서론
- 기존에 프로젝트를 진행하면서 문제를 생성을 일일이 Insert 해야되는 문제점을 발견하여 대량으로 Insert의 문제점을 발견을 하였습니다.
이러한 문제점을 해결하기 위해 처음에는 기존의 문제 생성의 서비스 로직을 재귀를 통하여 반복하여 Insert를 하여 문제를 해결을 하였습니다.
그러나 Page 성능을 테스트 하면서 대량의 데이터를 넣기 위해 10,000건의 데이터를 넣는데 시간이 너무 많이 걸리는 문제점을 발견을 하였습니다. 문제의 원인은 재귀를 통하여 Insert를 하기 때문에 순서대로 Insert를 하여 10,000건의 데이터를 넣기 위하여 많은 시간이 필요를 하였습니다.
본론
2-1 기존의 문제점
- 기존의 코드
@Override
@Transactional
public void createQuestionChoice(CreateQuestionAndCategoryRequestDto requestDto) {
String findCategoryTitle = requestDto.getCategoryRequestDto().getCategory();
Category category = categoryRepository.findByTitle(findCategoryTitle)
.orElseThrow(() -> new NotFoundCategoryTile(findCategoryTitle));
Question question = createQuestion(requestDto.getCreateQuestionRequestDto(), category);
List<Choice> choices = requestDto.getCreateChoicesAboutQuestionDto().stream()
.map(choiceDto -> {
boolean answer = isCollectAnswer(choiceDto.getAnswer());
return createChoice(choiceDto, question, answer);
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
question.setChoices(choices);
questionRepository.save(question);
choiceRepository.saveAll(choices);
}
private Question createQuestion(
CreateQuestionRequestDto questionDto,
Category category
) {
return Question.builder()
.title(questionDto.getQuestionTitle())
.description(questionDto.getQuestionDesc())
.explain(questionDto.getQuestionExplain())
.category(category)
.build();
}
private boolean isCollectAnswer(String answer) {
return COLLECT_ANSWER.equals(answer);
}
private Choice createChoice(
CreateChoicesAboutQuestionDto choiceDto,
Question question,
boolean isAnswer
) {
return Choice.builder()
.number(choiceDto.getNumber())
.content(choiceDto.getContent())
.question(question)
.answer(isAnswer)
.build();
}코드 설명
-
기존의 코드를 설명을 하겠습니다. ( 문제 생성 )
문제를 생성하기 위해서는 카테고리, 문제, 선택지에 대한 부분을 신경을 써야 정상적으로 해결이 가능합니다. -
Request Dto를 살펴보면
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class CreateQuestionAndCategoryRequestDto {
private CreateQuestionRequestDto createQuestionRequestDto;
private CategoryRequestDto categoryRequestDto;
private List<CreateChoicesAboutQuestionDto> createChoicesAboutQuestionDto;
}- DTO JSON
{
"createQuestionRequestDto": {
"questionTitle": "Sample Question_3",
"questionDesc": "This is a sample question.",
"questionExplain": "This is the explanation of the sample question."
},
"categoryRequestDto": {
"category": "네트워크"
},
"createChoicesAboutQuestionDto": [
{
"number": 1,
"content": "Choice 1"
},
{
"number": 2,
"content": "Choice 2"
},
{
"number": 3,
"content": "Choice 3",
"answer":"정답"
},
{
"number": 4,
"content": "Choice 4"
}
]
}- 3개의 DTO가 있습니다. 각각 Question, Category, Choice가 있습니다.
- Category의 Title을 기반해서 카테고리를 찾는다.
- Question을 생성을 합니다. 이때 Category를 기반으로 생성을 합니다.
- Question에 대한 문제를 4개를 Insert 합니다.
2-2 재귀 Bulk Insert 시간 측정
- 이러한 3개의 테이블에 데이터를 넣습니다.
