0. 실습 환경 배포
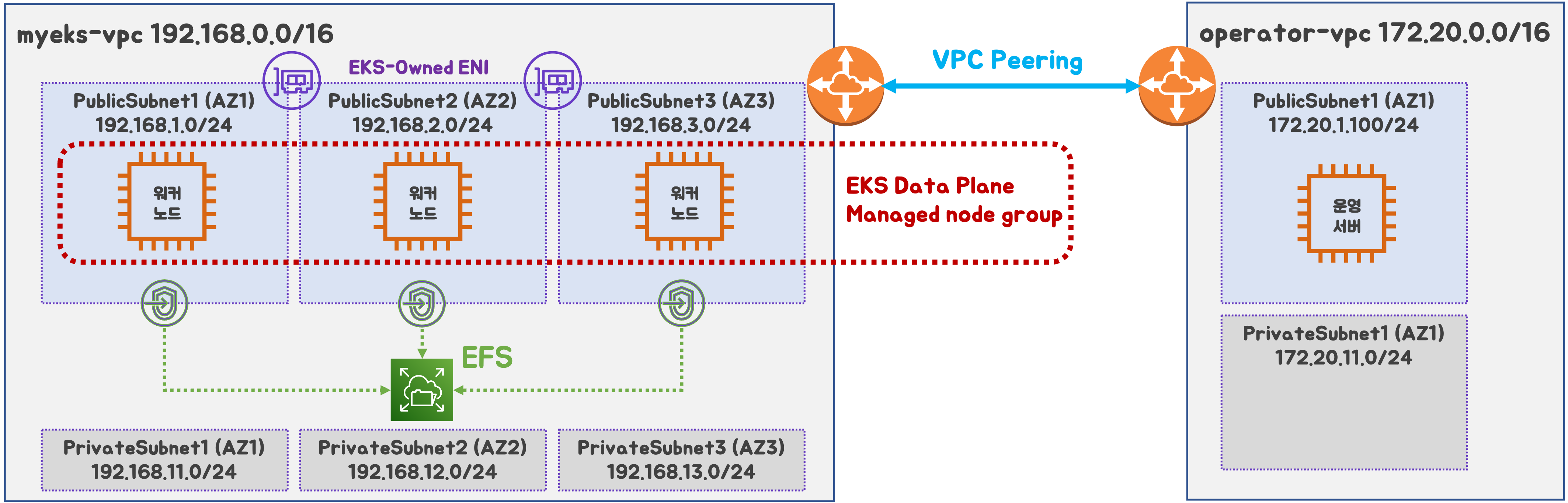
2개의 VPC (EKS 배포, 운영용 구분), myeks-vpc public에 EFS 추가
 출처 : AEWS 스터디 3기
출처 : AEWS 스터디 3기
- myeks-vpc 에 각기 AZ를 사용하는 퍼블릭/프라이빗 서브넷 배치
- operator-vpc 에 AZ1를 사용하는 퍼블릭/프라이빗 서브넷 배치 : 172.20.1.100 운영서버 EC2 배포
- 내부 통신을 위한 VPC Peering 배치
1. 스토리지
배경
k8s 데이터 지속성
- 데이터 저장하는 애플리케이션을 실행시 영구 스토리지가 없으면 Pod 또는 컨테이너에 적재
 출처 : AWS
출처 : AWS
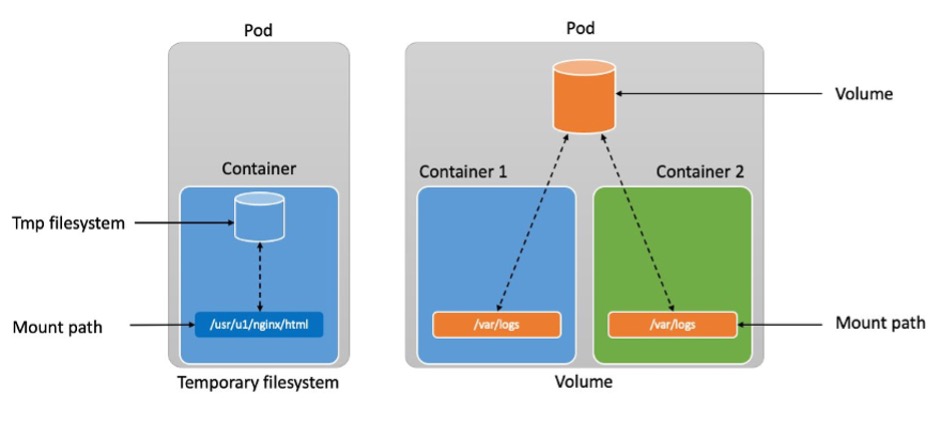
[임시 스토리지 (Ephemeral storage)]
- 컨테이너는 temporary filesystem(tmpfs)를 사용하여 파일을 읽고 쓸 수 있음
- 컨테이너가 충돌하는 경우 tmpfs는 손실되며, 깨끗한 상태로 재시작
- 컨테이너끼리 tmpfs 공유가 불가
[임시 볼륨(Ephemeral volumes)]
- 컨테이너는 tmpfs를 사용하여 파일을 읽을 수 있음
- 파드 내의 컨테이너끼리 데이터 공유 가능
- 파드 삭제되는 즉시 Volume도 삭제
결론적으로 Pod 혹은 Container가 종료되면 데이터가 손실 되는 한계가 발생
⇒ 데이터 보존이 필요함에 따라 Stateful 애플리케이션이 필요하였고, PV & PVC 개념이 등장
 출처 :
AWS
출처 :
AWS
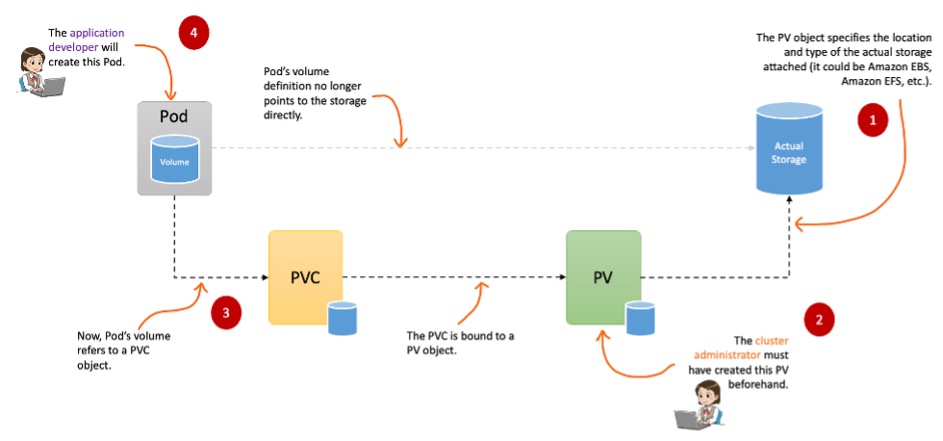
PV(Persistent Volume)는 연결된 실제 저장소 위치와 유형을 지정
PVC는 Pod가 실제 스토리지를 얻기 위해 수행하는 스토리지 요청을 나타냄
설명
Volume에는 크게 emptyDir, hostPath, PV/PVC가 있다.
emptyDir
파드가 노드에 할당될 때 처음 생성 되며, 해당 노드에서 파드가 실행하는 동안에만 존재한다.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: busybox
spec:
containers:
- image: busybox:1.35
name: busybox-container
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/log/busybox
name: log-volume
- image: nginx:17
name: nginx-container
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/log/nginx
name: log-volume
