
기본개념
transformation은 translation, rotation, scaling을 다룬다.
input과 output은 vector 혹은 porsition이다.
또한 다음 법칙이 성립한다.

Scaling
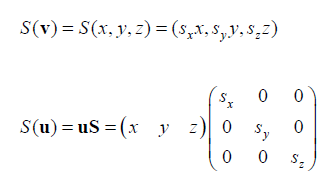
Rotation
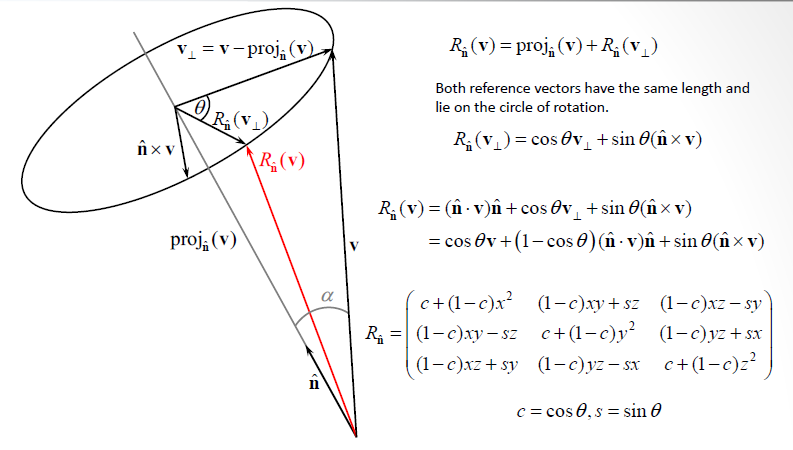
를 을 기준으로 만큼 회전변환 시킨 를 구한다.
를 로 를 로 두고 를 로 표현한다.
이러한 회전변환은 축 각각에 대하여 회전변환한다.
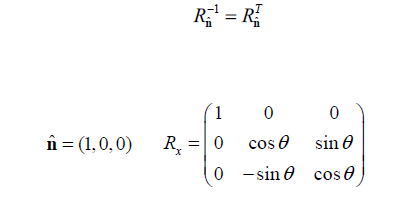
위는 축에 대한 회전변환이고,orthogonal matrix이기 때문에 inverse와 transpose의 결과가 같다.
회전변환의 세 가지 방법
이러한 회전변환에는 세 가지 방법이 있다. 오일러 각(Euler Angles), 축-각 표현(Axis-Angle), 단위 사원수(Unit Quaternions)가 있다.
오일러 각
3개의 직교 축(X, Y, Z)에 대해 순차적으로 회전을 적용하는 방식이다.
세 각을 알 때 사용하며, 짐벌락 문제가 있고 불연속성 문제도 있다. ( ~ )
Axis-Angle
회전변환 시킨 축과 그 축에대해 회전한 를 알 때 사용한다.
이 또한 불연속성 문제가 있다.
Unit Quaternions
회전변환 시킨 좌표를 알 때, 축 변환 방법이다.
Homogeneous Coordinates
Homogeneous Coordinates는 동일한 형식으로 points와 vectors를 나타낸다.
좌표를 더 높은 차원으로 확장한 표현이다.
- for vectors.
- for points.
이를 통해 행렬 연산으로 변환을 통합할 수 있다. (평행이동, 회전, 스케일 변환)
Affine Transformation
기존 선형 변환은 translation을 표현하지 못한다. 아핀 변환은 평행이동을 포함한 선형 변환을 처리한다.
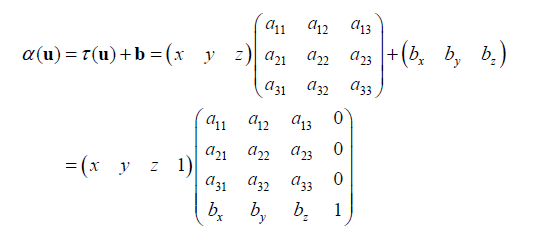
Composition of Transformations
- Matrix multiplication is associative
- Matrix multiplication is not commutative
Change of Coordinate Transformations
변환된 좌표축으로 계산
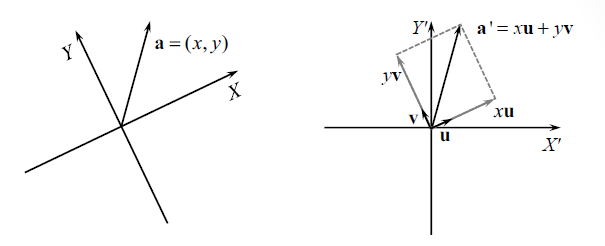
A vector in XY-plane.