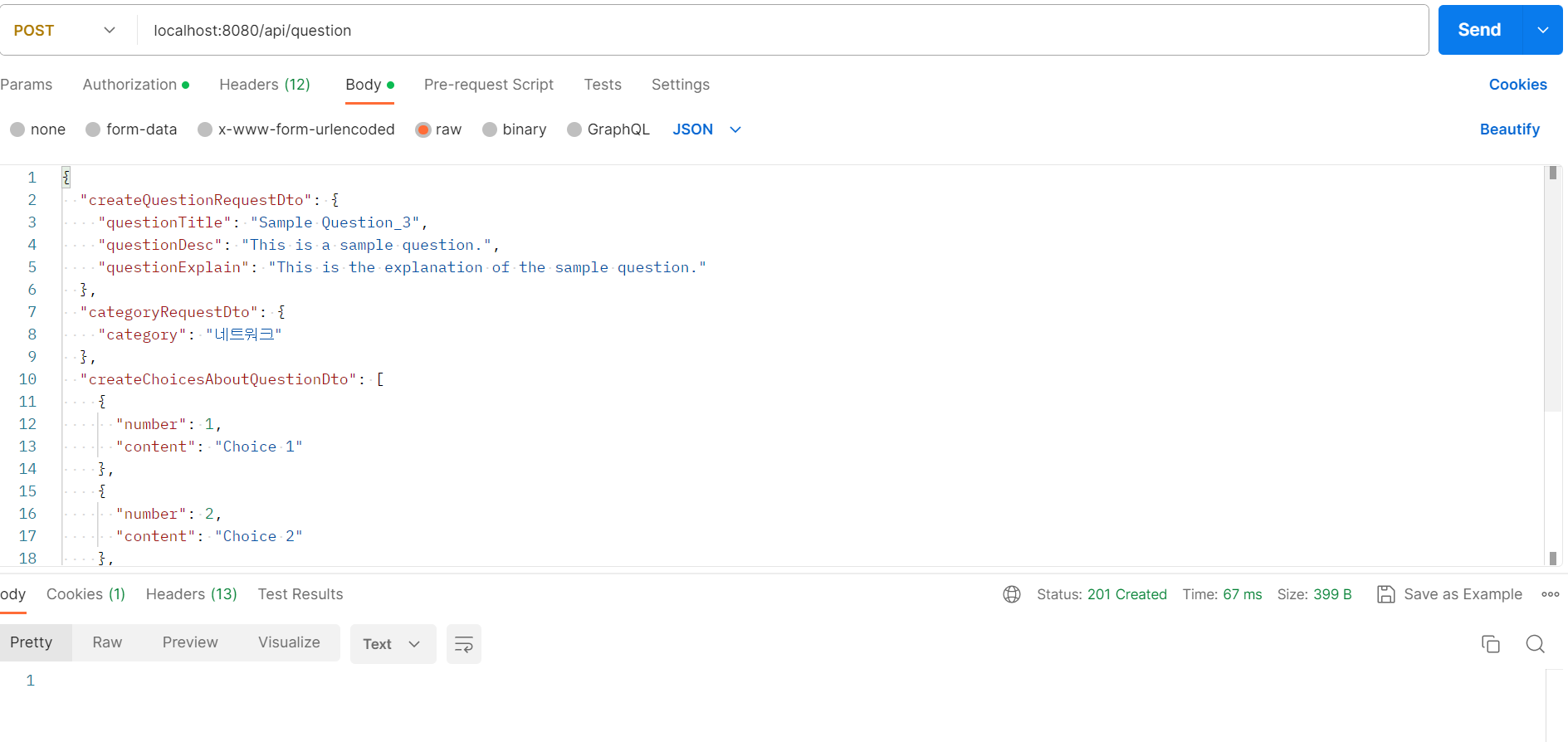
- 기존의 단일 데이터를 넣으면 67 ms가 발생을 합니다.
대량의 데이터를 Insert ( 리펙토링 이전 -> 재귀 )
@Override
@Transactional
public void recursiveCreateQuestionChoice(List<CreateQuestionAndCategoryRequestDto> requestDtos) {
for (CreateQuestionAndCategoryRequestDto requestDto : requestDtos) {
createQuestionChoice(requestDto);
}
}-
기존의 문제를 생성하는 서비스 로직을 호출하여 반복하여 문제를 생성하는 코드를 구현을 하였습니다.
-
기존의 이 코드를 기반으로 1,0000건의 데이터를 넣겠습니다.
-
아무래도 재귀를 통해서 3개의 테이블에 데이터를 넣고 10,000번을 반복하니깐 성능적으로 엄청난 문제가 발생한다.
