- Layer 별 입력 데이터에 대한 출력 Feature Map 산정 계산법
- 입력 데이터 높이 : H
- 입력 데이터 폭 : W
- 필터 높이 : FH
- 필터 폭 : FW
- Stride 크기 : S
- Padding 크기 : P
- 출력 데이터 크기 계산식
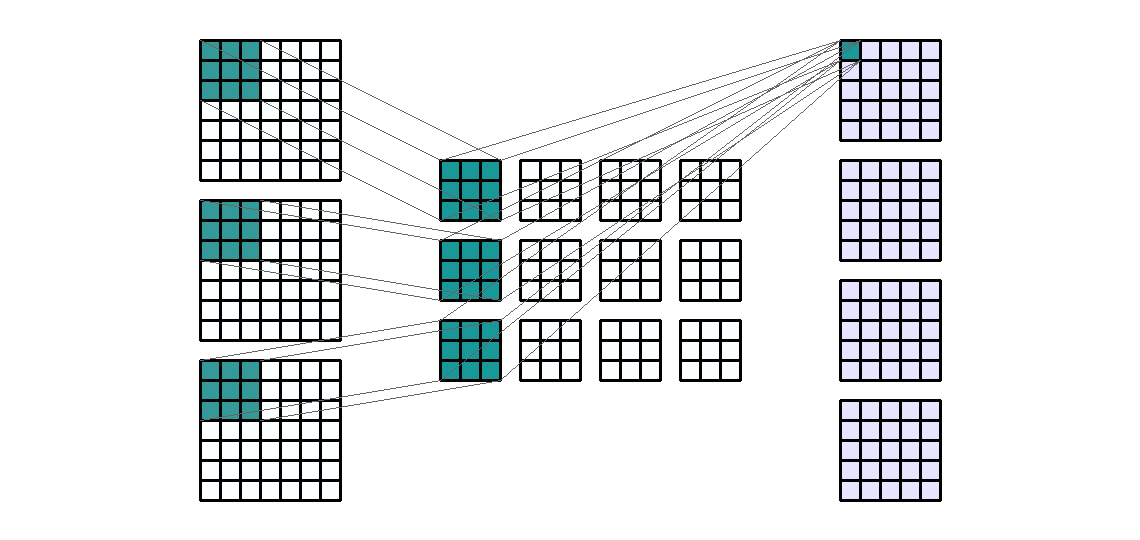