Schema 합치기
여러 table을 합치면 장단점이 있다.
장점: 정보를 찾기 편해짐
단점: 테이블이 커짐, 반복되는 값이 생김
Smaller schema
그렇다면, schema를 최대한 작게 쪼개는게 좋은 것일까?
각 attribute의 funcional dependency를 확인해보면 됨
어떤 attribute에 따라 결정되는 attribute들 <- functional dependency가 있다. (candidate key와 나머지 attribute의 관계)
candidate key가 아닌 걸 기준으로 쪼개면? lossy decomposition이 됨 말 그대로 데이터 손실이 생김
예시)
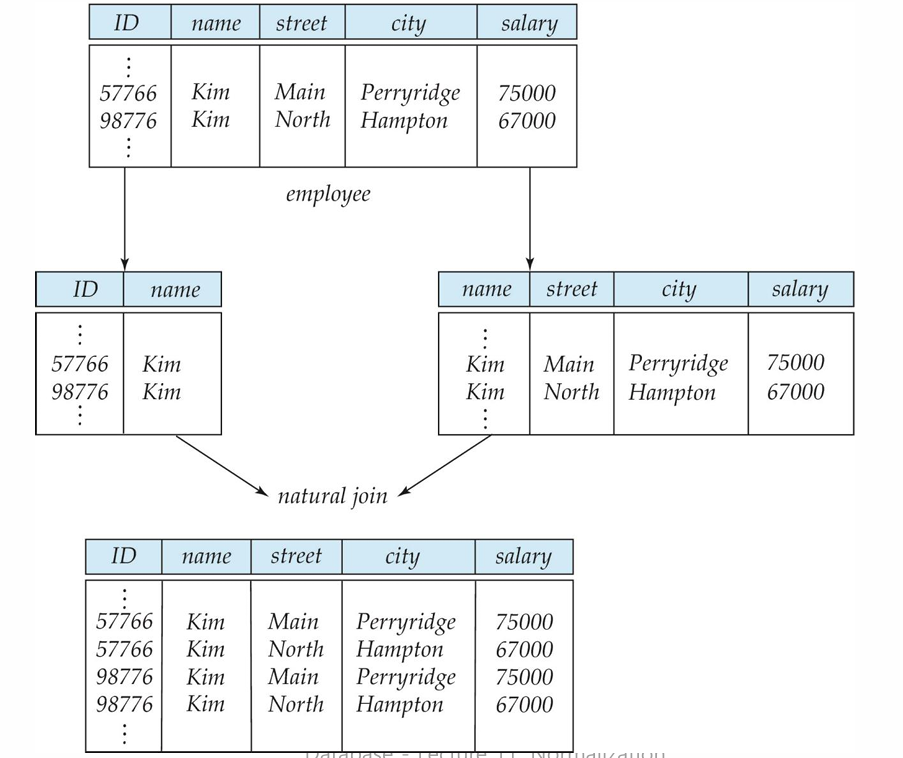
employee를 분해하고 다시 합치는 과정에서 원본 table과 데이터가 달라졌음을 확인 할 수 있다.
First normal form
모든 attribute의 value는 atomic해야 함.
즉, 한 attribute에다가 여러 value 넣지 마라, composite attribute 넣지 마라
예시) member 테이블에 phone_num attribute가 있다고 하면, 한 사람이 여러 전화번호를 가질 수 있다. 그렇다고 phone_num 에다가 (010-xxxx-xxxx, 010-yyyy-yyyy) 이렇게 넣지 말라는거다.
Functional Dependency
relation R이 있을 때,
functional dependency
이면, 두 tuple , 의 attribute 가 같으면, 도 같아야 함
예시)
| A | B |
|---|---|
| 1 | 4 |
| 1 | 5 |
| 3 | 7 |
이다. 하지만 는 성립한다.
relation R의 key K가 이면 K는 super key 이다.
이고, 어떤에 대해 이 되는 가 없으면 K는 candidate key이다 (최소 attribute super key라는 뜻)
Trivial
일 때, 이면 Trivial한 functional dependency라고 한다.
Closure
우리는 functional dependency 여러개로 또 다른 functional dependency를 추론해 낼 수 있다.
예시)가 있으면, 를 추론할 수 있음
functional dependency의 집합 F가 있을때, F로 추론할 수 있는 모든 functional dependency들의 집합을 F의 closure라고 하고, 로 표시한다.
는 F의 superset(원래 FD+추론된 FD)
Properties of FD
Subset property(Trivial)
Augmentation
Transitivity
Union
Decomposition
Pseudo-transitivity
Boyce-Codd Normal Form
relation R의 의 모든 FD 가 다음 조건 중 최소 하나를 만족해야 함
- is trivial (즉,
- is super key for R
Decomposing a Schema into BCNF
우선 BCNF를 깨는 FD를 찾는다 라고 하면,
R을 다음 두 relationd로 분해
예시)
instr_dept(ID, name, salary, dept_name, building, budget)
dept_name은 instr_dept의 super key도 아니고, 위 FD는 Trivial도 아니다. 따라서 BCNF를 깨는 FD이다.
에 해당
(dept_name, building, budget)
(ID, name, salary, dept_name)
하면 BCNF된 relation이 됨
dependency를 보존하면서 BCNF로 decomposition하는 것이 불가능 할 수도 있음
그래서 보통은 Third normal form으로 분해함
Third Normal Form
다음을 충족하면 relation R은 3NF이다.
모든 에 대해 다음 중 적어도 하나를 만족해야 함
- is trivial
- 는 R의 super key
- 의 각 attribute A는 R의 candidate key에 포함되어야 함
R이 BCNF면, 3NF임(모든 FD가 조건1 or 2를 충족하므로)
3번째 조건이 dependency preservation을 위한 조건
3NF의 장점
- dependency preservation 보장
3NF의 단점
- null value를 사용해야 할 수도 있음
- 중복되는 value가 있을 수 있음
Normalization의 목표
Benefits of normalization
- Less strage space
- Quicker update
- Less data inconsistency
- Clearer data relationships
- Easier to add data
- Flexible structure