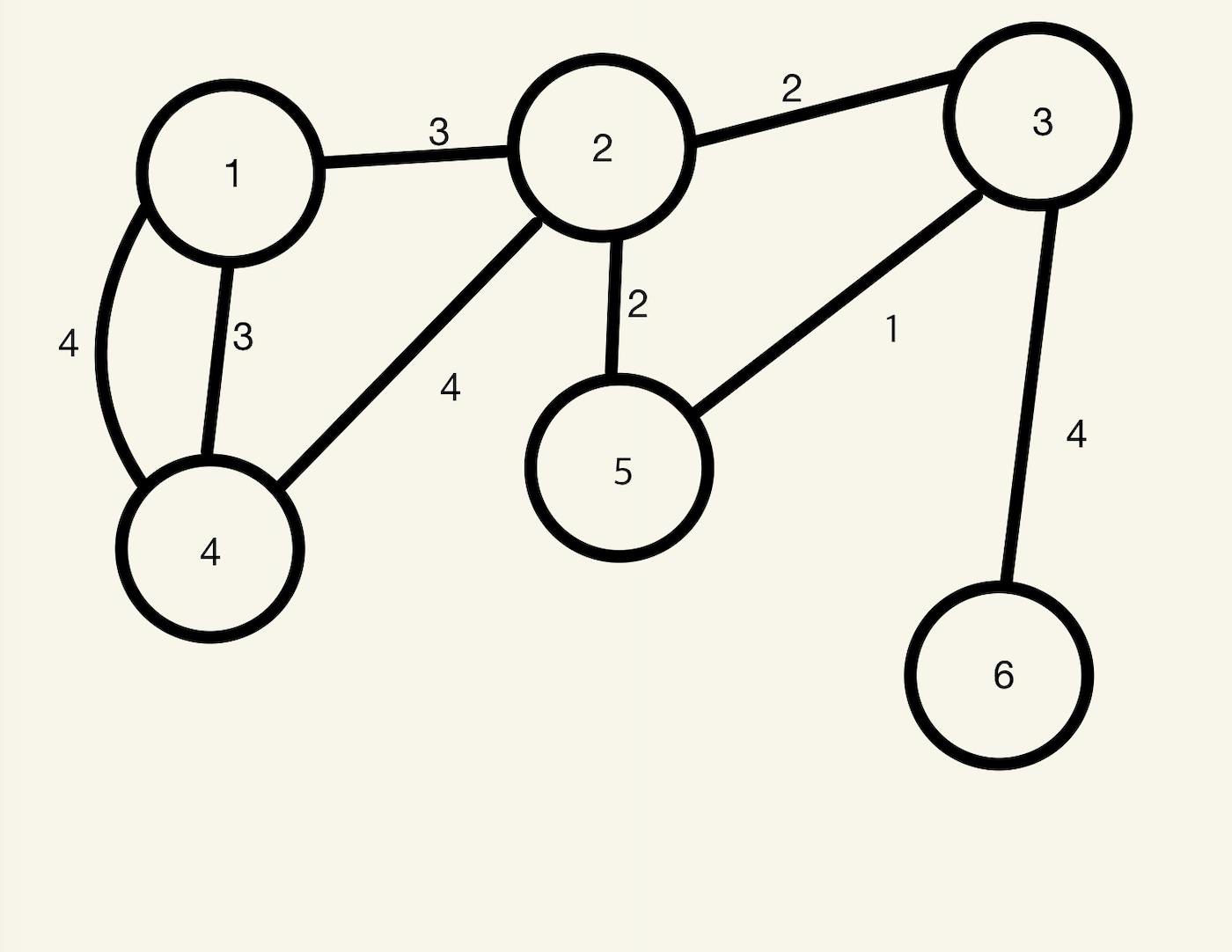
Step1 임의의 한 노드에 대하여 조사를 진행한다.(3번 노드를 선택한다고 가정하였다.)
.png)
Step2 선택된 간선으로 갈 수 있는 노드에 대하여 그 노드로도 뻗을 수 있는 간선을 고려하여 1) 간선의 가중치가 가장 작고 2) 조사를 하지 않는 노드를 선택하여 계속 조사를 진행한다.
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
-
우선순위 큐를 이용하여 구현
-
시간복잡도는 우선순위 큐의 구현에 따라서 달라 질 수 있다.
*소스코드
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class PrimAlgorithm {
static int[] visited = new int[7];
static class MapInfo{
int node;
int weight;
public MapInfo(int node, int weight){
this.node = node;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
static class Search implements Comparable<Search>{
int node1;
int node2;
int weight;
public Search(int node1, int node2, int weight){
this.node1 = node1;
this.node2 = node2;
this.weight =weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Search search) {
return this.weight - search.weight;
}
}
static List<List<MapInfo>> prim(int start, List<List<MapInfo>> map){
List<List<MapInfo>> mst = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 7; i++){
mst.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
int edgeCount = 0 ;
visited[start] = 1;
PriorityQueue<Search> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
//간선의 정보를 저장
for(int i = 0 ; i <map.get(start).size();i++){
pq.add(new Search(start,map.get(start).get(i).node,map.get(start).get(i).weight));
}
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
Search search = pq.poll();
//이미 방문한 노드는 조사하지 않음
if(visited[search.node2] == 1) continue;
//트리의 간선의 수가 노드의 수 - 1이면 더이상 조사하지 않음
if(edgeCount == map.size()-2) break;
//조사 노드를 저장
for(int i = 0 ; i <map.get(search.node2).size();i++){
pq.add(new Search(search.node2,map.get(search.node2).get(i).node,map.get(search.node2).get(i).weight));
}
visited[search.node2] = 1;
//트리의 간선을 저장
mst.get(search.node1).add(new MapInfo(search.node2,search.weight));
edgeCount++;
}
return mst;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//노드 연결정보 저장
List<List<MapInfo>> map = new ArrayList<>();
List<MapInfo> insert = new ArrayList<>();
map.add(insert);
insert = new ArrayList<>();
insert.add(new MapInfo(2,3));
insert.add(new MapInfo(4,3));
insert.add(new MapInfo(4,4));
map.add(insert);
insert = new ArrayList<>();
insert.add(new MapInfo(1,3));
insert.add(new MapInfo(4,4));
insert.add(new MapInfo(5,2));
map.add(insert);
insert = new ArrayList<>();
insert.add(new MapInfo(2,2));
insert.add(new MapInfo(5,1));
insert.add(new MapInfo(6,4));
map.add(insert);
insert = new ArrayList<>();
insert.add(new MapInfo(1,4));
insert.add(new MapInfo(1,3));
insert.add(new MapInfo(2,4));
map.add(insert);
insert = new ArrayList<>();
insert.add(new MapInfo(2,2));
insert.add(new MapInfo(3,1));
map.add(insert);
insert = new ArrayList<>();
insert.add(new MapInfo(3,4));
map.add(insert);
List<List<MapInfo>> mst = prim(3,map);
for(int i = 0 ; i < mst.size(); i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j< mst.get(i).size(); j++){
System.out.println("node1 : " + i + " node2 : " + mst.get(i).get(j).node
+ " weight : " + mst.get(i).get(j).weight);
}
}
}
}.png)
