배경
이번에는 메모리 파편화를 위한 Memory Pool에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
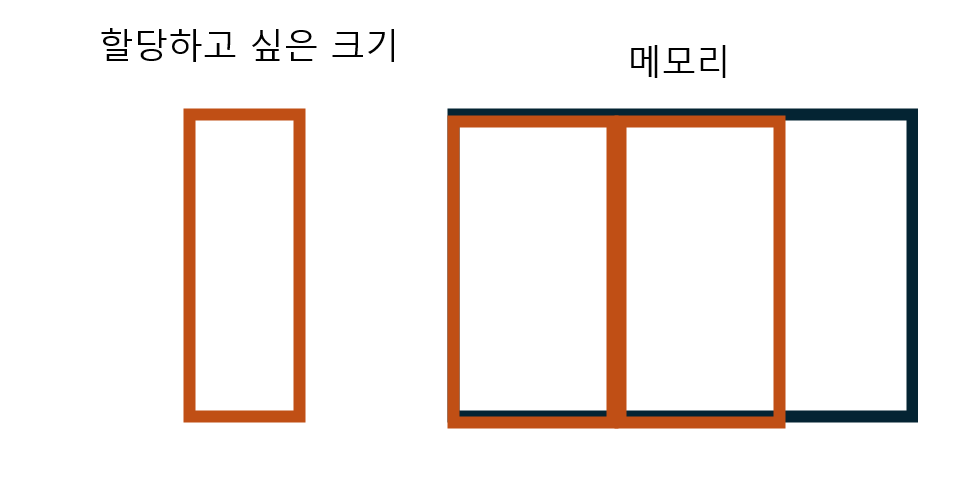
메모리 파편화는 메모리에 할당할 수 있는 공간이 있지만 할당하지 못하는 상황을 의미합니다. 어떻게 이럴 수 있냐하면 이미지를 보여드리겠습니다.
오른쪽은 메모리 공간이라고 봅시다. 그리고 왼쪽은 할당하고 싶은 크기라고 했을 때 메모리에 빈 공간이 있으므로 할당이 가능할 것입니다.
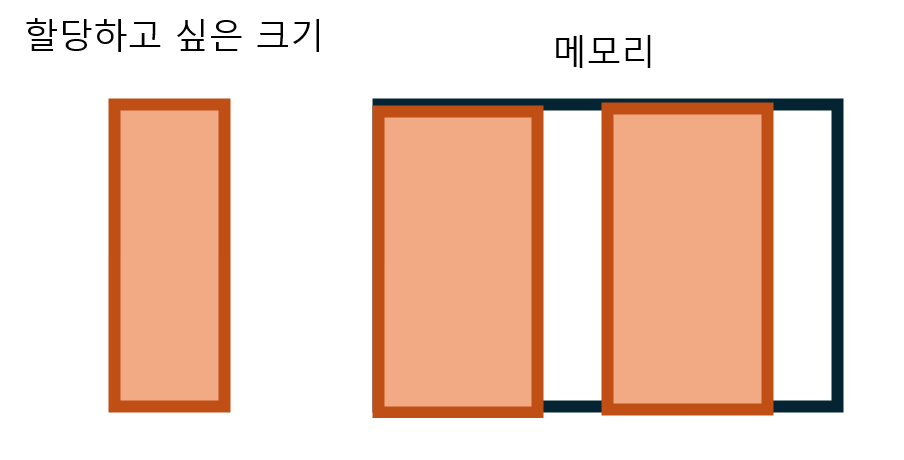
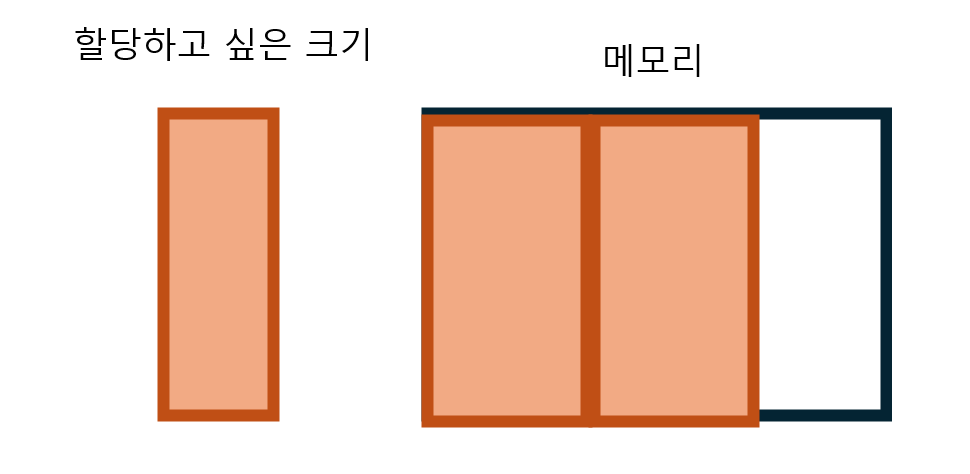
그러나 메모리를 할당하고 해제하고 하다보면 이렇게 메모리 공간이 설정되어 있을 수도 있습니다. 그렇다면 아까와 같은 크기의 용랴잉 메모리에 할당되어 있지만 빈 공간이 나뉘어져 있어 할당을 하지 못하게 될 것입니다.
이를 해결하기 위해서는 억지로 운영체제에게 추가로 할당받아 사용할 수 밖에 없을 것입니다. 그렇다면 낭비가 되겠죠
구현
Memory Pool을 이런 일이 없도록 하기 위해 만든 것입니다.
MemoryPool에서는 미리 다양한 크기의 메모리 공간을 할당하여 보관합니다. 그래서 만약 요청이 온다면 최대한 비슷한 크기의 메모리 공간을 가져와 사용권을 줍니다. 그렇다면 아까처럼 비효율적인 상황이 줄어들 것입니다.
//데이터를 할당할 때 해당 데이터의 크기를 데이터 앞에 붙여줌
struct MyMemoryHeader {
MyMemoryHeader(int32 size) : allocSize(size) {
}
static void* AttachHeader(MyMemoryHeader* header, int32 size) {
new(header)MyMemoryHeader(size);
return reinterpret_cast<void*>(++header);
}
static MyMemoryHeader* DetachHeader(void* ptr) {
MyMemoryHeader* header = reinterpret_cast<MyMemoryHeader*>(ptr) - 1;
return header;
}
int32 allocSize;
};
class MyMemoryPool {
public:
MyMemoryPool(int32 allocSize) : _allocSize(allocSize) {
}
~MyMemoryPool() {
while (!_queue.empty()) {
MyMemoryHeader* header = _queue.front();
_queue.pop();
free(header);
}
}
void Push(MyMemoryHeader* ptr) {
WRITE_LOCK;
ptr->allocSize = 0;
_queue.push(ptr);
_allocCount.fetch_sub(1);
}
MyMemoryHeader* Pop() {
MyMemoryHeader* header = nullptr;
WRITE_LOCK;
if (!_queue.empty()) {