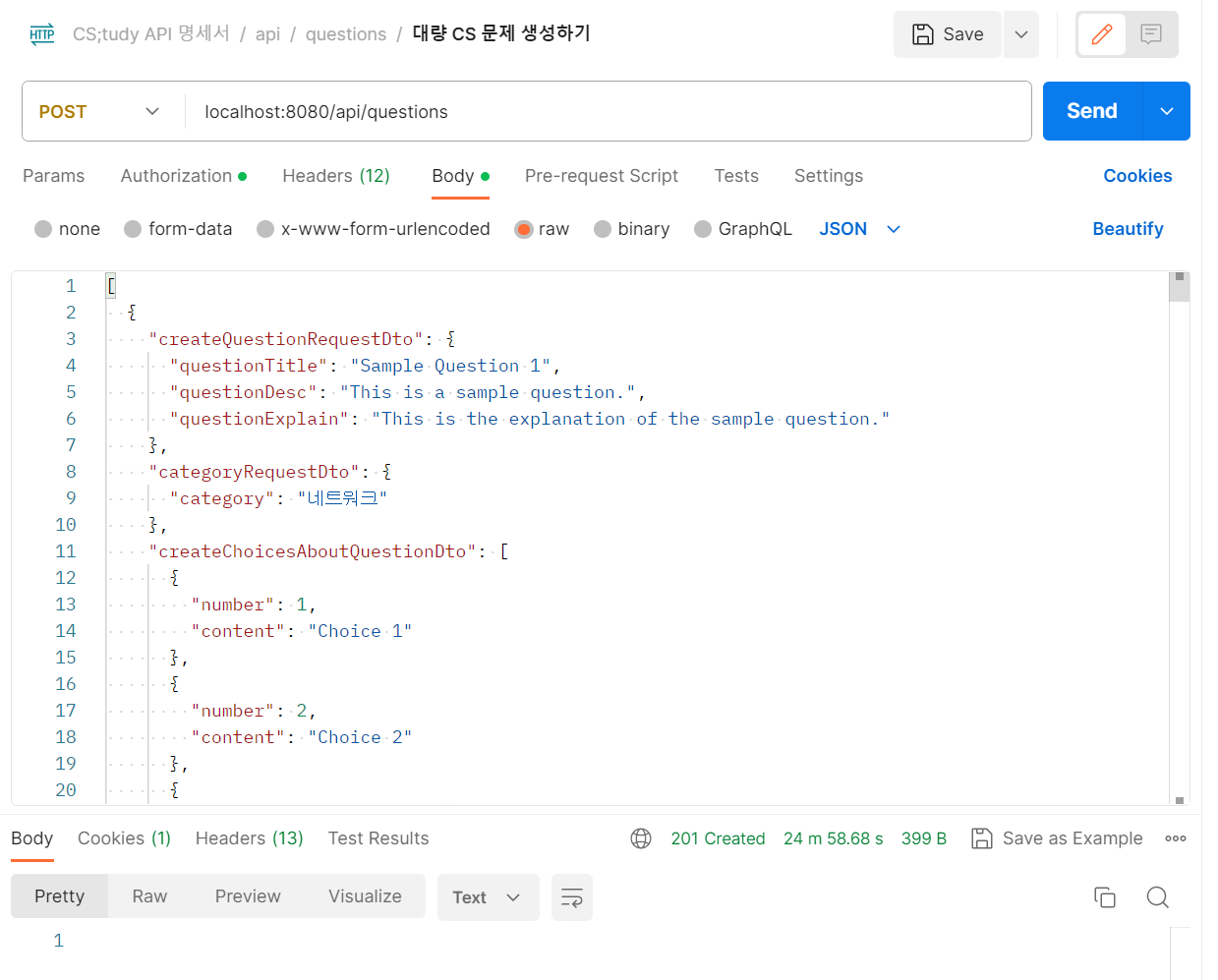
-
위 사진을 보면 24m 59.68s 발생을 합니다.
-
1,000건을 기준으로 데이터를 넣었을 때 초 단위로 삽입이 되기 때문에 성능에 문제가 있다고 확신을 했습니다.
-
이 부분을 Bulk Insert를 성능을 최적화를 하겠습니다.
3 Bulk Insert 성능 최적화
3-1 해결방안
-
처음에 이 문제를 만났을 때 인터넷의 검색을 하였더니 저와 비슷한 문제를 경험한 사람들이 많았습니다.
-
대표적으로 JDBC를 이용하여 문제를 해결을 하였습니다.