volumes:
- name: log-volume
**emptyDir**: {}hostPath
호스트 노드의 파일 시스템에서 파일이나 디렉터리를 파드로 마운트
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: hostpath-example-linux
spec:
os: { name: linux }
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
containers:
- name: example-container
image: registry.k8s.io/test-webserver
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /foo
name: example-volume
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: example-volume
# mount /data/foo, but only if that directory already exists
**hostPath**:
path: /data/foo # directory location on host
type: Directory # this field is optionalPV (Persistent Volumes)
- 클러스터에서 관리하는 스토리지 리소스
- 다양한 물리적 스토리지 (NFS, Ceph, AWS EBS, GCE Persistent Disk)와 연결됨
- 참조 : k8s Storage
- 관리자가 미리 생성하거나 스토리지 클래스를 통하여 동적으로 생성 할수 있다.
- PV는 파드의 수명 주기에 구속되지 않음, PV 객체에 연결된 파드를 삭제해도 해당 PV는 유지
- PV는 클러스터 전체에 적용된다. 클러스터의 모든 노드에서 실행중인 모든 파드 연결 가능
- Reclame Policy (해당 PV 연결이 끝났을때 해당 볼륨을 어떻게 초기화 할지 정책) 크게 Retain, Delete 방식이 있다. (기본값 : Retain)
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: pv0003
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
storageClassName: slow
mountOptions:
- hard
- nfsvers=4.1
nfs:
path: /tmp
server: 172.17.0.2PVC (Persistent Volume Claim)
- Pod가 스토리지를 사용하기 위해 요청하는 객체
- 사용자가 필요한 용량과 접근모드를 지정하면, 적절한 PV가 연결 됨
- 만약 PV가 없다면, 스토리지 클래스를 통하여 동적으로 생성 할수 있다.
