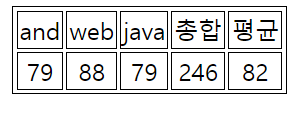
- 사용자에게 과목수 입력받고, 총합, 평균구하는 표 만드는 예제
과목수 -> prompt를 Number로 형변환해주고 변수에 넣어줌
입력한 수 만큼 과목이름을 입력받음 -> for문에 넣어 수만큼 반복하고 배열에 넣어주기
해당 과목의 점수를 입력받고 총점과 평균 구함 -> 배열에 .push 로 맨 뒤에 값 넣기
html문서 내 table을 만들어 출력=>2행 고정, 열은 유동적
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
table,
td {
border: 1px solid;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//1.사용자에게 과목수 입력받음
//2.1에서 입력한 수 만큼 과목이름을 입력받음
//3.해당 과목의 점수를 입력받고 총점과 평균 구함
//4.html문서 내 table을 만들어 출력=>2행 고정, 열은 유동적
// <table>, <tr>, <td>
let num = Number(prompt('과목 수 입력'))
let list = [];
let score = [];
for (let i = 0; i < num; i++) {
list[i] = prompt('점수를 입력할 과목을 입력하세요')
}
let total = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
score[i] = Number(prompt(list[i] + '의 점수를 입력'))
total += score[i]
}
let avg = parseInt(total / score.length)
list.push('총합')
list.push('평균')
score.push(total)
score.push(avg)
// 아래부터 테이블
document.write('<table>')
document.write('<tr>')
for (let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
document.write('<td>')
document.write(list[i])
document.write('</td>')
}
document.write('</tr>')
document.write('<tr>')
for (let i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
document.write('<td>')
document.write(score[i])
document.write('</td>')
}
document.write('</tr>')
document.write('</table>')
</script>
</body>
</html>함수
-
특정기능을 수행하는 소스코드를 하나로 묶어 필요할 때마다 호출하여 사용하기 위한 구조 >> 코드의 재사용성 용이
-
함수는 소괄호, 객체는 중괄호
-
실행코드를 묶어서 실행하기 위함
-
중복되는 코드 최소화
-
실행코드 블록화 >> 코드 조각화
-
function함수명(매개변수자리, 쓸수도 안쓸수도있음){
로직& 기능구현 코드작성
} ====>함수선언
함수명(); => 함수호출 -
특징
데이터타입이 동일한지 검사하지않음
매개변수와 입력값의 개수가 같지 않아도 오류가 나지 않음
입력값의 개수가 매개변수보다 적다면 undefined -
JS의 호이스팅
함수안에 있는 선언들을 끌어 올려서 최상단에 선언해주는 것 -
함수예제



<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//리턴일때
function addNum(num1, num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
//출력함수
function addNum2(num1,num2){
alert(num1+num2)
}
let num1 = Number(prompt('첫 번째 정수 입력'))
let num2 = Number(prompt('두 번째 정수 입력'))
alert(addNum(num1, num2));
</script>
</body>
</html>- 함수예제 2
공포의 별찍기 JS버전