내가 생각하는 JDBC로 문제를 해결한 이유
-
저는 일단 JPA의 Insert에서 Batch Insert로 변경을 하였습니다.
Batch Insert란 무엇인가?
배치 Insert란 Insert Rows 여러 개 연결해서 한 번에 입력하는 것을 Batch Insert라고 말한다. 이때 Batch Insert는 하나의 트랜잭션으로 묶이게 됩니다.
INSERT INTO table1 (a1, a2) VALUES (v1, v11);
INSERT INTO table1 (a1, a2) VALUES (v2, v22);
INSERT INTO table1 (a1, a2) VALUES (v3, v33);
INSERT INTO table1 (col1, col2) VALUES
(val11, val12),
(val21, val22),
(val31, val32);3-2 제약 사항
Hibernate의 Batch Insert 제약 사항
-
Hibernate 문서를 살펴보면 다음과 같이 작성이 되어져 있습니다.
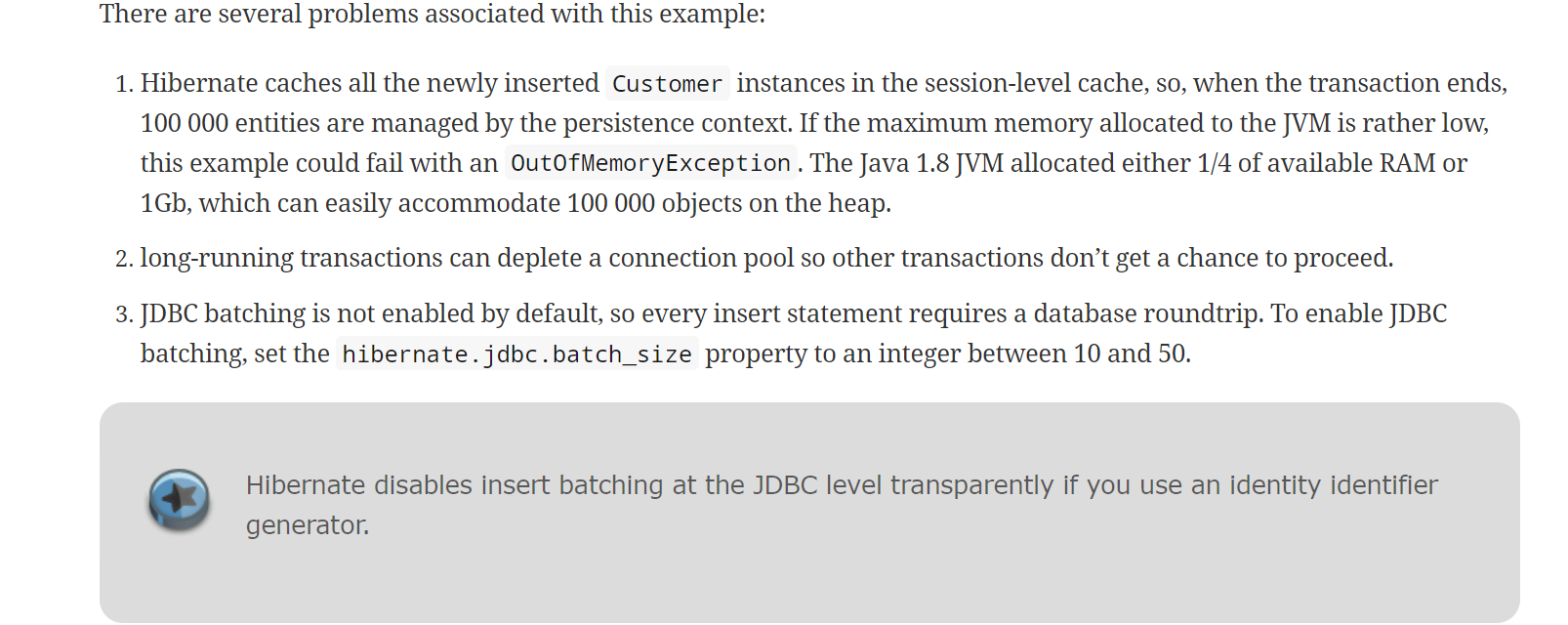
-
키 전략이 Identify이면 Hibernate가 JDBC 수준에서 Batch Insert가 비활성화 한다고 나와있다.
