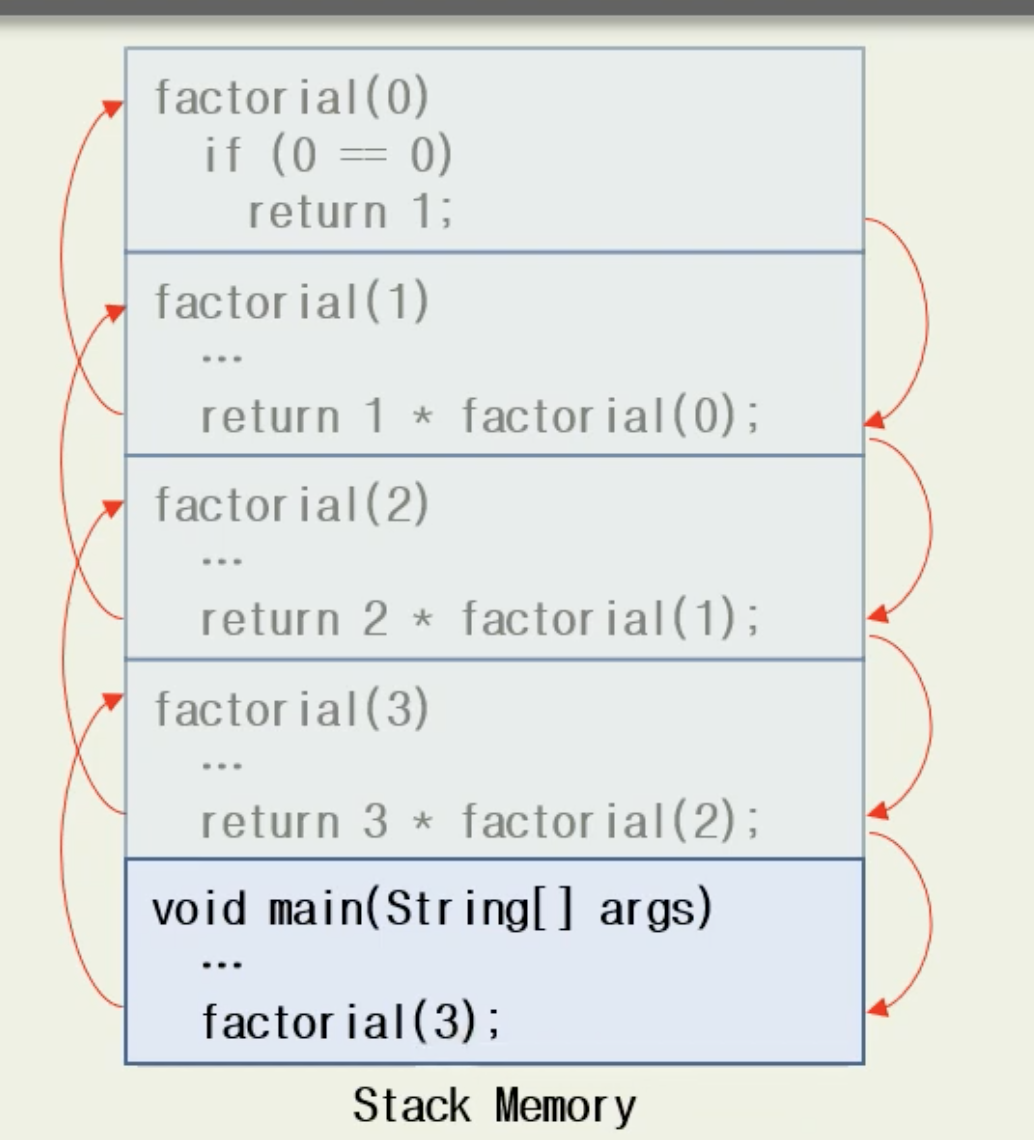
Recursion(재귀호출) 이란
자기 자신을 호출하는 함수이다. Base case와 Recursive case로 구분되는데 Base case는 간단히 결과를 반환하는 부분이고, Recursive case는 자기 자신을 호출하는 부분이다.
int factorial(int n) {
// Base case
if(n == 0)
return 1;
// Recursive case
return n * factorial(n-1);
}- stack memory
재귀와 메모이제이션 (피보나치 활용)
재귀가 뻗어나갈 때 한 번 계산한 값을 배열에 저장해놓고 한번 구한 계산은 더 이상 계산하지 않고 가져다 쓴다.
public class Main4 {
static int[] fibo;
public int DFS(int n){
if(fibo[n] > 0) return fibo[n];
if (n == 1) return fibo[n]=1;
else if (n == 2) return fibo[n]=1;
else {
return fibo[n] = DFS(n-2) + DFS(n-1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main4 T = new Main4();
int n = 45;
fibo = new int[n+1];
T.DFS(n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.print(fibo[i] + " ");
}
}
}Flood fill 알고리즘
임의의 위치에서 상하좌우로 재귀호출 하는 알고리즘이다. 다음은 임의의 위치에서 시작하여 0은 빈 곳 1은 벽을 의미하고 경계면이나 1을 만날 때까지 1로 채우는 부분이다.
public class recursiveEx1 {
static int N;
static int[][] Board = new int[100][100];
static void fill(int row, int col) {
// Base case
if(row < 0 || row > N-1 || col < 0 || col > N-1){
return;
}
// 벽을 만났거나 이미 1로 마킹 되어 있는 경우이므로 return
if(Board[row][col] != 0){
return;
}
Board[row][col] = 1;
// 위로 올라가는 부분
fill(row-1, col);
// 아래로 가는 부분
fill(row+1, col);
// 왼쪽으로 가는 부분
fill(row, col-1);
// 오른쪽으로 가는 부분
fill(row, col+1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
Board[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// 시작 위치
int sRow, sCol;
sRow = sc.nextInt();
sCol = sc.nextInt();
fill(sRow, sCol);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
System.out.print(Board[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}