## PVC yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: block-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
volumeMode: Block
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
---
### Pod yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-with-block-volume
spec:
containers:
- name: fc-container
image: fedora:26
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args: [ "tail -f /dev/null" ]
volumeDevices:
- name: data
devicePath: /dev/xvda
volumes:
- name: data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: block-pvc
CSI (Contaier Storage Interface)
CSI Driver 등장 배경
- k8s 소스코드 내부에 존재하는 AWS EBS provisioner는 k8s Release lifecycle에 따라 배포
- provisioner 신규 기능을 사용시 k8s version을 업그레이드 해야 하는 제약 사항 발생
- 따라서 k8s 개발자는 Kubernetes 내부에 내장된 provisioner (in-tree)를 모두 삭제 하고 별도의 controller 파드를 통해 동적 provisioner를 사용할수 있도록 변경
CSI를 사용하면, k8s 공통화된 CSI를 통해 다양한 프로바이더를 사용할수 있다.
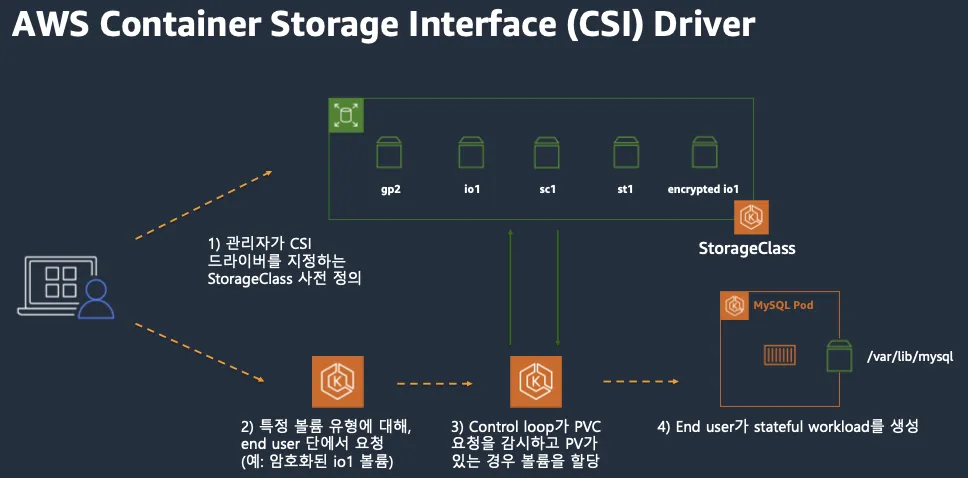 출처 : AWS 문서
출처 : AWS 문서
[CSI Driver 구조]
- 일반적인 CSI 구조 (AWS EBS CSI 드라이버도 동일한 구조)
- 컨트롤러 파드 / 노드 파드 차이
| 역할 | 배포방식 | 기능 |
|---|---|---|
| 컨트롤러 파드(StatefulSet / Deployment) | 클러스터 전체에서 단일 또는 복제된 파드로 실행 (중앙 집중식) | AWS API를 통해 EBS 볼륨의 라이프사이클(생성/삭제/확장/스냅샷) 관리 |
| 노드 파드 (DaemonSet) | 각 워커 노드마다 1개의 파드 실행 (노드별 작업) | 실제 노드(EC2 인스턴스)에 EBS 볼륨 연결(Attach) 및 파일 시스템 마운트 처리 |
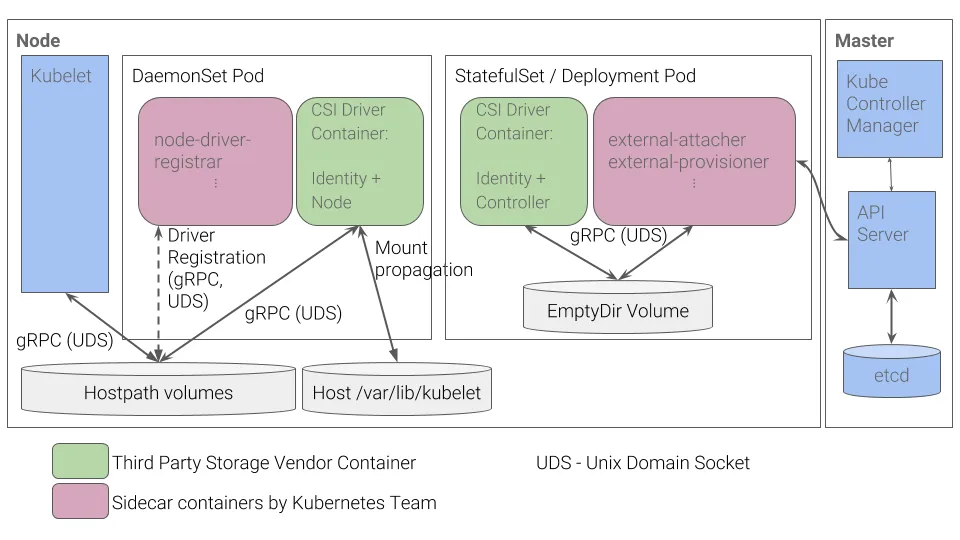
파드 기본 및 empty 저장소 동작 확인
[파드 기본 저장소 동작 확인]
- Redis 파드 생성
# 모니터링
k get pod -w
# redis 파드 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: redis
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis
EOF- Redis 저장소 확인
# redis 파드 내에 파일 작성
kubectl exec -it redis -- pwd
kubectl exec -it redis -- sh -c "echo hello > /data/hello.txt"
kubectl exec -it redis -- cat /data/hello.txt
# ps 설치
kubectl exec -it redis -- sh -c "apt update && apt install procps -y"
kubectl exec -it redis -- ps aux
# redis 프로세스 강제 종료 : 파드가 어떻게 되나요? hint) restartPolicy
kubectl exec -it redis -- kill 1