<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//1.사용자에게 기호 이모지를 입력받음
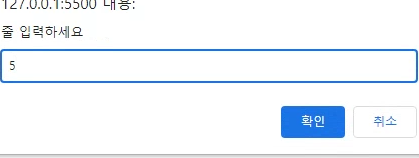
//2. 몇줄 출력할지 입력하시오
//3.이모지피라미드를 만들어주는 function pyramid선언
//4.피라미드 호출
let emoji = prompt('이모지를 입력하세요')
let rows = Number(prompt('줄 입력하세요'))
function pyramid(emoji, rows) {
for (let i = 1; i <= rows; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
document.write(emoji)
} document.write('<br>')
}
}
pyramid(emoji, rows)
//js의 호이스팅 : 함수안에 있는 선언들을 끌어 올려서 최상단에 선언해주는 것
</script>
</body>
</html>객체 = {}
- 데이터의 속성, 동작이 모두 포함한 개념
- 여러 속성을 하나의 변수에 저장할 수 있도록 해줌
- key & value
- 객체는 속성과 기능으로 구성됨
- 객체 내 데이터에 접근하는 방법 마침표.key 를 이용함
- 객체 내 기본데이터타입, 함수, Array, Object 등을 담을 수 있다.
let 객체명 = {
속성명1 : 값1,
속성명2 : 값2,
function(){
}
};
let pokemon1 = {};
pokemon1.name = '피카츄';
pokemon1.age = 2;
pokemon1.skill = function(){
console.log('백만볼트!');
}
console.log(pokemon1)
console.log('포켓몬의 이름은 >> ' + pokemon1.name)
console.log('포켓몬의 나이는 >> ' + pokemon1.age)
pokemon1.skill();
let 객체명 = {};
객체명.속성명1 = 값1;
객체명.속성명2 = 값2;
객체명.함수명 = function() {
};
let pokemon2 = {
name:'꼬북이',
age:1,
skill:function(){
console.log('물대포!')
}
};
console.log('포켓몬의 이름은 >> ' + pokemon2.name)
console.log('포켓몬의 나이는 >> ' + pokemon2.age)
pokemon2.skill();DOM Document Object Model
-
HTML CSS JS 구성
-
서로 다른 언어가 소통할 수 있도록 쪼개서 객체화 시켜주는 것
-
HTML문서에 접근하기 위해, 객체 접근할때 최상위객체인 document.속성명 ~~
-
특정태그에 접근하고자할때 document.___
getElement 요소를 가지고 오는 속성
리턴=> HTMLElement 타입(모든 종류의 요소를 나타내는 인터페이스) -
getElement
getElementbyId(id) #안씀 특정 id가진 요소 조회 => HTMLElement 객체 반환
getElementsbyName(name) 네임속성 요소 조회
getElementsbyTagName(tagname) 태그 이름 기준 요소 조회
getElementsbyClassName(class) 특정클래스 요소 조회
Elements==>HTMLCollection객체 반환 -
요소 안에 내용만! 가지고 올때 .innerText
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="text">Hello, World!</p>
<button onclick="innerFunc()">Click!</button>
<script>
function innerFunc(){
//버튼 클릭시
let str = document.getElementById('text')
// alert(str)
console.log(str)
console.log(str.innerText) //요소 안 내용만 가지고 오고싶을때
// str.innerText = '<h1>텍스트 수정!</h1>'
//태그까지 적용하고 싶을 때
str.innerHTML = '<h1>텍스트수정</h1>'
}
</script>
</body>
</html>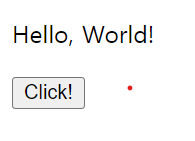

- 버튼 클릭시 각 함수 호출하고 화면에 누적되어 보여지도록 하기
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>클릭 한번 해볼까요?</h1>
<button onclick="mkH1()">h1태그 생성</button>
<button onclick="mkA()">a태그 생성</button>
<button onclick="mkUl()">ul태그 생성</button>
<!-- div는 생성한 태그를 누적할 공간-->
<div id="div1"></div>
<script>
//1. 태그 생성위치 -> 변수div
let div = document.getElementById('div1')
//2. 함수선언 - div공간안에 태그 누적 추가
function mkH1(){
div.innerHTML += '<h1>DOM활용하기</h1>'
}
function mkA(){
div.innerHTML += '<a href="www.google.com">Google로 이동</a>'
}
function mkUl(){
div.innerHTML += '<ul><li>HTML</li><li>CSS</li><li>JS</li></ul>'
}
</script>
</body>
</html>결과 :


- 버튼 클릭시 +1혹은 -1씩 증가 or 감소하는 함수
단, 0일때는 감소되지않음
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2 id="num">0</h2>
<button style="border-radius: 15px;" onclick="plus()">+1증가</button>
<button style="border-radius: 15px;" onclick="minus()">-1감소</button>
<script>
let num = document.getElementById('num')
let inner_num = Number(num.innerText)
function minus(){
if (inner_num != 0) {
inner_num--;
num.innerText = inner_num;
}
}
function plus(){
inner_num++;
num.innerText = inner_num;
}
</script>
</body>
</html> 초기화면
초기화면


함수 적용 화면

