Allocator
배경
- new/delete는 문맥전환의 확률이 있음
- new/delete는 메모리 단편화의 가능성이 있음
- 한번에 많은 양을 할당 받고 거기서 잘 쪼개서 사용하자!
new/delete override
- new/delete 또한 오버라이딩의 대상
- 전역으로 오버라이드 혹은 원하는 클래스 내부에서 오버라이드 가능
class Knight
{
public:
Knight()
{
cout << "Knight()" << endl;
}
Knight(int32 hp) : _hp(hp)
{
cout << "Knight(hp)" << endl;
}
~Knight()
{
cout << "~Knight()" << endl;
}
int32 _hp = 100;
int32 _mp = 50;
};
void* operator new(size_t size)
{
cout << "new!" << size << endl;
void* ptr = ::malloc(size);
return ptr;
}
void operator delete(void* ptr)
{
cout << "delete!" <<endl;
::free(ptr);
}
void* operator new[](size_t size)
{
cout << "new![]" << size << endl;
void* ptr = ::malloc(size);
return ptr;
}
void operator delete[](void* ptr)
{
cout << "delete![]" << endl;
::free(ptr);
}
int main()
{
Knight* kinght = new Knight();
delete kinght;
}
사용자 정의 할당/소멸 (Allocator)
- new/delete 기능에 원하는 기능을 넣을 수 있음
- placement new
- 이미 할당된 메모리에 대해서 생성자를 호출
new(memory)Type(std::forward<Args>(args)...);- 이미 할당된 메모리 memory 위치에서 Type클래스의 생성자 Type(args)를 호출해줘
class BaseAllocator
{
public:
static void* Alloc(int32 size);
static void Release(void* ptr);
};
#include "Allocator.h"
void* BaseAllocator::Alloc(int32 size)
{
return ::malloc(size);
}
void BaseAllocator::Release(void* ptr)
{
::free(ptr);
}
#include "Allocator.h"
template <typename Type, typename... Args>
Type* xnew(Args&&... args)
{
Type* memory = static_cast<Type*>(BaseAllocator::Alloc(sizeof(Type)));
new(memory)Type(std::forward<Args>(args)...);
return memory;
}
template <typename Type>
void xdelete(Type* obj)
{
obj->~Type();
BaseAllocator::Release(obj);
}
int main()
{
Knight* kinght = new Knight();
delete kinght;
Knight* k2 = xnew<Knight>();
xdelete(k2);
Knight* k3 = xnew<Knight>(100);
xdelete(k3);
int a = 0;
}

Allocator for Debug
배경
- 기존의 포인터를 사용하면 메모리 오염 문제 발생
- Use-After-Free
- 캐스팅에 의한 오염 (주로 오버플로우)
- 이를 개발 단계에서 찾아내기 위해 Guard Pages Allocator 사용
- 스마트 포인터를 사용하면 Use-After-Free는 거의 해결
- Unreal 에서는 Stomp Allocator라 부르는 듯
개념
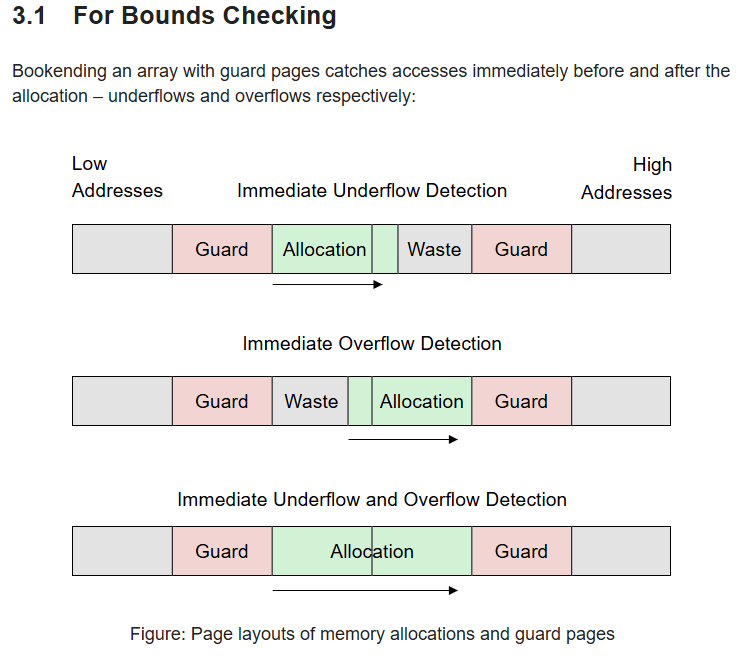
Guard Pages Allocator
- 페이지의 블록 단위로 메모리 할당을 받지 말고 페이지 통으로 받자
- 페이지의 앞 뒤로 보호 페이지를 넣어서 다른 페이지에 접근하지 못하도록하자.
- 페이지를 통으로 받으니까 반납도 한 번에 이루어짐
- User 페이지 내부에서의 언더/오버 플로우에는 취약
- 아래 그림과 같이 한쪽으로 붙여서 오버/언더 플로우 확인 가능
구현
void* GuardAllocator::Alloc(int32 size)
{
const int64 pageCount = (size + PAGE_SIZE - 1) / PAGE_SIZE;
const int64 totalPage = pageCount + 2;
void* baseAddress = ::VirtualAlloc(
NULL,
totalPage * PAGE_SIZE,
MEM_RESERVE | MEM_COMMIT,
PAGE_READWRITE
);
if (!baseAddress) return nullptr;
DWORD oldProtect;
::VirtualProtect(
baseAddress,
PAGE_SIZE,
PAGE_NOACCESS,
&oldProtect
);
::VirtualProtect(
static_cast<int8_t*>(baseAddress) + ((totalPage - 1) * PAGE_SIZE),
PAGE_SIZE,
PAGE_NOACCESS,
&oldProtect
);
const int64 dataOffset = PAGE_SIZE + (pageCount * PAGE_SIZE) - size;
return static_cast<void*>(static_cast<int8_t*>(baseAddress) + dataOffset);
}
void GuardAllocator::Release(void* ptr)
{
if (!ptr) return;
const int64 address = reinterpret_cast<int64>(ptr);
const int64 baseAddress = address - (address % PAGE_SIZE) - PAGE_SIZE;
::VirtualFree(reinterpret_cast<void*>(baseAddress), 0, MEM_RELEASE);
}
- 많은 메모리 사용
- 상대적으로 엄격한 버그 탐지
void* StompAllocator::Alloc(int32 size)
{
const int64 pageCount = (size + PAGE_SIZE - 1) / PAGE_SIZE;
const int64 dataOffset = pageCount * PAGE_SIZE - size;
void* baseAddress = ::VirtualAlloc(
NULL, pageCount * PAGE_SIZE,
MEM_RESERVE | MEM_COMMIT,
PAGE_READWRITE
);
return static_cast<void*>(static_cast<int8*>(baseAddress) + dataOffset);
}
void StompAllocator::Release(void* ptr)
{
const int64 address = reinterpret_cast<int64>(ptr);
const int64 baseAddress = address - (address % PAGE_SIZE);
::VirtualFree(reinterpret_cast<void*>(baseAddress), 0, MEM_RELEASE);
}
- 적은 메모리 사용
- 상대적으로 덜 엄격한 탐지 (대부분은 경우는 탐지 가능하다고...)




