이 글은 블로그주인장이 여태 공부했던 알고리즘 독학 및 강의들의 내용을 정리하는 포스팅입니다.
스택(Stack)
- Last In First Out -> LIFO 후입선출
- 빨래더미 처럼 쌓이는 특징
- 파이썬에선 리스트가 이 특징을 갖음
# 파이썬 소스코드
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
#push 기능 구현
def push(self, value):
new_head=Node(value) #새로운 머리 생성
new_head.next=self.head # 새로운 머리가 기존 머리를 가르킴
self.head=new_head
return
# pop 기능 구현
def pop(self):
delete_head = self.head # 제거할 node 를 변수에 잡습니다.
self.head = self.head.next # 그리고 head 를 현재 head 의 다음 걸로 잡으면 됩니다.
return delete_head
# peek 기능 구현
def peek(self):
if self.is_empty():
return "Stack is empty!"
return self.head.data
# isEmpty 기능 구현
def is_empty(self):
return self.head is None// c 소스코드
typedef struct {
int data;
struct Node* next;
}Node;
typedef struct {
Node* top;
}Stack;
void push(Stack* stack, int data) {
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = stack->top;
stack->top = node;
}
int pop(Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top == NULL) {
printf("스택 언더플로우 발생\n");
return -INF;
}
Node* node = stack->top;
int data = node->data;
stack->top = node->next;
free(node);
return data;
}
void show(Stack* stack) {
Node* cur = stack->top;
printf("--- 스택의 최상단 --\n");
while (cur!=NULL){
printf("%d\n", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("--- 스택의 최하단 ---\n");
}큐(Queue)
- First In First Out -> FIFO 선입선출
- 대기줄 같은 구조
- python에서는 deque란 라이브러리를 이용
# 파이썬 소스코드
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
# head -> tail
# [4] -> [2]
def enqueue(self, value): #맨 뒤에 데이터 추가하기
new_node = Node(value)
if self.is_empty(): # 만약 비어있다면,
self.head = new_node # head 에 new_node를
self.tail = new_node # tail 에 new_node를 넣어준다.
return
self.tail.next = new_node
self.tail = new_node
# 그리고 tail을 [3] 으로 지정합니다.
def dequeue(self): #맨 위 데이터 빼기
if self.is_empty():
return "Queue is empty!" # 만약 비어있다면 에러!
delete_head = self.head # 제거할 node 를 변수에 잡습니다.
self.head = self.head.next # 그리고 head 를 현재 head 의 다음 걸로 잡으면 됩니다.
return delete_head.data
def peek(self): #맨 앞의 데이터 보기
if self.is_empty():
return "Queue is empty!"
return self.head.data
def is_empty(self): #큐가 비었는지 안 비었는지 여부 반환해주기
return self.list.head is None// c소스코드
int queue[SIZE];
int front = 0; //앞
int rear = 0; //뒤
typedef struct {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
typedef struct {
Node* front;
Node* rear;
int cnt;
} Queue; //구조체로 큐 선언
void push(Queue *queue,int data) {
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->next = NULL;
if (queue->cnt == 0) { //아무도 없으면
queue->front = node; // 이 노드가 앞이
}
else {
queue->rear->next=node; //큐의 뒤의 다음이 노드
}
queue->rear = node;
queue->cnt++;
}
void pop(Queue*queue) {
if (queue->cnt==0) {
printf("큐 오버플로우 발생\n");
return -INF;
}
Node* node = queue->front;
int data = node->data;
queue->front = node->next;
free(node);
queue->cnt--;
return data; // data 반환
}
void show(Queue*queue) {
Node* cur = queue->front;
printf("---- 큐의 앞 ----\n");
while(cur != NULL) {
printf("%d\n", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("---- 큐의 뒤 ----\n");