kubectl get pod파드 정책상 강제로 프로세스 종료 하는 경우 재기동 되는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
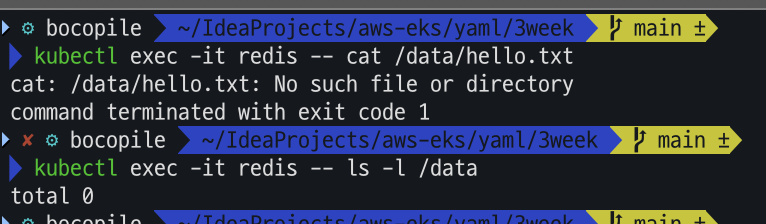
# redis 파드 내에 파일 확인
kubectl exec -it redis -- cat /data/hello.txt
kubectl exec -it redis -- ls -l /data파드가 재기동 되면서 직전에 생성해 놓은 hello.txt 파일이 삭제 된 것을 알수 있다.
[emptyDir 동작 확인]
- Redis 생성
# 모니터링
kubectl get pod -w
# redis 파드 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: redis
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis
volumeMounts:
- name: redis-storage
mountPath: /data/redis
volumes:
- name: redis-storage
emptyDir: {}
EOF- Redis 저장소 확인
# redis 파드 내에 파일 작성
kubectl exec -it redis -- pwd
kubectl exec -it redis -- sh -c "echo hello > /data/redis/hello.txt"
kubectl exec -it redis -- cat /data/redis/hello.txt
- Redis 강제 종료
# ps 설치
kubectl exec -it redis -- sh -c "apt update && apt install procps -y"
kubectl exec -it redis -- ps aux
# redis 프로세스 강제 종료 : 파드가 어떻게 되나요? hint) restartPolicy
kubectl exec -it redis -- kill 1
kubectl get pod직전의 Redis 파드와 마찬가지로 강제로 프로세스 종료 하는 경우 재기동 되는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
# redis 파드 내에 파일 확인
kubectl exec -it redis -- cat /data/redis/hello.txt
kubectl exec -it redis -- ls -l /data/redis아까와는 다르게 hello.txt 파일이 존재하는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
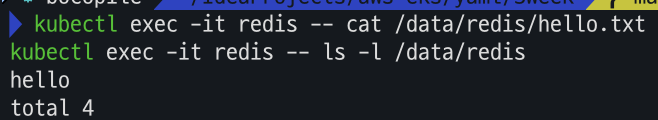
이번엔 프로세스 강제 종료 대신 파드를 삭제하고 재생성 해봅시다.
kubectl delete pod redis
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: redis
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis
volumeMounts:
- name: redis-storage
mountPath: /data/redis
volumes:
- name: redis-storage
emptyDir: {}
EOF 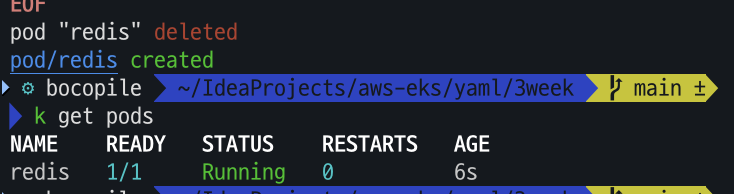
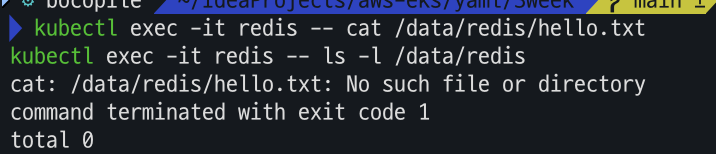
- Redis 저장소 확인
# redis 파드 내에 파일 확인 kubectl exec -it redis -- cat /data/redis/hello.txt kubectl exec -it redis -- ls -l /data/redis
파드를 삭제 하고 재기동 하는 경우 아까 생성 하였던 hello.txt 파일이 존재하지 않음을 확인할수 있다.
