Read Chapter 8.
1. Prove that the smallest height for any tree on n nodes is Ω(lg n) = - 1 + lg(n+1).
2. When you shrink the space of direct access arrays, you might want to use a linked list data structure. What would be the problem if you use the linked list? Show your answer with explaining the time complexity.
3. In the hash family function, a should not equal to 0. Why? Please give me a simple answer (one sentence).
4. Use the birthday dataset, Do the followings:
4.1. Put them into your unordered array using set.
4.2. Put them into the sorted array set.
4.3. Put them into the direct access array set
4.4. Put them into the hash table set.
4.5. Compare their size.
4.6. Compare their interfaces: build, find, insert, delete, find_min, find_max, find_next, find_prev.
1. n개의 노드에서 트리의 가장 작은 높이가 Ω(lg n) = - 1 + lg(n+1)임을 증명
트리에서 높이란, 루트에서 해당 노드에 이르는 경로에 있는 간선의 수를 의미한다.
즉, 해당 노드의 레벨에서 루트 노드의 레벨(0)을 빼준 값이다.
완전 이진트리에서, n을 노드의 개수라고 했을 때
n = 1 : 높이 0 (루트 노드 그 자체)
n = 2 ~ 3 : 높이 1
n = 4 ~ 7 : 높이 2
n = 8 ~ 15 : 높이 3이런 식으로 진행된다.
높이가 h인 이진트리가 가질 수 있는 노드의
-
최소 개수는
(h+1)개이다.
한 레벨에 최소한 한 개의 노드가 있어야 하므로 높이가 h인 이진트리의 최소 노드의 개수는 (h+1)개가 된다.
-
최대 개수는
2^(h+1)-1개이다.- 하나의 노드는 최대 2개의 자식 노드를 가질 수 있으므로, 레벨 i에서 노드의 최대 개수는
2^i이다.레벨 0에서의 노드의 최대 개수 : 1 레벨 1에서의 노드의 최대 개수 : 2^1 = 2 레벨 2에서의 노드의 최대 개수 : 2^2 = 4 레벨 3에서의 노드의 최대 개수 : 2^3 = 8 ... 높이가 3인 이진 트리에서 최대 노드의 개수 = 레벨 0에서의 노드의 최대 개수 + 레벨 1에서의 노드의 최대 개수 + 레벨 2에서의 노드의 최대 개수 + 레벨 3에서의 노드의 최대 개수 = 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 = 2^(3+1) - 1 = 15 ... 이를 일반화하면 따라서 높이가 h인 이진 트리에서 최대 노드의 개수 : 2^(h + 1) - 1
- 하나의 노드는 최대 2개의 자식 노드를 가질 수 있으므로, 레벨 i에서 노드의 최대 개수는
위와 같은 과정을 통해 최대 개수는 2^(h+1)-1 개인 것을 알 수 있다.
따라서 이 식에서 출발하면
2^(h + 1) - 1 = n
2^(h + 1) = n + 1
양변에 로그를 취하면
h + 1 = log(n + 1)
따라서 h = log(n + 1) - 1으로 증명할 수 있다.
출처 : https://leejinseop.tistory.com/40, https://kuminkyu93.tistory.com/69
2. Direct access arrays의 공간을 축소할 때 Linked list data 구조를 사용할 수 있는데, Linked list를 사용한다면 어떤 문제가 생기는가(시간 복잡도로 설명)
Direct access arrays는 일반 Array 배열이나 자바에서의 ArrayList를 생각해 볼 수 있겠고,
Linked list는 포인터를 이용해 다음 노드를 가리키는 LinkedList를 생각해 볼 수 있다.
대표적으로 자바의 ArrayList와 LinkedList를 예로 들어서 생각해보겠다.
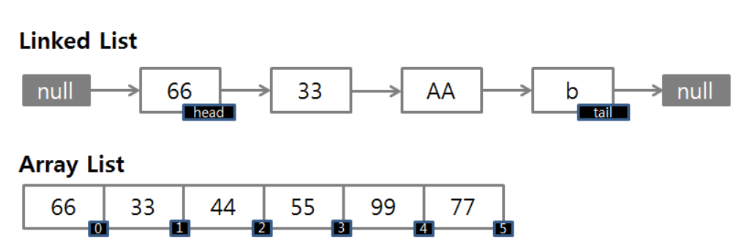
ArrayList는 데이터들이 순서대로 쭉 늘어선 배열의 형식을 취하고 있고, 인덱스로 접근한다.
LinkedList는 자료의 주소 값으로 서로 연결되어 있는 구조이고, 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터를 통해 접근한다.
ArrayList
- 조회 : 빠르게 조회가 가능하다. 인덱스를 통한 무작위 접근이 가능하다. → 조회에서의 시간 복잡도가 O(1)이다.
- 삽입, 삭제 : 삽입 삭제 시 일반 Array배열처럼 뒤에 있는 값들을 앞으로 땡겨주거나 뒤로 한 칸씩 밀어줘야 하기 때문에 시간이 조금 더 걸린다고 한다. → 삽입,삭제 시의 시간 복잡도 : O(N)
- O(N)만큼의 연산 속도가 걸리기 때문에 자료의 최대 개수에 영향을 받는다.
