
[이것이 C#이다] 18장 파일 다루기
파일과 디렉터리
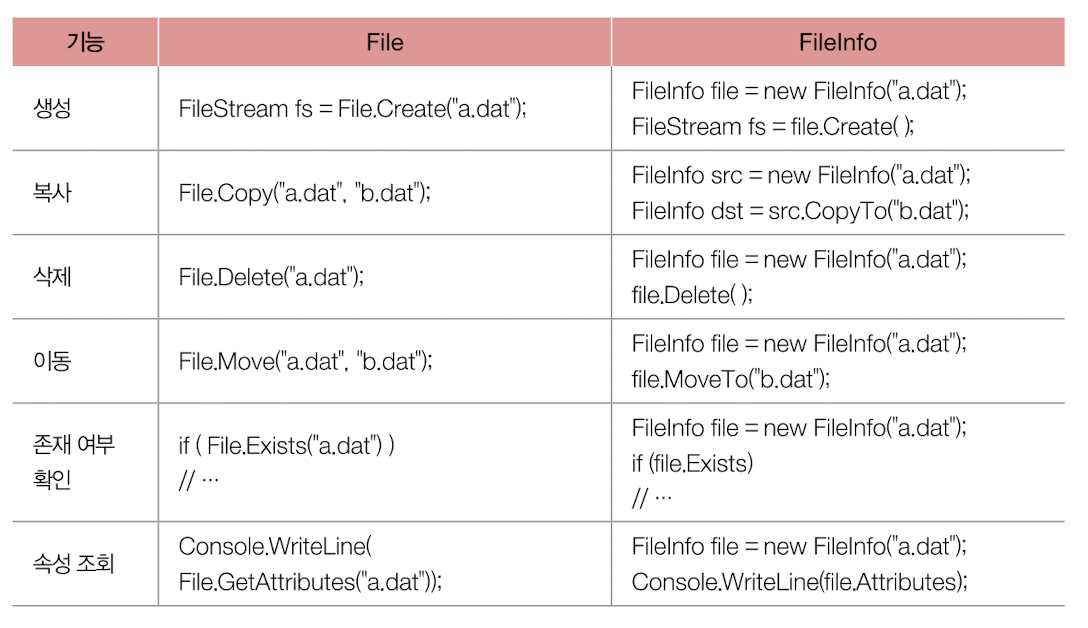
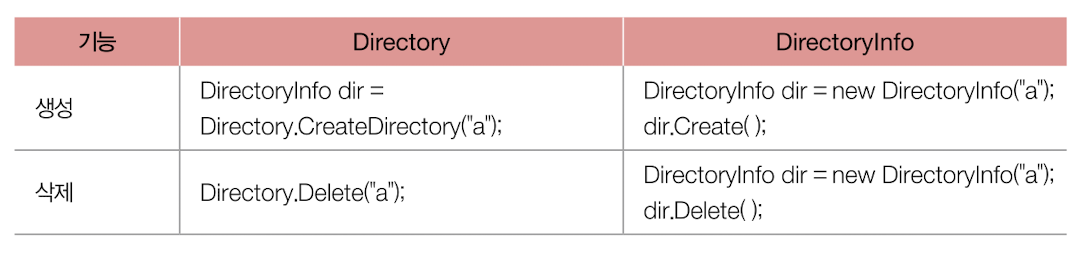
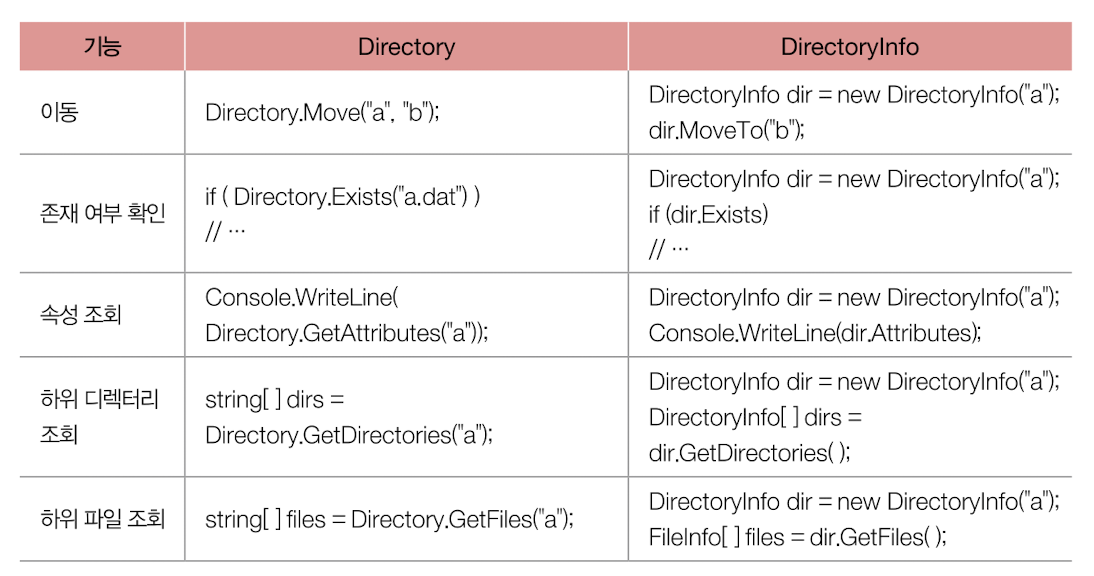
👉 .NET은 파일과 디렉터리 정보를 손쉽게 다룰 수 있도록 System.IO 네임스페이스 아래에 다음과 같은 클래스들 제공

🔗 각 메소드 및 프로퍼티 사용 예
파일 입출력
스트림 (stream): 데이터가 흐르는 통로
👉 하드디스크와 메모리 사이를 스트림으로 연결한 후 파일에 담긴 데이터를 바이트 단위로 옮김
-
순차 접근 (Sequential Access) : 처음부터 끝까지 순서대로 읽고 쓰는 방식
-> 파일이 아닌 네트워크로도 데이터 입출력 가능
-> 단방향성 -
임의 접근 (Random Access) : 하드디스크를 디스크의 어떤 위치에 기록된 데이터라도 임의로 접근 가능
System.IO.Stream
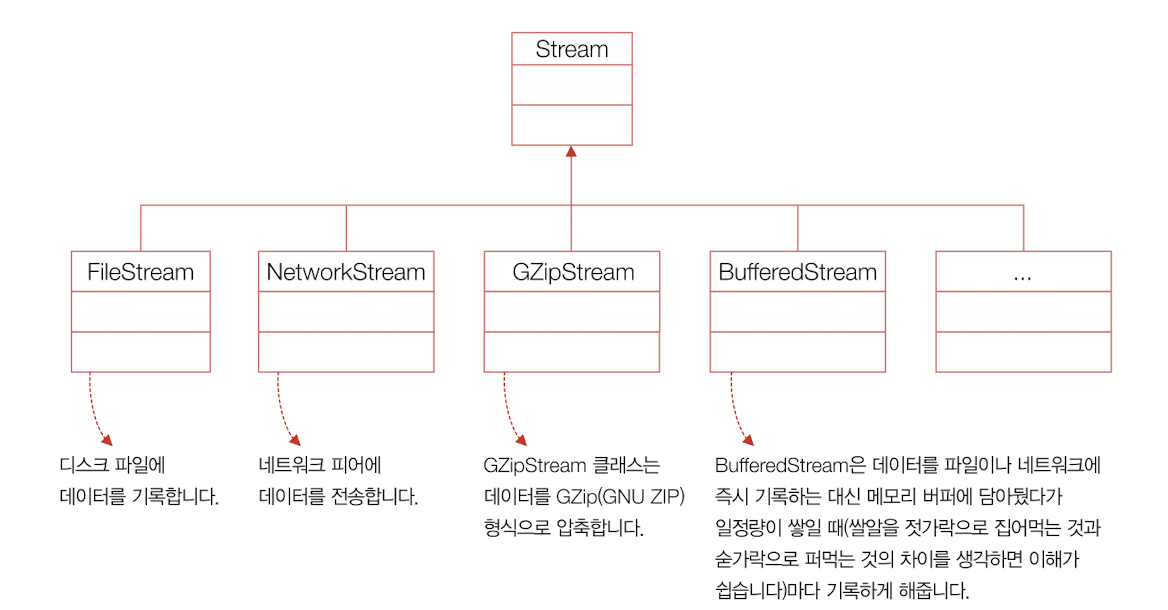
Stream 클래스 : 입력, 출력 스트림의 역할과 순차, 임의 접근 방식 모두를 지원하는 추상 클래스
💡 Stream 클래스와 파생 클래스들의 계보
FileStream
생성
🔗 FIleStream 인스턴스 생성 예
Stream stream1 = new FileStream("a.dat",FileMode.Create); FileMode 종류
