부스트캠프 그룹프로젝트에서 우리 팀은 Three.js를 사용해보기로 했다.
정확히 말하면 Three.js를 React에서 더 편리하게 사용할 수 있게 도와주는 라이브러리인 React Three Fiber (R3F)를 사용하기로 했다.
하지만 R3F도 결국엔 Three.js 기반의 라이브러리이기 때문에 Three.js에 대한 기본적인 이해가 필요하다.
그래서 Three.js 공식문서를 읽어보며 학습해보기로 했다.

난 사실 Three.js로 만들어진 결과물들을 보고 굉장히 설렜다.
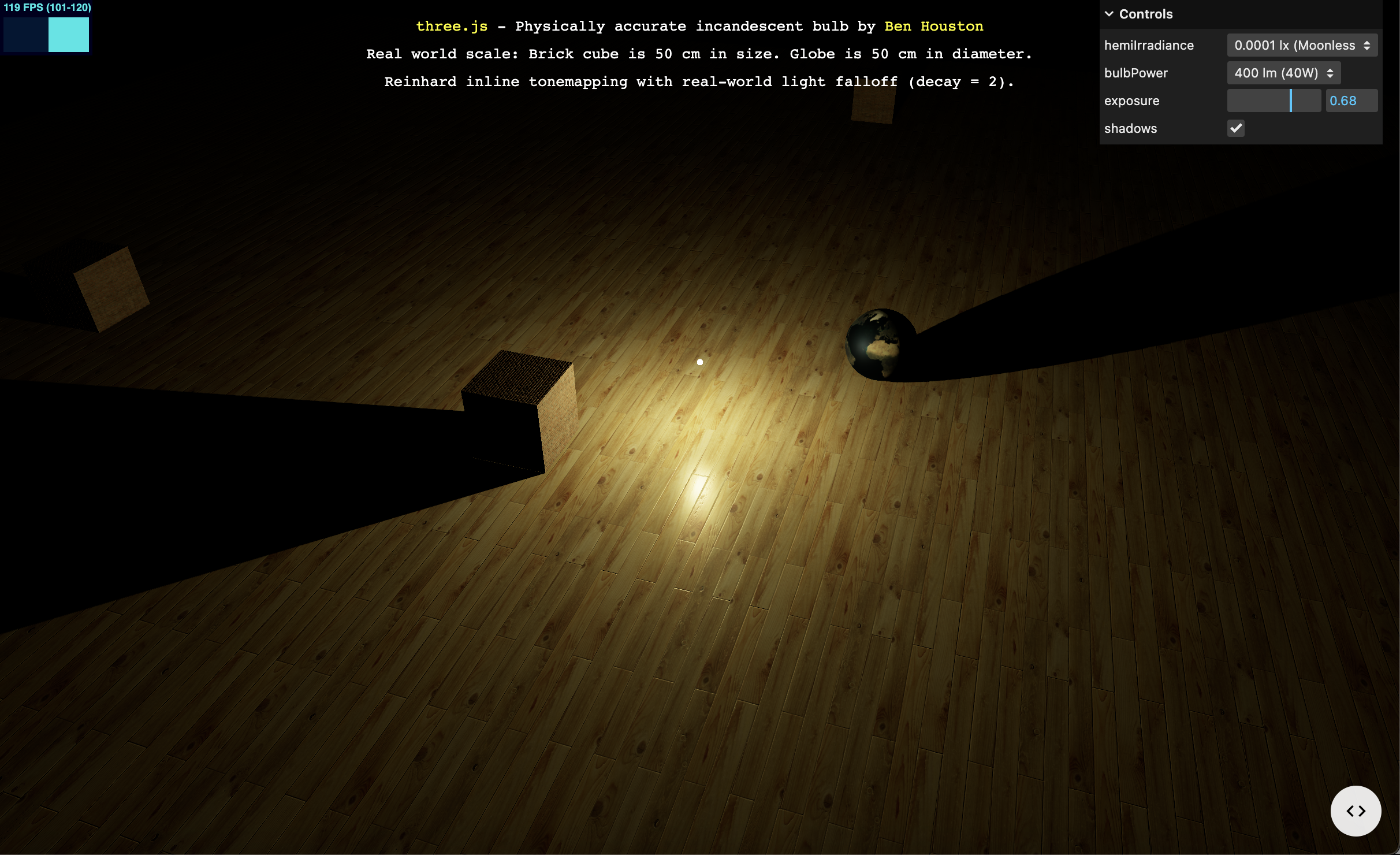 https://threejs.org/examples/#webgl_lights_physical
https://threejs.org/examples/#webgl_lights_physical