Local Path Provisioner
Local Path Provisioner ??
- k8s에서 로컬 스토리지를 동적으로 프로비저닝 하는 CSI 기반의 StorageClass
- hostPath를 기반으로 하는 동적 볼륨 프로비저닝 솔루션
- 각 노드의 특정 경로를 PV로 할당
HostPath와는 무슨 차이?
| hostPath | Local Path Provisioner | |
|---|---|---|
| 정의 | 특정 노드의 파일 시스템 경로를 파드에 마운드 | hostPath를 기반으로 동적 볼륨 프로비저닝 |
| 볼륨 프로비저닝 방식 | Static | Dynamic |
| Storage Class | 지원 안함 | 지원함 |
| 다중 노드 | 특정 노드에 종속 | 특정 노드에 종속 |
| 볼륨 삭제 정책 | 수동 관리 필요 | StorageClass의 정책에 따라 자동 삭제 가능 |
[설치]
-
Local Path Provisioner 설치
- 설치
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rancher/local-path-provisioner/v0.0.31/deploy/local-path-storage.yaml - 확인
kubectl get-all -n local-path-storage kubectl get pod -n local-path-storage -owide kubectl describe cm -n local-path-storage local-path-config kubectl get sc local-path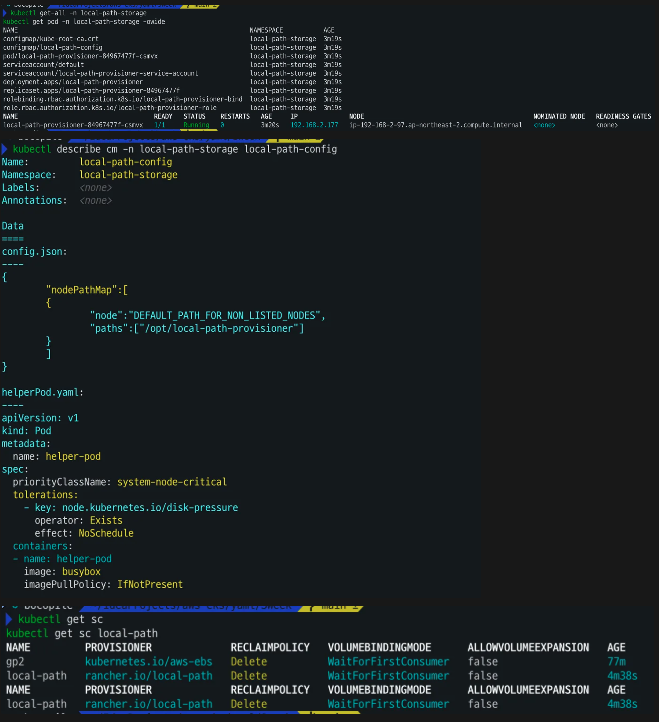