| Create | Open | OpenOrCreate | Truncate | Append |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 새 파일 생성 | 파일 열기 | 파일 열기 혹은 없으면 생성 | 파일을 비워서 열기 | 덧붙이기 모드로 열기 |
쓰기
⭐️ Stream 클래스로 물려받은 두 쓰기 메소드
public override void Write(
byte[] array, // 쓸 데이터가 담겨 있는 byte 배열
int offset, // byte 배열 내 시작 오프셋
int count // 기록할 데이터의 총 길이(단위는 바이트)
};
public override void WriteByte(byte value);- 각종 형식을 byte 배열로 변환해주는
BitConverter 클래스를 활용하여 주로 사용
🔗 쓰기 - 사용 예
int num = 1;
// 1) 파일 스트림 생성
Stream outStream = new FileStream("a.dat",FileMode.Create);
// 2) num(int 형식)를 byte 배열로 변환
byte[] wBytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(num);
// 3) 변환한 byte 배열을 파일 스트림을 통해 파일에 기록
outStream.Write(wBytes, 0, wBytes.Length);
// 4) 파일 스트림 닫기
outStream.Close();읽기
⭐️ Stream 클래스로 물려받은 두 읽기 메소드
public override void Read(
byte[] array, // 읽을 데이터가 담을 byte 배열
int offset, // byte 배열 내 시작 오프셋
int count // 읽을 데이터의 최대 바이트 수
};
public override void ReadByte();🔗 읽기 - 사용 예
byte[] rBytes = new byte[8];
// 1) 파일 스트림 생성
Stream inStream = new FileStream("a.dat",FileMode.Open);
// 2) rBytes의 길이만큼(8바이트) 데이터를 읽어 rBytes에 저장
inStream.Read(rBytes,0,rBytes.Length);임의 접근
Seek() 메소드 로 Stream 클래스의 Position 프로퍼티에 직접 원하는 주소 혹은 위치를 대입
Position 프로퍼티: 현재 스트림의 읽는 위치 또는 쓰는 위치
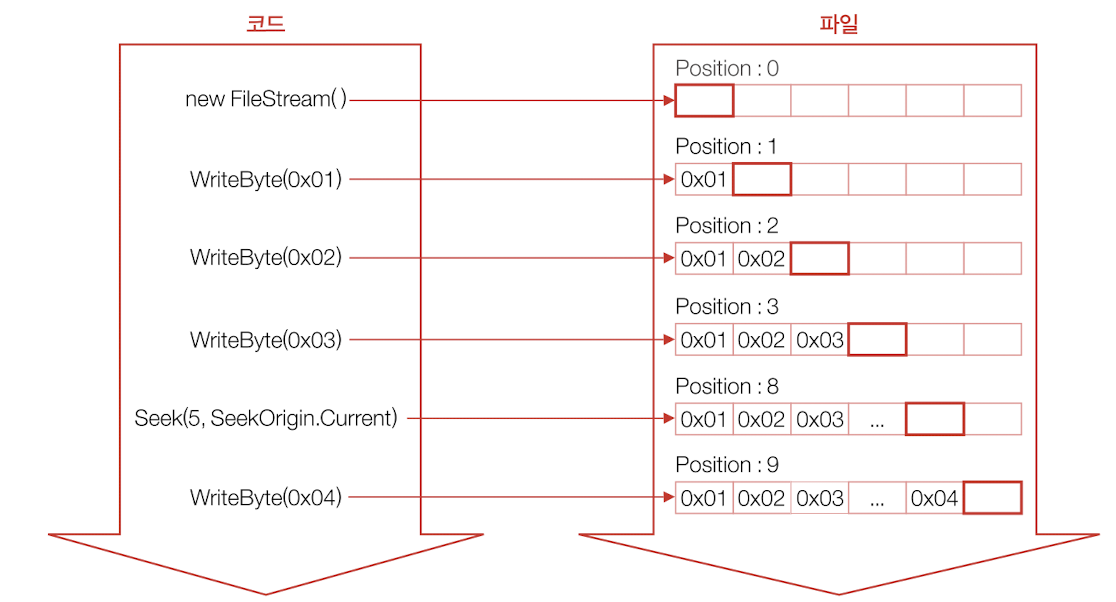
🔗 임의 접근 - 사용 예
Stream outStream = new FileStream("a.dat", FileMode.Create);
...