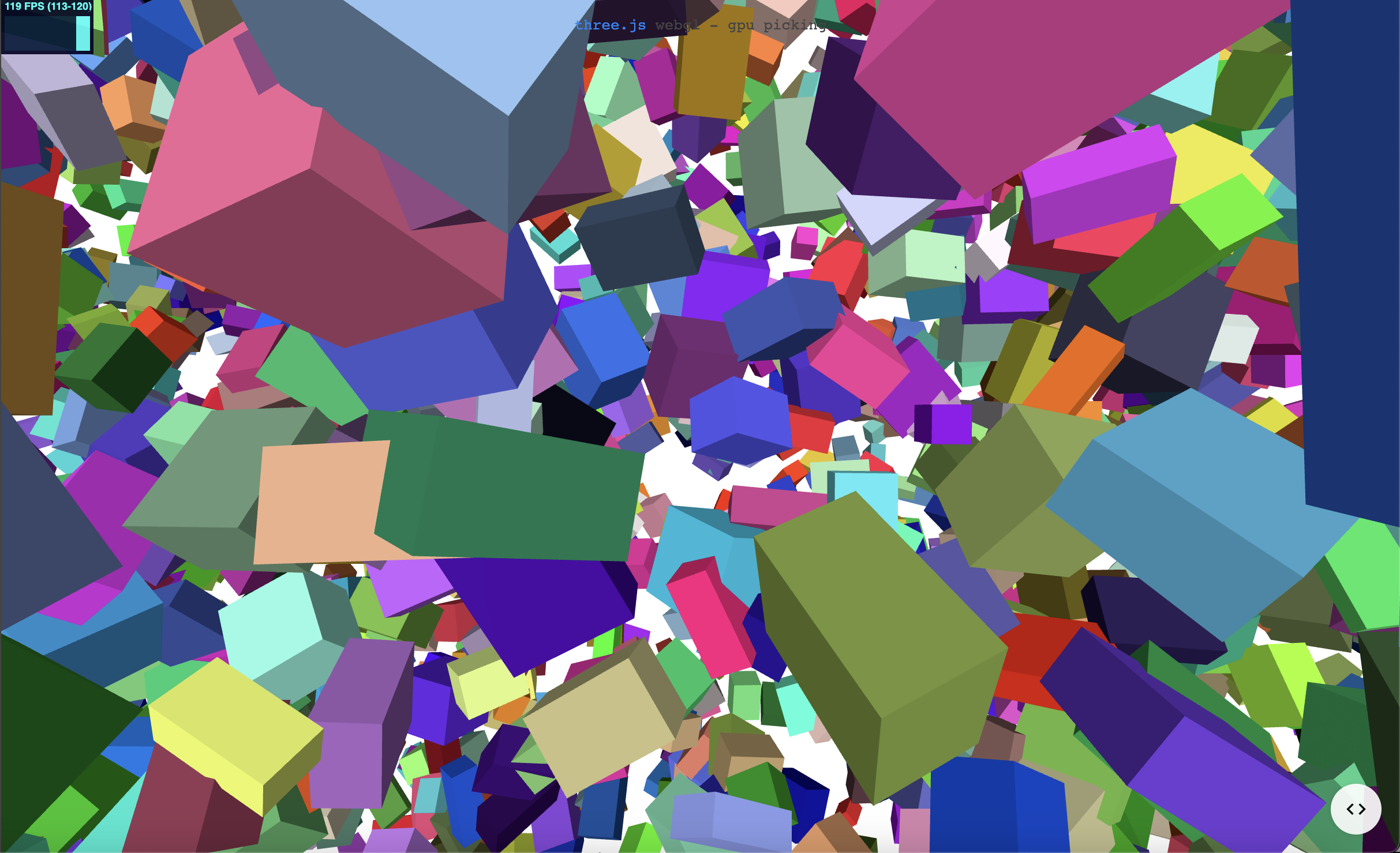 https://threejs.org/examples/#webgl_interactive_cubes_gpu
https://threejs.org/examples/#webgl_interactive_cubes_gpu
 https://threejs.org/examples/#webgl_animation_keyframes
https://threejs.org/examples/#webgl_animation_keyframes
위의 화면들이 모두 Three.js로 만들어진 것이다..
너무 예쁘다..
물론 지금 당장 저런 것들을 만들어내긴 힘들겠지만, 흥미를 가지고 학습할 수 있을 것 같다.
나와 함께 Three.js 문서를 읽으며 천천히 공부해보자!
🍞 목표
Three.js가 무엇인지 알아보고, Three.js를 구성하는 기본 요소들을 학습해보자.
🍞 Three.js란?
