🖍️ DFS
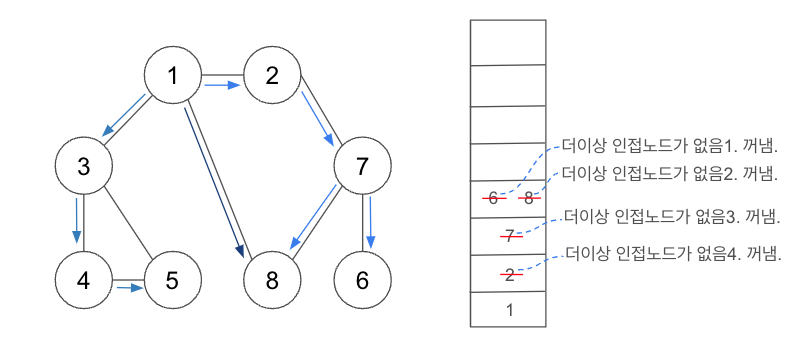
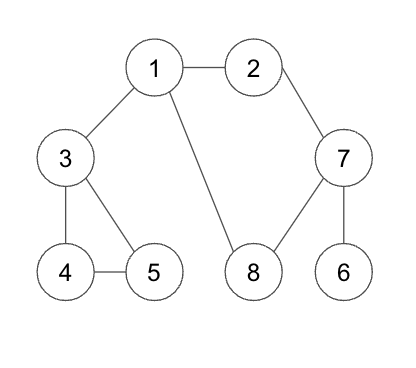
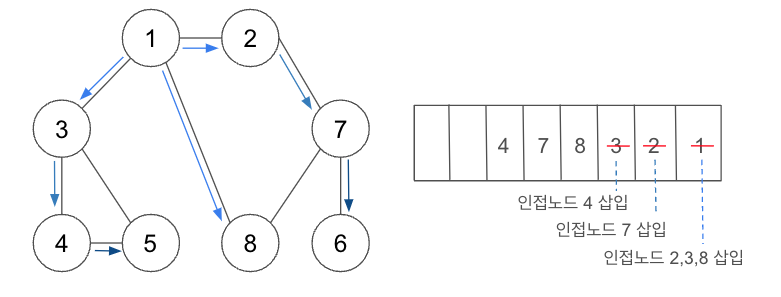
- DFS의 기본 동작과정
1) 탐색 시작 노드를 스택에 삽입. 방문 처리.
2) 스택의 최상단 노드의 방문하지 않은 인접 노드가 있다면 그 인접 노드를 스택에 삽입. 방문처리. 방문하지 않은 인접 노드가 없다면 스택에서 최상단 노드를 꺼냄.
3) 2번을 더이상 수행할 수 없을 때까지 반복 << 재귀함수 사용
public class DFS {
public static boolean[] visited = new boolean[9];
public static int[][] graph = {{}, {2,3,8}, {1,7}, {4,5}, {3}, {3}, {7}, {2,6,8}, {1,7}};
// graph의 각 배열 요소는 하나의 노드. 배열 요소에는 하나의 노드에 연결된 인접 노드들이 삽입됨.
public static void main(String[] args) {
dfs(1);
}
static void dfs(int nodeIndex) {
visited[nodeIndex] = true; // 해당 노드 방문처리
System.out.print(nodeIndex + " ");
for (int node : graph[nodeIndex]) {
if (!visited[node]) {
dfs(node);
}
}
}
// 결과물: 1 2 7 6 8 3 4 5
}🖍️ BFS
- BFS의 기본 동작과정
1) 탐색 시작 노드를 큐에 삽입. 방문 처리.
2) 큐에서 노드를 꺼내 해당 노드의 인접 노드 중에서 방문하지 않은 노드를 모두 큐에 삽입. 해당 노드들 방문처리.
3) 2번을 더이상 수행할 수 없을 때까지 반복
public class BFS {
public static boolean[] visited = new boolean[9];
public static int[][] graph = {{}, {2,3,8}, {1,7}, {4,5}, {3}, {3}, {7}, {2,6,8}, {1,7}};
// graph의 각 배열 요소는 하나의 노드. 배열 요소에는 하나의 노드에 연결된 인접 노드들이 삽입됨.
public static void main(String[] args) {
bfs(1);
}
static void bfs (int startIndex) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(startIndex);
visited[startIndex] = true; // 방문처리
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int currentNode = queue.poll();
System.out.print(currentNode + " ");
for (int node : graph[currentNode]) {
if (!visited[node]) {
queue.offer(node);
visited[node] = true; // 방문처리
}
}
}
}
// 결과물: 1 2 3 8 7 4 5 6
}🖍️ 정리
| DFS | BFS | |
|---|---|---|
| 동작원리 | Stack | Queue |
| 구현방법 | 재귀함수 이용 | 큐 자료구조 이용 |