- 설치
-
PV / PVC를 사용하는 파드 생성
-
pvc 생성
# PVC 생성 cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: localpath-claim spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce storageClassName: local-path resources: requests: storage: 1Gi EOF # PVC 확인 kubectl get pvc kubectl describe pvc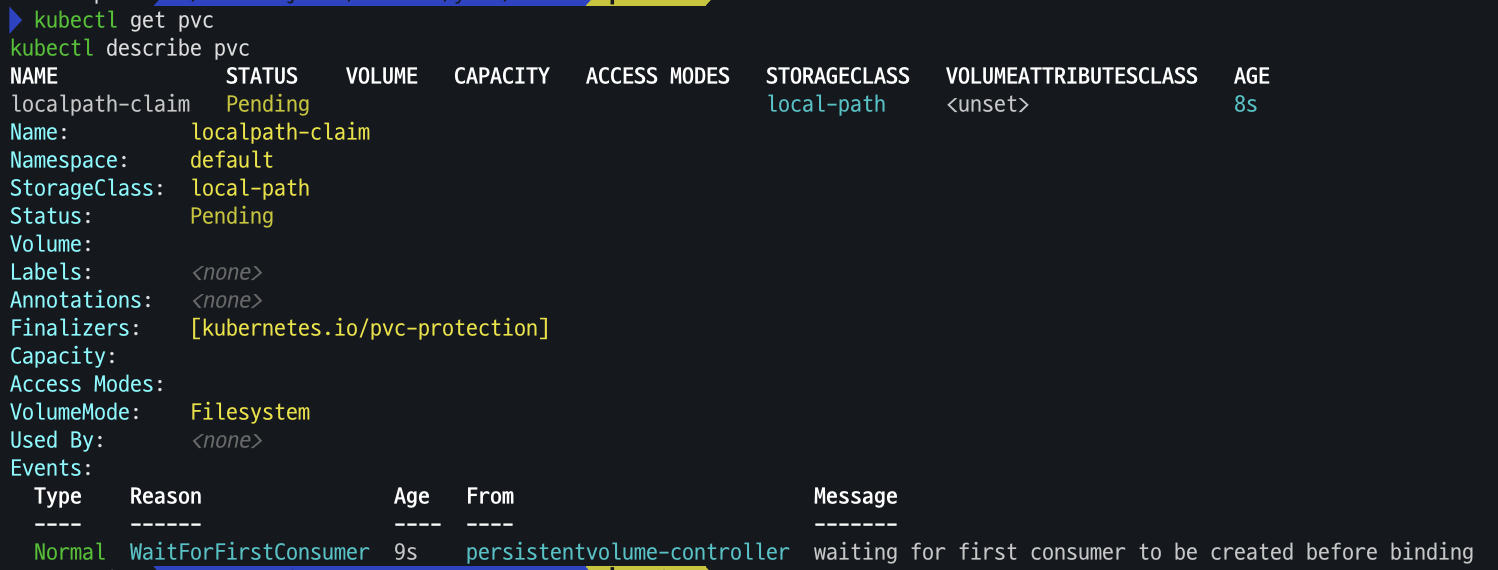
-
파드 생성
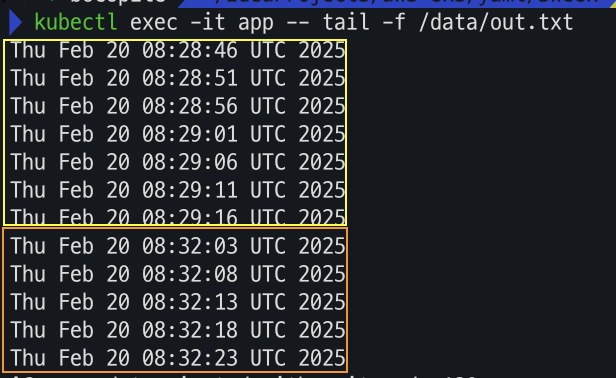
# 파드 생성 cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: app spec: terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 3 containers: - name: app image: centos command: ["/bin/sh"] args: ["-c", "while true; do echo \$(date -u) >> /data/out.txt; sleep 5; done"] volumeMounts: - name: persistent-storage mountPath: /data volumes: - name: persistent-storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: localpath-claim EOF # 파드 확인 kubectl get pod,pv,pvc kubectl describe pv # Node Affinity 확인 kubectl exec -it app -- tail -f /data/out.txt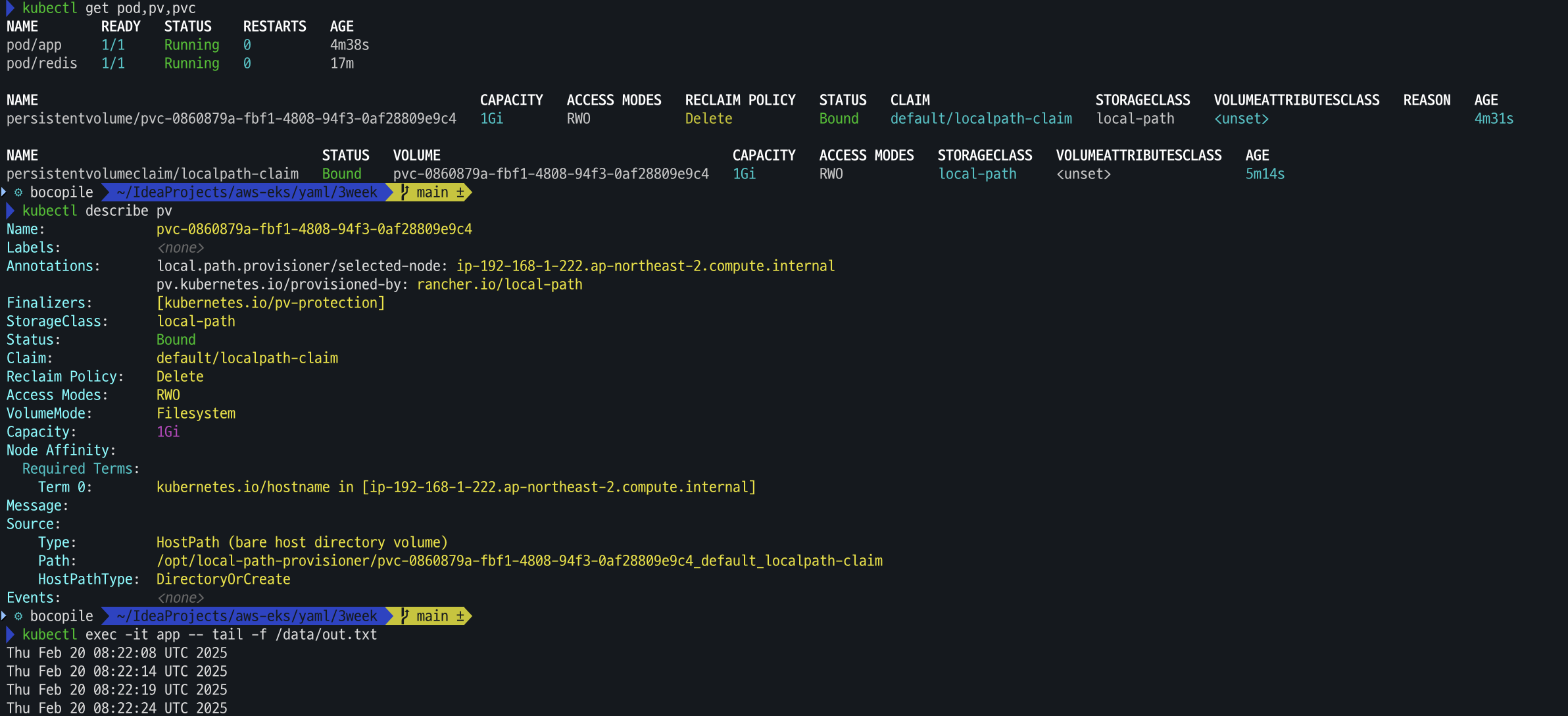
-
-
out.txt 파일 존재 확인
for node in $N1 $N2 $N3; do ssh ec2-user@$node tree /opt/local-path-provisioner; done ssh ec2-user@$N1 tail -f /opt/local-path-provisioner/pvc-0860879a-fbf1-4808-94f3-0af28809e9c4_default_localpath-claim/out.txt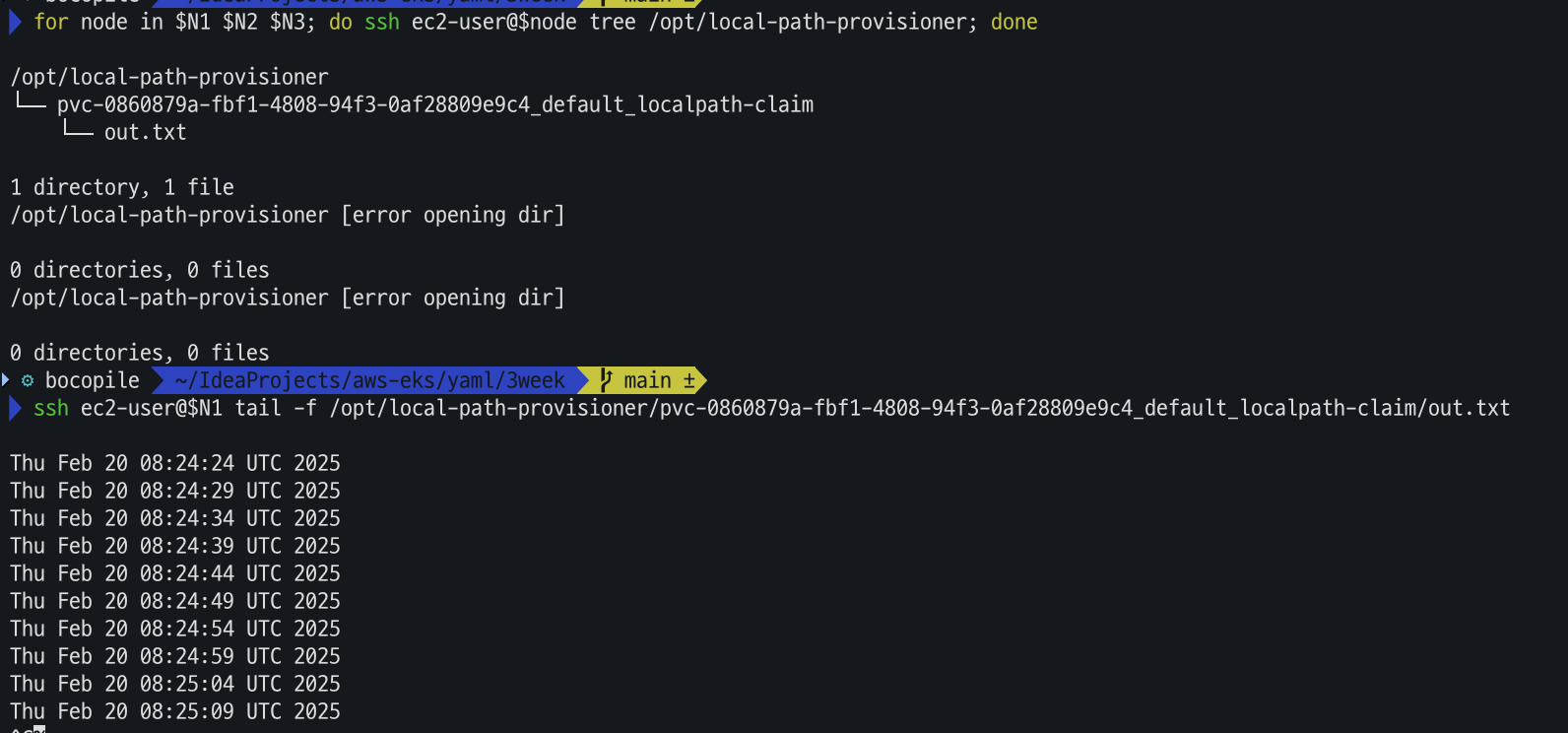
-
파드 삭제 후 재생성해서 데이터 유지 확인
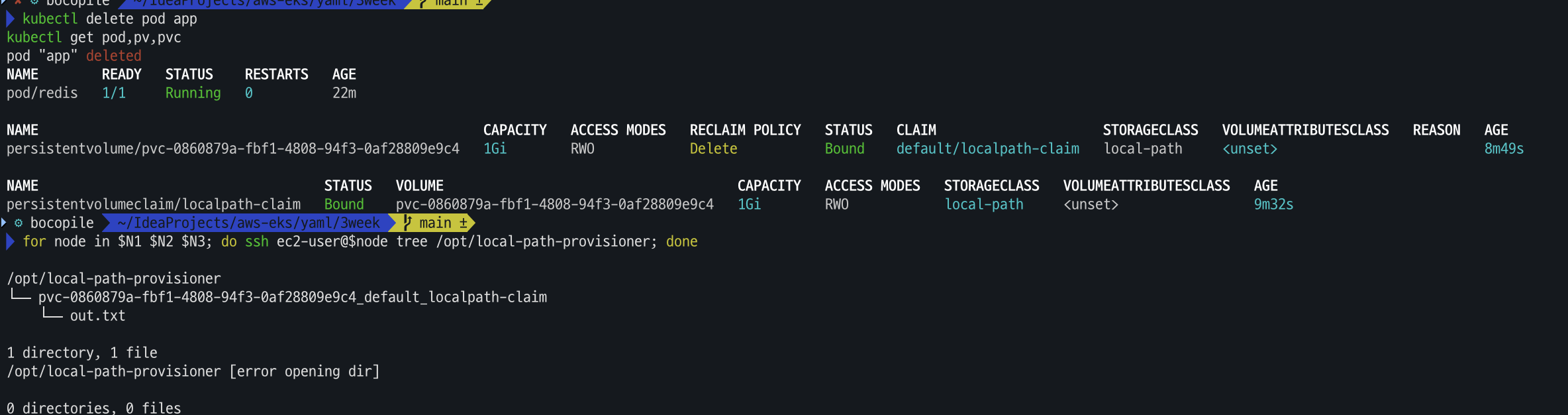
# 파드 삭제 후 PV/PVC 확인 kubectl delete pod app kubectl get pod,pv,pvc for node in $N1 $N2 $N3; do ssh ec2-user@$node tree /opt/local-path-provisioner; done해당 파드를 삭제 해도 데이터는 유지 된다.
# 파드 다시 실행 cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: app spec: terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 3 containers: - name: app image: centos command: ["/bin/sh"] args: ["-c", "while true; do echo \$(date -u) >> /data/out.txt; sleep 5; done"] volumeMounts: - name: persistent-storage mountPath: /data volumes: - name: persistent-storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: localpath-claim EOF # 확인 kubectl exec -it app -- head /data/out.txt kubectl exec -it app -- tail -f /data/out.txt해당 파일이 유지 되나 파드가 삭제 되어 있는 동안에는 로그가 쌓이지 않는 것을 확인 할수 있다.