먼저 Three.js가 무엇인지에 대해 간단히 알아보고 넘어가자.
공식문서에 따르면 Three.js는 웹페이지에 3D 객체를 쉽게 렌더링하도록 도와주는 자바스크립트 3D 라이브러리이다.
WebGL로도 3D 객체를 만들 수 있는데, WebGL과 Three.js는 어떤 차이점이 있을까?
WebGL은 점, 선, 삼각형만을 그리는 단순한 시스템이다.
그래서 WebGL로 무언가를 만드려면 굉장히 많은 양의 코드를 작성해야 한다.
Three.js는 WebGL을 사용하여 3D 요소의 처리를 돕기 때문에 보다 간단하게 코드를 짤 수 있다.
쉽게 말해서 WebGL - Three.js는 Vanilla JS - React의 관계와 유사한 것이다.
Vanilla JS로 작성한다면 방대해질 코드를 React를 사용한다면 훨씬 짧고 간단하게 작성할 수 있는 것처럼, Three.js를 사용하면 개발자가 같은 기능도 더 간단히 구현할 수 있다.
그럼 Three.js 앱의 구조를 간단히 살펴보자.

-
Renderer
- Three.js의 핵심 객체이다.
- Scene과 Camera 객체를 넘겨받아 카메라의 Frustrum 안 3D Scene의 일부를 평면 이미지로 렌더링한다.
- Three.js에서 Frustrum은 카메라 시야 안에 들어갈 내용물을 결정하는 데 쓰인다. 쉽게 말하면 카메라 렌즈를 통해 보이는 특정 공간을 의미한다.
-
Scene Graph
- Scene 혹은 다수의 Mesh, Light, Group, Object3D, Camera로 이루어진 트리 구조와 유사하다.
- Scene은 Scene Graph의 최상위 노드이다. background color, fog 등의 요소를 포함한다.
- Scene에 포함된 객체들도 부모 / 자식의 트리 구조로 이루어져있다.
- 여기서 자식 객체의 위치와 방향은 부모 기준이다.
-
Mesh
- Material로 하나의 Geometry를 그리는 객체이다.
- 쉽게 이야기하면 하나의 덩어리이다.
- 여러 개의 Mesh가 하나의 Material 혹은 Geometry를 동시에 참조할 수 있다.
-
Geometry
- Gemoetry 객체의 정점 (vertex, 꼭짓점) 데이터이다.
- 구, 정육면체, 면, 개, 고양이 등 다양한 모양이 될 수 있다.
-
Material
- Geometry 객체를 그리는 데 사용하는 표면 (Texture) 속성이다.
- 색, 밝기, 텍스처, 반질거림, 투명도 등을 설정할 수 있다.
- 하나의 Material은 여러 개의 Texture를 사용할 수 있다.
🍞 Scene 만들기
지금까지 Three.js가 무엇인지와, Three.js를 구성하고 있는 기본적인 요소들에 대해 알아보았다.
이제 Three.js 공식문서의 Creating a scene이라는 부분을 읽어보며 직접 코드를 작성해보자.
1. Three.js 설치하기
일단 아래의 명령어를 통해 Three.js를 설치하자.
npm install three그리고 아래와 같은 방법으로 코드에서 불러올 수 있다.
// Three.js 전체 불러오기
import * as THREE from 'three';
const scene = new THREE.Scene();// 내가 필요한 부분만 불러오기
import { Scene } from 'three';
const scene = new Scene();이제 html 파일을 생성하자.
지금은 이 html 파일 하나에 간단한 코드를 작성해볼 것이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>My first three.js app</title>
<style>
body { margin: 0; }
canvas { display: block; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from "three";
// 여기다가 코드를 작성할 것이다.
</script>
</body>
</html>2. Scene, Camera 생성하기
우리는 Scene, Camera, Renderer로 무언가를 표현할 수 있다.
먼저 Scene, Camera를 설정해보자.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>My first three.js app</title>
<style>
body { margin: 0; }
canvas { display: block; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from "three";
// Scene 생성
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
// Camera 생성
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
75, // field of view
window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, // aspect ratio
0.1, // near
1000 // far
);
</script>
</body>
</html>Three.js에는 여러 종류의 카메라가 있다.
여기서는 PerspectiveCamera를 사용했다.
첫 번째 속성은 field of view (FOV, 시야각)이다.
FOV는 해당 시점의 화면이 보여지는 정도를 나타내며, 각도 값으로 설정한다.
두 번째 속성은 aspect ratio (종횡비)이다.
대부분의 경우는 요소의 높이와 너비에 맞추어 표시한다.
이렇게 하지 않으면 이미지가 틀어져보일 수 있다.