}해쉬(Hash)
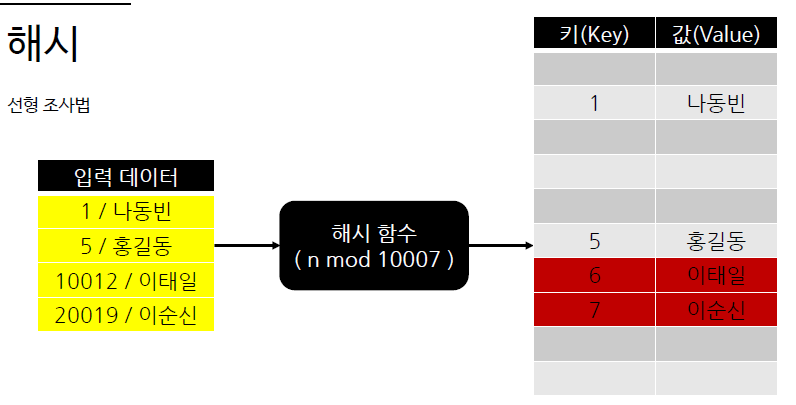
- 컴퓨팅에서 키를 값에 매핑할 수 있는 구조인, 연관 배열 추가에 사용되는 자료 구조
dict = {"fast" : "빠른", "slow": "느린"}
# 파이썬에서는 딕셔너리로 이용- 특정한 값 (Value) 을 찾고자 할 때는 그 값의 키(key)로 접근할 수 있음
- 일반적으로 해시 함수는 모듈로 (Modulo) 연산 등의 수학적 연산으로 이루어져 있으므로 O(1) 만에 값에 접근할 수 있음
- 해시 함수의 입력 값으로는 어떠한 값이나 모두 들어갈 수 있지만 , 해시 함수를 거쳐 생성되는 키 (key)의 경우의 수는 한정적이기 때문에 키 (Key) 중복이 발생할 수 있음
해싱알고리즘
나눗셈 법 (Division Method)이 가장 많이 활용
입력 값을 테이블의 크기로 나눈 나머지를 키 (key) 로 이용하는 방식입니다 . 테이블의 크기는 소수 (Prime Number) 로 설정하는 것이 효율성이 높음
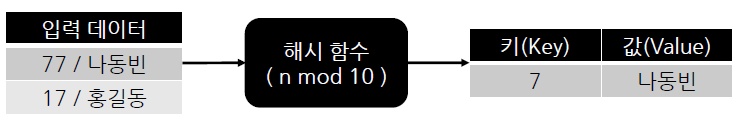
- 키가 중복되는 경우 충돌이 발생했다고 표현
충돌을 피하려면?
- 충돌을 발생시키는 항목을 해시 테이블의 다른 위치에 저장 : 선형 조사법 , 이차 조사법 등
- 해시 테이블의 하나의 버킷 ( 에 여러 개의 항목을 저장 : 체이닝 (Chaining) 등
체이닝(Chaining)
- 연결 리스트를 활용해 특정한 키를 가지는 항목들을 연결하여 저장
- 동적 할당을 위한 추가적인 메모리 공간이 소모된다는 단점이 존재
python 소스코드
# 파이썬 소스코드
class LinkedTuple:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def add(self, key, value):
self.items.append((key, value))
def get(self, key):
for k, v in self.items:
if k == key:
return v
class LinkedDict:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
for i in range(8):
self.items.append(LinkedTuple())
def put(self, key, value): #체이닝(Chaining)
index = hash(key) % len(self.items)
# LinkedTuple
# []
# [(key, value)]
self.items[index].add(key, value)C 소스코드
// c 소스코드
typedef struct {
int id;
char name[20];
} Student;
typedef struct {
Student* data;
struct Bucket* next;
} Bucket;
//해시 테이블 초기화
void init(Bucket** hashTable) {
for (int i = 0; i < TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
hashTable[i] = NULL;
}
}
//해시 테이블의 메모리를 반환
void destructor(Bucket** hashTable) {
for (int i = 0; i < TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
if (hashTable[i] != NULL) {
free(hashTable[i]);
}
}
}
//체이닝 데이터 탐색함수
int isExist(Bucket** hashTable,int id) {
int i = id % TABLE_SIZE;
if (hashTable[i] == NULL) return 0;
else {
Bucket* cur = hashTable[i];
while (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->data->id == id) return 1;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return 0;
}
//특정한 키 인덱스에 데이터를 삽입
void add(Bucket** hashTable, Student* input) {
int i = input->id % TABLE_SIZE;
if (hashTable[i] = NULL) {
hashTable[i] = (Bucket*)malloc(sizeof(Bucket));
hashTable[i]->data = input;
hashTable[i]->next = NULL;
}
else {
Bucket* cur = (Bucket*)malloc(sizeof(Bucket));
cur->data = input;
cur->next = hashTable[i];
hashTable[i] = cur;
}
}
//해시 테이블에 존재하는 모든 데이터를 출력합니다.
void show(Bucket** hashTable) {
for (int i = 0; i < TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
if (hashTable[i] != NULL) {
Bucket* cur = hashTable[i];
while (cur!=NULL){
printf("키: [%d] 이름: [%s]\n", i, cur->data->name);
cur = cur->next;
}
}
}
}참고
- 학부생 시절 자료구조 강의
- 알고보면 알기 쉬운 알기쉬운 알고리즘 -스파르타 코딩클럽
- 컴퓨터공학 전공 올인원패키지 - sw베이직 파트
- 이것이 코딩테스트다 with 파이썬 - 나동빈
- 소스코드
https://github.com/BOLTB0X/Sparta-Algorithm/tree/main/week_3
https://github.com/BOLTB0X/DataStructure_Argolithm/tree/main/09_Binary%20Tree%20Graph