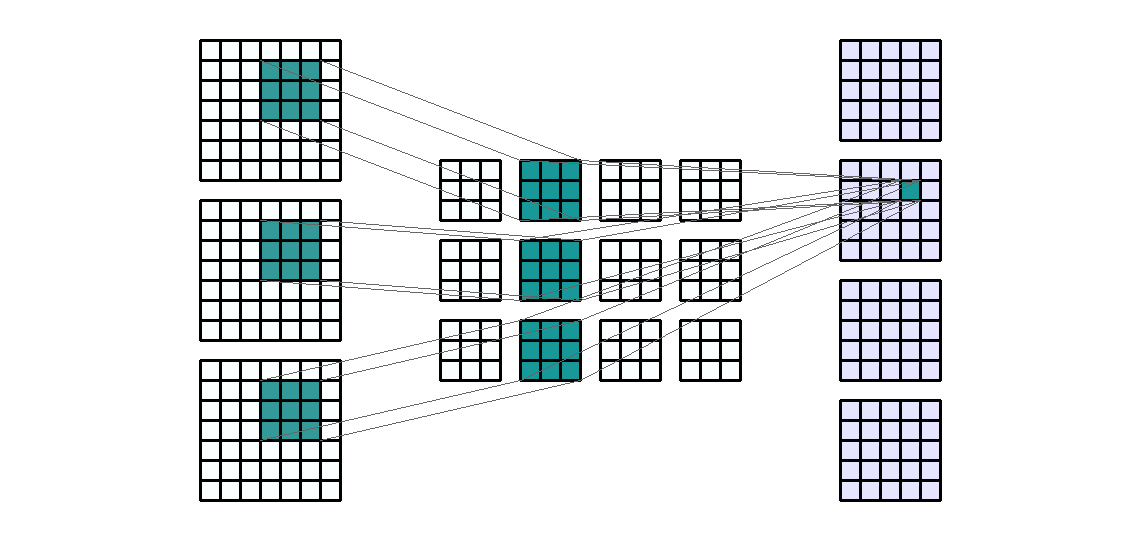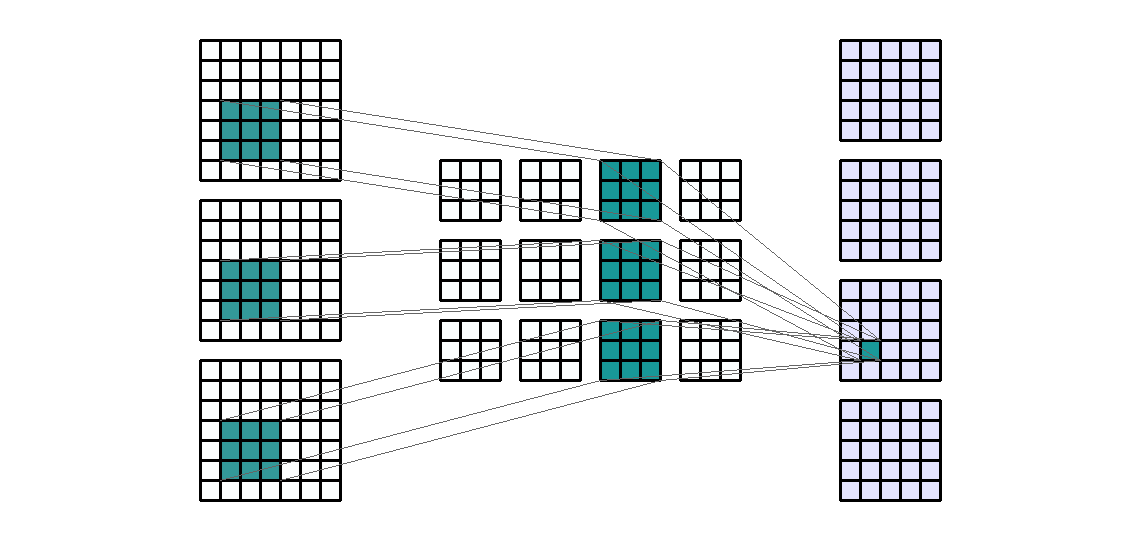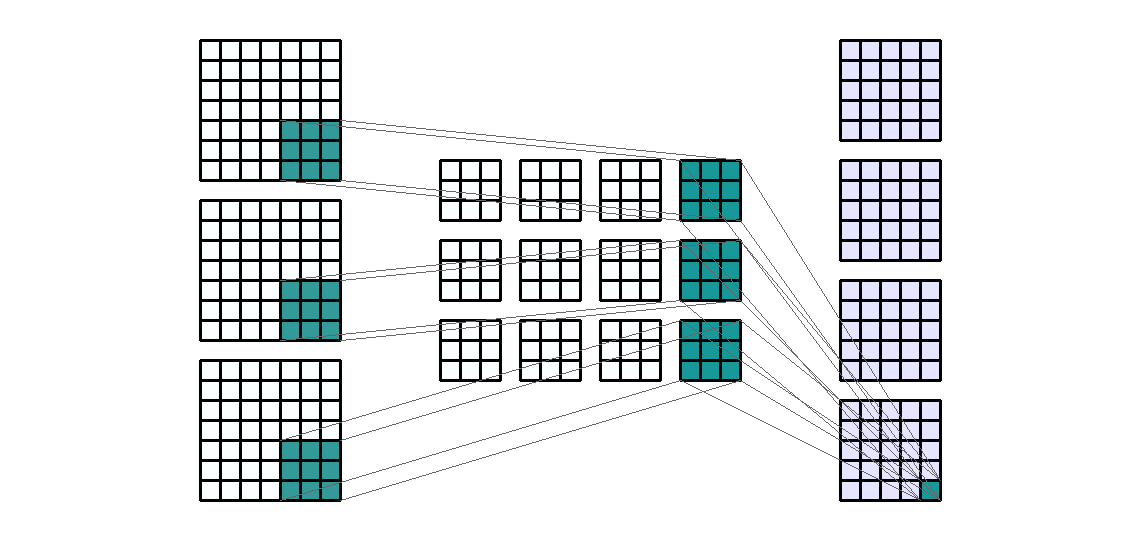
Input Shape: (7, 7, 3) Output Shape : (5, 5 ,4) K : (3, 3) P : (0, 0) S : (1, 1) Filter : 4