세 번째 속성과 네 번째 속성은 near과 far이다.
far 값보다 멀리 있는 요소나 near 값보다 가까이 있는 오브젝트는 렌더링되지 않는다.
3. Renderer 생성하기
다음으로 Renderer를 설정해주자.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>My first three.js app</title>
<style>
body { margin: 0; }
canvas { display: block; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from "three";
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 );
// Renderer 생성
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
// 렌더링할 곳 크기 설정
renderer.setSize( window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight );
// Renderer 요소를 추가
// renderer.domElement는 <canvas> 요소로, Renderer가 Scene을 나타내는 구역
document.body.appendChild( renderer.domElement );
</script>
</body>
</html>WebGLRenderer 외에도 Three.js는 WebGL을 지원하지 않을 때를 대비해 다른 Renderer들을 더 제공하고 있다.
Renderer 인스턴스 생성과 동시에 우리는 렌더링할 곳의 크기를 정해줘야 한다.
여기서는 렌더링할 구역의 높이와 너비를 브라우저 윈도우의 크기와 같게 설정했다.
사이즈는 그대로 유지하되 더 낮은 해상도로 렌더링하고 싶다면, setSize의 세 번째 인자인 updateStyle을 false로 설정할 수 있다.
setSize(window.innerWidth/2, window.innerHeight/2, false)
이렇게 사용한다면 <canvas> 가 100%의 높이, 너비 기준으로 절반의 해상도로 렌더링된다.
4. Geometry, Material 생성하기
이제 큐브 모양을 추가해보자.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>My first three.js app</title>
<style>
body { margin: 0; }
canvas { display: block; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from "three";
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 );
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize( window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight );
document.body.appendChild( renderer.domElement );
// Geometry 생성
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(
1, // 가로
1, // 세로
1 // 높이
);
// Material 생성
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( { color: 0x00ff00 } );
// 큐브 만들고 Scene에 추가
const cube = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material );
scene.add( cube );
// Camera 위치 수정
camera.position.z = 5;
</script>
</body>
</html>BoxGeometry에는 큐브에 필요한 모든 꼭짓점 (vertices)와 면 (faces)가 포함되어 있다.
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry( 1, 1, 1 ); 코드를 통해 가로, 세로, 높이가 모두 1인 정육면체 Geometry를 만든 것이다.
여기서 1은 1px이나 1cm같은 것이 아니라, 3D 공간에서의 상대적인 크기를 나타낸다.
다음으로 const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( { color: 0x00ff00 } ); 를 통해 표면의 색상이 0x00ff00인 Material를 생성한다.
그리고 Mesh 객체를 생성해보자.
Mesh 객체 생성을 위해서는 Geometry와 Material 두 가지가 필요하다.
Geometry에 Material을 적용하고, 화면에 삽입하여 우리가 자유롭게 움직일 수 있도록 해준다.
scene.add(); 를 호출하면 scene에 추가된 모든 것들은 (0, 0, 0) 속성을 가진다.
이 경우 카메라와 큐브가 동일한 위치에 있게 되므로, 여기서는 카메라의 위치를 수정했다.
5. Scene 렌더링
화면에 우리가 만든 큐브를 띄우기 위해서는 Scene을 렌더링해야 한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>My first three.js app</title>
<style>
body { margin: 0; }
canvas { display: block; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from "three";
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 );
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize( window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight );
document.body.appendChild( renderer.domElement );
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry( 1, 1, 1 );
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( { color: 0x00ff00 } );
const cube = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material );
scene.add( cube );
camera.position.z = 5;
// 화면이 새로고침될 때마다 렌더링
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
renderer.render( scene, camera );
}
animate();
</script>
</body>
</html>추가된 코드는 화면이 새로고침될 때마다 계속 렌더링해주는 역할을 한다.
이 부분은 render loop 또는 animate loop라고 한다.
setInterval을 쓰지 않고 requestAnimationFrame을 사용하는 데에는 여러 이유가 있지만, 가장 큰 장점은 유저가 브라우저 창에서 이탈했을 때 렌더링을 멈춰준다는 것이다.
여기까지 코드를 작성하면 아래와 같은 화면이 띄워진다.