// 현재 위치에서 5바이트 뒤로 이동
outStream.Seek(5, SeekOrigin.Current);
outStream.WriteByte(0x04);using 활용
using선언을 통해 자동으로 파일 스트림을 닫을 수 있음
IDisposable상속하여Dispose()메소드를 구현하는 모든 객체에 대해 사용 가능
🔗 사용 예
💡 using 선언을 통해 생성된 객체는 코드 블록이 끝나면서 outStream.Dispose() 호출
{
using Stream outStream = new FileStream("a.dat",FileMpde.Create);
byte[] wBytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(someValue);
outStream.Write(wBytes, 0, wBytes.Length);
}🔗 사용 예 2 - 자원의 수명을 세부적으로 조절하고 싶을 때 유용
💡 using 선언을 통해 생성된 객체는 코드 블록이 끝나면서 outStream.Dispose() 호출
using (Stream outStream = new FileStream("a.dat",FileMpde.Create))
{
byte[] wBytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(someValue);
outStream.Write(wBytes, 0, wBytes.Length);
}별칭 지시문
긴 이름의 클래스를 using을 활용하여 간단한 별칭으로 지정 가능
🔗 사용 예
<using System.IO;
using FS = System.IO.FileStream;
...
using Stream inStream = new FS("a.dat", FileMode.Open");
이진 데이터 처리
BinaryWriter : 스트림에 이진 데이터를 기록하기 위한 목적으로 만들어진 클래스
BinaryReader : 스트림으로부터 이진 데이터를 읽어들이기 위한 목적으로 만들어진 클래스
👉 파일 처리의 도우미 역할이기 때문에 Stream 으로부터 파생된 클래스의 인스턴스가 있어야 사용 가능
🔗 사용 예 - BinaryWriter
<BinaryWriter bw = new BinaryWriter(new FileStream("a.dat", FileMode.Create));
bw.Write(32);
bw.Write("Good Morning!");
bw.Write(3.14);
bw.CLose();Write()메소드는 C#이 제공하는 모든 기본 데이터 형식에 대해 오버로딩되어있음- 문자열을 저장할 때는 문자열의 길이를 저장할 데이터의 가장 첫 번째 바이트에 저장 후 문자열 데이터 저장
🔗 사용 예 - BinaryReader
BinaryReader br = new BinaryReader(new FileStream("a.dat", FileMode.Open));
int a = br.ReadInt32();
string b = br.ReadString();
double c = br.ReadDouble();
br.CLose();BinaryReader는 읽을 데이터 형식별로Read데이터_형식()메소드를 제공
텍스트(.txt) 파일 처리
StreamWriter : 스트림에 텍스트 파일을 기록하기 위한 목적으로 만들어진 클래스
StreamReader : 스트림으로부터 텍스트 파일 데이터를 읽어들이기 위한 목적으로 만들어진 클래스
👉 파일 처리의 도우미 역할이기 때문에 Stream 으로부터 파생된 클래스의 인스턴스가 있어야 사용 가능
🔗 사용 예 - StreamWriter
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(new FileStream("a.dat", FileMode.Create));
sw.Write(32);
sw.WriteLine("Good Morning!");
sw.WriteLine(3.14);
sw.CLose();Write()와WriteLine()메소드는 C#이 제공하는 모든 기본 데이터 형식에 대해 오버로딩되어있음
🔗 사용 예 - StreamReader
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(new FileStream("a.dat", FileMode.Open);
while(sr.EndOfStream == false)
{
Console.WriteLine(sr.ReadLine());
}
sr.Close();EndOfStream프로퍼티 : 스트림의 끝에 도달했는지를 알려줌
객체 직렬화
직렬화 (Serialization): 객체의 상태를 메모리나 영구 저장 장치에 저장이 가능한 0과 1의 순서로 바꾸는 것
👉 프로그래머가 직접 정의한 클래스나 구조체 같은 복합 데이터 형식을 스트림으로 읽고 쓰기 위해 필요
💡 직렬화할 프로퍼티를 public으로 한정하면 해당 클래스는 메모리나 영구 저장 장치에 저장할 수 있는 형식이 됨
Stream과JsonSerializer클래스를 활용- 직렬화하고 싶지 않은 프로퍼티는
[JsonIgnore]애트리뷰트로 수식
🔗 사용 예 - 직렬화
class NameCard
{
public string Name {get; set;}
[JsonIgnore]
public int Age {get; set;}
}
Stream ws = new FileStream(fileName, FileMode.Create);
NameCard nc = new NameCard();
// 직렬화
string jsonString = JsonSerializer.Serialize<NameCard>(nc);
byte[] jsonBytes = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(jsonString);
ws.Write(jsonBytes,0,jsonBytes.Length);🔗 사용 예 - 역직렬화
Stream rs = new FileStream(fileName, FileMode.Open);
byte[] jsonBytes = new byte[rs.Length];
rs.Read(jsonBytes, 0, jsonBytes.Length);
string jsonStrong = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(jsonBytes);
NameCard nc = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<NameCard>(jsonString);