-
왜냐하면 Identifty는 MySQL과 의존적인 관계를 가집니다. 새로 할당하는 키를 미리 알 수 없기 때문입니다. 왜냐하면 새로운 레코드를 삽입할 때마다 키를 증가를 시킵니다. 이때 영속화 하지 않는 식별자 값을 미리 알 수 없기 때문에 Batch Insert를 진행하면 flush의
TransactionalWrite Behind’와 충돌이 발생하기 때문에 정상적인 동작을 하지 않습니다. -
기존의 코드는 다
Identify로 설정이 되어져 있기 때문에 문제를 수정하기 위해서는 너무 많은 코드를 수정하고 사이드 이펙트를 체크하기 어려움을 가졌습니다. 이 방식을 우회하기 위하여 JdbcTemplate을 사용을 하였습니다.
3-3 성능 개선
성능 개선
- 리펙토링 한 코드
@Override
@Transactional
public void recursiveCreateQuestionChoice(List<CreateQuestionAndCategoryRequestDto> requestDtos) {
String questionSql = "INSERT INTO question (category_id, question_description, question_explain, question_title) " +
"VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)";
String choiceSql = "INSERT INTO choice (answer, content, choice_number, question_id) " +
"VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)";
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(questionSql, new BatchPreparedStatementSetter() {
@Override
public void setValues(@NotNull PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i) throws SQLException {
CreateQuestionAndCategoryRequestDto questionDto = requestDtos.get(i);
Long categoryId = getCategoryIdByTitle(questionDto.getCategoryRequestDto().getCategory());
preparedStatement.setLong(1, categoryId);
preparedStatement.setString(2, questionDto.getCreateQuestionRequestDto().getQuestionDesc());
preparedStatement.setString(3, questionDto.getCreateQuestionRequestDto().getQuestionExplain());
preparedStatement.setString(4, questionDto.getCreateQuestionRequestDto().getQuestionTitle());
}
@Override
public int getBatchSize() {
return requestDtos.size();
}
});
for (CreateQuestionAndCategoryRequestDto questionDto : requestDtos) {
Long questionId = getQuestionIdByTitle(questionDto.getCreateQuestionRequestDto().getQuestionTitle());
List<CreateChoicesAboutQuestionDto> choiceDtos = questionDto.getCreateChoicesAboutQuestionDto();
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(choiceSql, new BatchPreparedStatementSetter() {
@Override
public void setValues(@NotNull PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i) throws SQLException {
CreateChoicesAboutQuestionDto choiceDto = choiceDtos.get(i);
boolean answer = isCollectAnswer(choiceDto.getAnswer());
preparedStatement.setBoolean(1, answer);
preparedStatement.setString(2, choiceDto.getContent());
preparedStatement.setInt(3, choiceDto.getNumber());
preparedStatement.setLong(4, questionId);
}
@Override
public int getBatchSize() {
return choiceDtos.size();
}
});
}
}
private Long getCategoryIdByTitle(String categoryTitle) {
String sql = "SELECT category_id FROM category WHERE category_title = ?";
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Long.class, categoryTitle);
}
private Long getQuestionIdByTitle(String questionTitle) {
String sql = "SELECT question_id FROM question WHERE question_title = ?";
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Long.class, questionTitle);
}-
기존의 JSON 데이터에 카테고리의 이름을 찾아 Question에 Insert를 해야되기 때문에 별도로 쿼리를 하나 불리하고 작성을 하였습니다.
-
Batch Insert를 하기 때문에 이전에 하나씩 Insert방식이 아닌 하나의 쿼리에서 Value를 여러개를 저장하는 방식으로 동작을 합니다.
- 데이터 10,000건을 기준으로 비교를 하였을 때 기존의 재귀로 Insert를 하게 되면 1498.68ms가 발생을 하며 이후 Batch Insert(JDBC)로 하였을 때 15.75s 발생을 하였습니다.
- 성능 개선의 퍼센트를 알기 위해서 ((이전 시간 - 개선된 시간)/이전시간)*100을 진행을 하겠습니다.
원래 시간 = 1440초
개선된 시간 = 1분 45초 = 60초 + 45초 = 105초
성능 개선율(%) = ((원래 시간 - 개선된 시간) / 원래 시간) 100
= ((1440 - 105) / 1440) 100
= (1335 / 1440) * 100
≈ 92.81%

글이 많은 도움이 되었습니다, 감사합니다.