header = _queue.front();
_queue.pop();
}
if (header == nullptr) {
header = reinterpret_cast<MyMemoryHeader*>(malloc(_allocSize));
}
_allocCount.fetch_add(1);
return header;
}
private:
int32 _allocSize = 0;
atomic<int32> _allocCount = 0;
USE_LOCK;
queue<MyMemoryHeader*> _queue;
};
class MyMemory {
enum {
POOL_COUNT = (1024 / 32) + (1024 / 128) + (2048 / 256),
MAX_ALLOC_SIZE = 4096
};
public:
MyMemory() {
int32 size = 0;
int32 tableIndex = 0;
for (size = 32; size <= 1024; size += 32) {
MyMemoryPool* pool = new MyMemoryPool(size);
_pools.push_back(pool);
while (tableIndex <= size) {
_poolTable[tableIndex] = pool;
tableIndex++;
}
}
for (size = 1024; size <= 2048; size += 128) {
MyMemoryPool* pool = new MyMemoryPool(size);
_pools.push_back(pool);
while (tableIndex <= size) {
_poolTable[tableIndex] = pool;
tableIndex++;
}
}
for (size = 2048; size <= 4096; size += 256) {
MyMemoryPool* pool = new MyMemoryPool(size);
_pools.push_back(pool);
while (tableIndex <= size) {
_poolTable[tableIndex] = pool;
tableIndex++;
}
}
}
~MyMemory() {
for (MyMemoryPool* pool : _pools) {
delete pool;
}
_pools.clear();
}
void* Allocate(int32 size) {
MyMemoryHeader* header = nullptr;
const int32 allocSize = size + sizeof(MyMemoryHeader);
if (allocSize > MAX_ALLOC_SIZE) {
header = reinterpret_cast<MyMemoryHeader*>(malloc(allocSize));
}
else {
header = _poolTable[allocSize]->Pop();
}
return MyMemoryHeader::AttachHeader(header, allocSize);
}
void Release(void* ptr) {
MyMemoryHeader* header = MyMemoryHeader::DetachHeader(ptr);