A vector in X'Y'-plane ().
- points
DirectX 코드
Math Transformation Functions
// Constructs a scaling matrix:
XMMATRIX XM_CALLCONV XMMatrixScaling(
float ScaleX, float ScaleY, float ScaleZ); // Scaling factors요소를 Scaling하고 XMMATRIX를 반환한다.
// Constructs a scaling matrix from components in vector:
XMMATRIX XM_CALLCONV XMMatrixScalingFromVector(FXMVECTOR Scale);
// Scaling factors (sx, sy, sz)요소를 FXMVECTOR로 받는다.
// Constructs a x-axis rotation matrix Rx: clockwise angle θ
XMMATRIX XM_CALLCONV XMMatrixRotationX(float Angle);
// Constructs a y-axis rotation matrix Ry:
XMMATRIX XM_CALLCONV XMMatrixRotationY(float Angle);
// Constructs a z-axis rotation matrix Rz:
XMMATRIX XM_CALLCONV XMMatrixRotationZ(float Angle);축과 를 받아 회전변환을 수행한다.
// Constructs an arbitrary axis rotation matrix Rn:
XMMATRIX XM_CALLCONV XMMatrixRotationAxis(
FXMVECTOR Axis, // Axis n to rotate about
float Angle); // Clockwise angle θ to rotate축 n에 대하여 회전변환을 수행한다.
// Constructs a translation matrix:
XMMATRIX XM_CALLCONV XMMatrixTranslation(
float OffsetX, float OffsetY, float OffsetZ);
// Translation factors
// Constructs a translation matrix from components in a vector:
XMMATRIX XM_CALLCONV XMMatrixTranslationFromVector(FXMVECTOR Offset);
// Translation factorstranslation을 수행한다.
// Computes the vector-matrix product vM where vw = 1
// for transforming points:
XMVECTOR XM_CALLCONV XMVector3TransformCoord(
FXMVECTOR V, CXMMATRIX M); // Input V and M
// Computes the vector-matrix product vM where vw = 0
// for transforming vectors:
XMVECTOR XM_CALLCONV XMVector3TransformNormal(
FXMVECTOR V, CXMMATRIX M); // Input V and Mtransformed 된 벡터를 반환하며, 위는 w = 1인 points로 보고, 아래는 w = 0인 vectors로 본다.
예제
int main() {
if (!DirectX::XMVerifyCPUSupport()) {
std::cout << "directx math not supported" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(10);
DirectX::XMMATRIX A = DirectX::XMMatrixAffineTransformation( // 아핀 변환
DirectX::XMVECTOR({ 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f }),
DirectX::XMVECTOR({ 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f }),
DirectX::XMVECTOR({ DirectX::XM_PIDIV4, DirectX::XM_PIDIV4,
0.0f, 0.0f }),
DirectX::XMVECTOR({ 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f }));
std::cout << "A = " << std::endl << A << std::endl;
DirectX::XMVECTOR X, Y;
X = DirectX::XMVectorSet(-2.0f, 1.0f, -3.0f, 0.0f);
Y = DirectX::XMVector3TransformNormal(X, A); // X를 변환시킨 벡터
std::cout << "X = " << std::endl << X << std::endl;
std::cout << "Y = " << std::endl << Y << std::endl;
DirectX::XMMATRIX A2 = DirectX::XMMatrixInverse(nullptr, A); // A의 역행렬
X = DirectX::XMVector3TransformNormal(Y, A2); // Y를 다시 변환시킨 행렬
std::cout << "X = " << std::endl << X << std::endl; // 거의 유사한 결과가 나온다.
return 0;
}실행결과
A =
-0.2337006330 1.2337006330 0.0000000000 0.0000000000
1.2337006330 -0.2337006330 0.0000000000 0.0000000000
0.0000000000 0.0000000000 -1.4674012661 0.0000000000
1.0000000000 0.0000000000 0.0000000000 1.0000000000
X =
(-2.0000000000, 1.0000000000, -3.0000000000, 0.0000000000)
Y =
(1.7011018991, -2.7011017799, 4.4022035599, 0.0000000000)
X =
(-2.0000000000, 1.0000001192, -3.0000000000, 0.0000000000) // 거의 유사하게 나옴