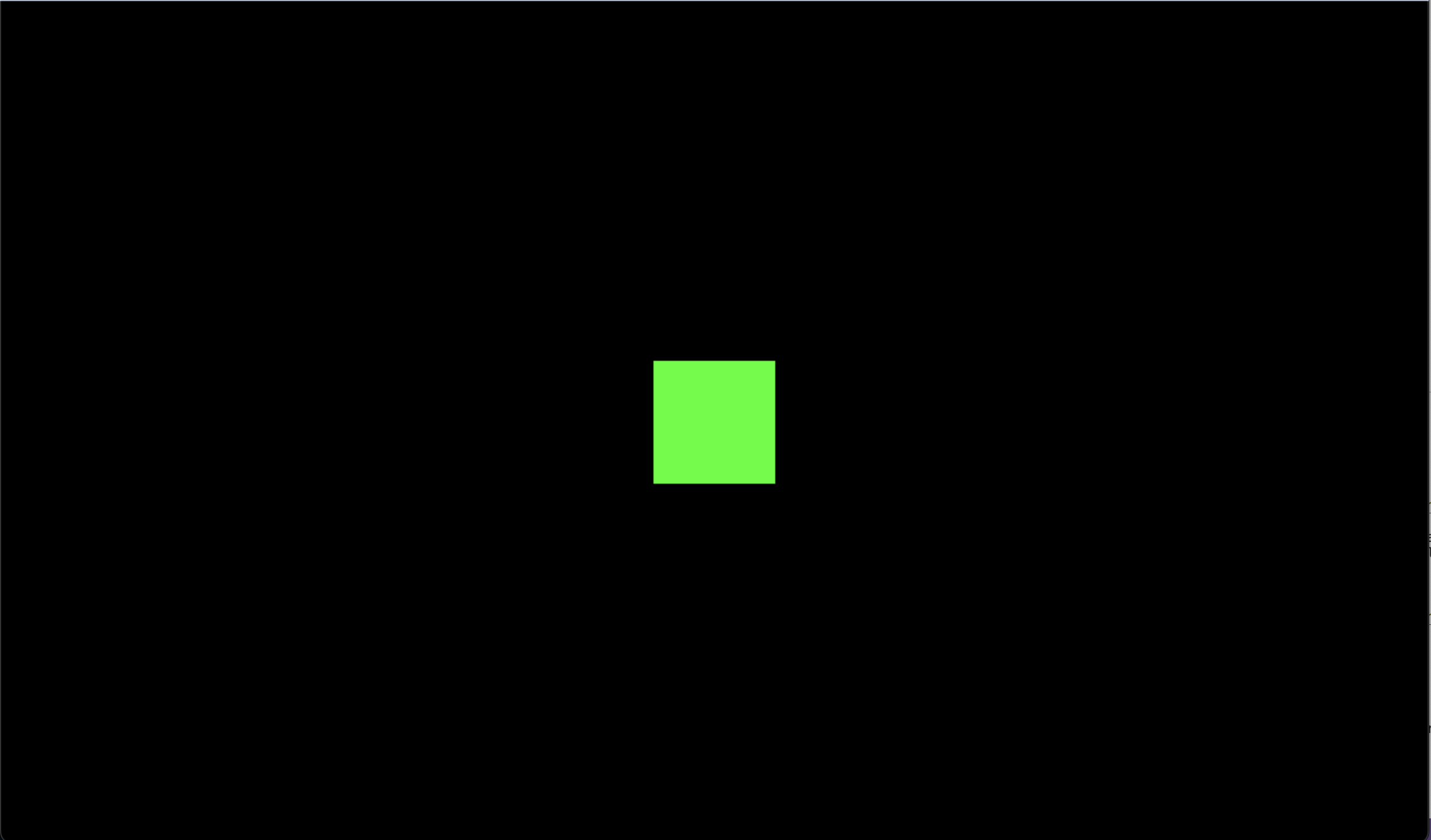
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>My first three.js app</title>
<style>
body { margin: 0; }
canvas { display: block; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from "three";
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 );
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize( window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight );
document.body.appendChild( renderer.domElement );
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry( 1, 1, 1 );
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( { color: 0x00ff00 } );
const cube = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material );
scene.add( cube );
camera.position.z = 5;
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
// 큐브 회전시키기
cube.rotation.x += 0.01;
cube.rotation.y += 0.01;
renderer.render( scene, camera );
}
animate();
</script>
</body>
</html>코드를 조금 더 추가해서 큐브를 회전시켜보자.
이 코드는 매 프레임마다 (일반적으로는 1초에 60번가량) 실행되면서 큐브가 회전하도록 해준다.
여기까지 코드를 작성한다면 아래와 같은 결과물이 나온다.

실제로는 조금 더 빨리 회전하는데 Gif로 변환해서 그런지 조금 더 느리게 회전하는 것처럼 보인다.
이렇게 Three.js 공식문서의 내용을 따라가며 기본적인 내용들을 학습해보았다.
이후 글부터는 이 코드를 바탕으로 더 구체적인 내용을 적용해볼 예정이다.