const int32 allocSize = header->allocSize;
if (allocSize > MAX_ALLOC_SIZE) {
free(header);
}
else {
_poolTable[allocSize]->Push(header);
}
}
private:
vector<MyMemoryPool*> _pools;
MyMemoryPool* _poolTable[MAX_ALLOC_SIZE + 1];
};
MyMemory* MyGMemory = new MyMemory();
void* MemoryAlloc(int32 size) {
return MyGMemory->Allocate(size);
}
void MemoryRelease(void* ptr) {
MyGMemory->Release(ptr);
}
template<typename Type, typename... Args>
Type* xxnew(Args&&... args) {
Type* memory = static_cast<Type*>(MemoryAlloc(sizeof(Type)));
new(memory)Type(::forward<Args>(args)...);
return memory;
}
template<typename Type>
void xxdelete(Type* ptr) {
ptr->~Type();
MemoryRelease(ptr);
}
int main() {
for (int32 i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
GThreadManager->Launch([]() {
while (true) {
Knight* knight = xxnew<Knight>();
xxdelete<Knight>(knight);
}
});
}
}MemoryPool
여기서 MemoryPool을 생성자에서 본인이 할당한 메모리의 크기를 입력받습니다. 그리고 내부적으로 큐를 가지고 있습니다. 이 큐에 요청을 받을 때마다 Pop을 통해 큐에 들어있는 할당된 메모리 공간을 반환합니다. 만약 없을 경우 새로 만들어줍니다.
다 사용한 후에는 Push를 통해 다시 큐에 집어넣습니다.
Memory
Memory에서 MemoryPool을 관리합니다. Memory가 생성이 되면 최대 4096 바이트 공간을 할당합니다. 1024바이트까지는 다양한 크기의 할당이 이루어질 것으로 예상이 되므로 32바이트로 잘게 쪼개줍니다.
즉 1024바이트까지는 32, 64, 96, ... 크기의 메모리 공간을 할당해서 보관하는 MemoryPool을 가지고 있을 것입니다.
2048까지는 128바이트 단위로 증가하고 그렇게 4096까지 MemoryPool을 생성합니다.
내부적으로 _poolTable을 가지고 있습니다. 여기서는 32바이트까지는 32바이트 MemoryPool 하나를 넣도록 하고 64바이트는 64바이트 MemoryPool을 넣도록 합니다.
그렇게 한다면 예를 들어 28바이트를 할당받고 싶다면 _poolTable[28]에 접근할 것입니다. 그러면 32바이트의 MemoryPool 큐에 들어있는 메모리 공간을 받을 것입니다.
이런 식으로 while문으로 구현된 것입니다.