LinkedList
- 조회 : LinkedList는 앞 노드부터 순차 접근만 가능하고, 자료들을 불연속적인 단위로 저장하면서 이곳저곳 산재해 저장되어 있는 노드들을 접근하기 때문에 ArrayList보다 느리다. → 조회에서의 시간 복잡도 : O(N)
- 삽입, 삭제 : 몇 개의 참조자만 바꿈으로써 삽입 삭제가 더 빠른 시간 안에 수행할 수 있다. → 삽입, 삭제 시의 시간 복잡도 : O(1) ~ O(N)
- 자료의 최대 개수의 제약을 받지 않는다.
LinkedList로 바꾸면 조회 시 시간 복잡도가 O(N)으로 증가한다는 단점이 있다.
출처 : https://www.nextree.co.kr/p6506/
4.
package week3;
import java.util.*;
public class homework3_compare {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CSVReader csvReader = new CSVReader();
List<List<String>> list = csvReader.readCSV();
// 4.1. set을 이용해 정렬되지 않은 배열에 넣기
HashSet<List<String>> set = new HashSet<>();
for (List<String> node : list) {
set.add(node);
}
// 4.2. 정렬된 배열 집합에 넣기
// 정렬된 배열 집합 자동으로 정렬해주는 우선순위 큐에 저장했습니다.
// 틀릴 수도 있지만 자동으로 정렬해준다는 점에서 이용해 보았습니다.
PriorityQueue<List<String>> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<List<String>>() {
@Override
public int compare(List<String> o1, List<String> o2) {
return (int) (Double.parseDouble(o1.get(2)) - Double.parseDouble(o2.get(2)));
}
});
for (List<String> node : list) {
pq.add(node);
}
// 4.3. Direct Access Array set에 넣기
// 직접 접근할 수 있는 것은 ArrayList라고 판단해 ArrayList를 이용해 보았습니다.
ArrayList<List<String>> al = new ArrayList();
for (List<String> node : list) {
al.add(node);
}
// 4.5. 크기 비교
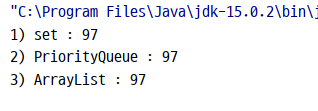
System.out.println("1) set : " + set.size());
System.out.println("2) PriorityQueue : " + pq.size());
System.out.println("3) ArrayList : " + al.size());
}
}크기 비교 결과 사진 :
4.6. Compare their interfaces: build, find, insert, delete, find_min, find_max, find_next, find_prev.
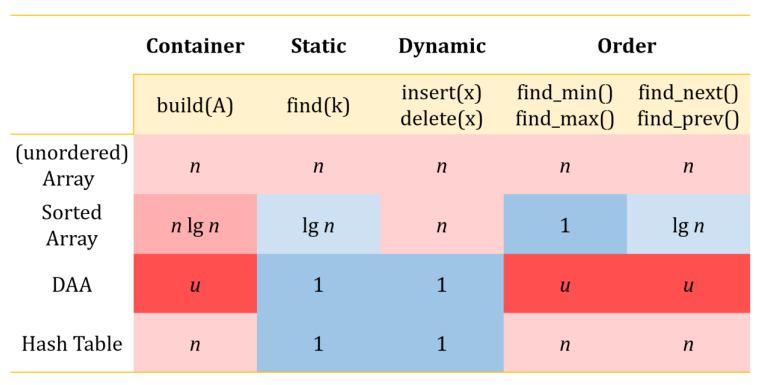
위의 표를 통해 비교해볼 수 있다.
정렬되지 않은 일반 Array의 경우
- build에 O(n)
- find - O(n) : 최악의 경우 일일이 돌면서 타겟 값을 찾아야 한다.
- insert, delete - O(n) : 최악의 경우 해당 위치를 삽입, 삭제를 진행한 후 한 칸씩 당기거나 밀어야 하기 때문에 O(n)이다.
- find_min, find_max - O(n) : 최악의 경우 find로 일일이 min, max값을 찾아야 한다.
- find_next, find_prev - O(n) : 최악의 경우 일일이 find로 타겟 값을 찾은 후 그 전후를 찾을 수 있다.
정렬된 Array의 경우
- build에 O(n)
- find - O(lg n) : 이미 정렬이 되어 있기 때문에 중간값과 비교하면서 절반씩 없애면서 나갈 수 있다.
- insert, delete - O(n) : 빨리 위치를 찾았다 하더라도 해당 위치를 삽입, 삭제를 진행한 후 한 칸씩 당기거나 밀어야 하기 때문에 O(n)이다.
- find_min, find_max - O(1) : 맨 앞의 값, 맨 뒤의 값을 가져오면 되기 때문에 O(1)이다.
- find_next, find_prev - O(lg n) : 최악의 경우 find (lg n)로 타겟 값을 찾은 후 그 전후를 찾을 수 있다.
Direct Access Array set의 경우
- build에 O(u)
- find - O(1)
- insert, delete - O(1)
- find_min, find_max - O(u)
- find_next, find_prev - O(u)