(출처 - https://miro.medium.com/max/1100/1*ubRrYAZJUlCcqg7WoKjLgQ.gif)
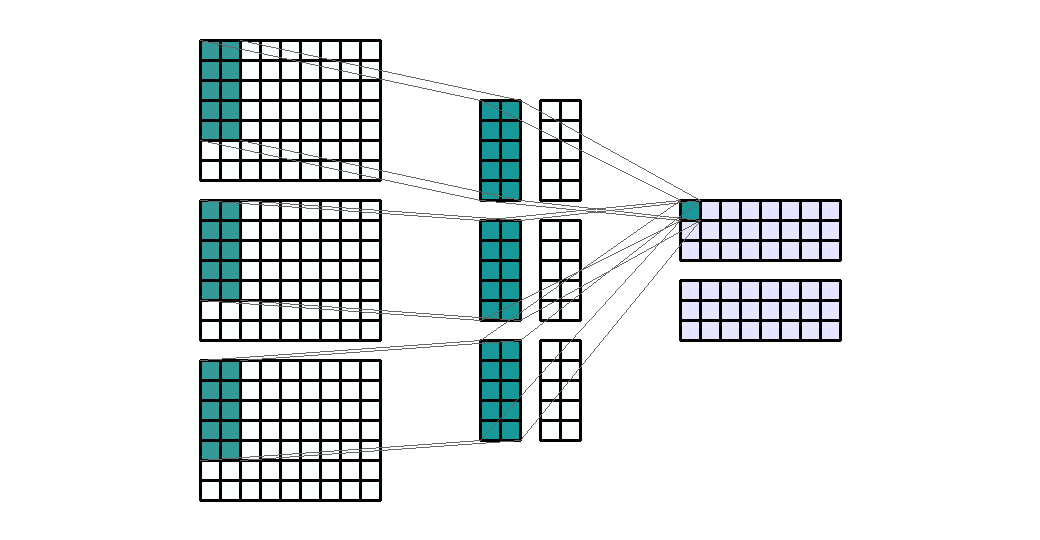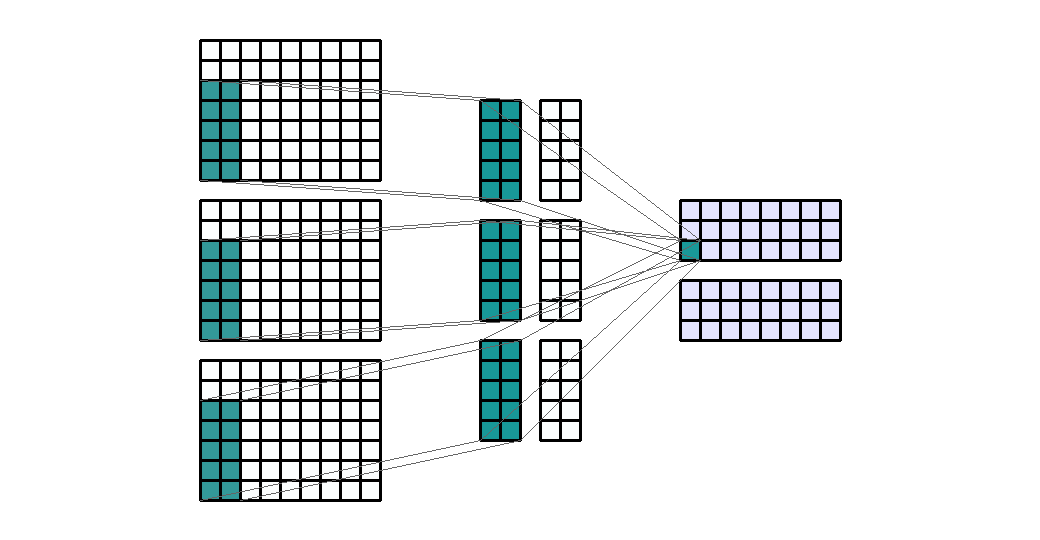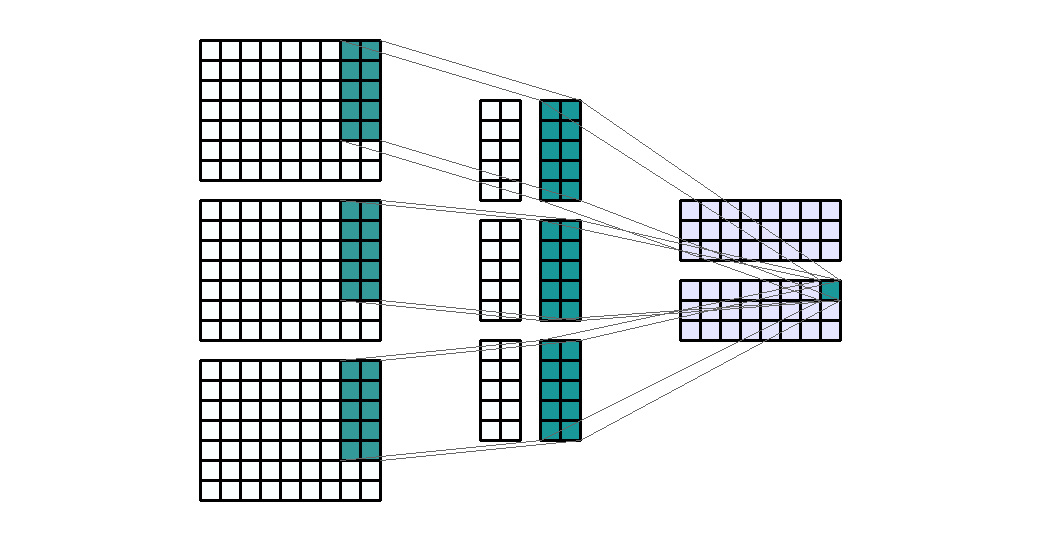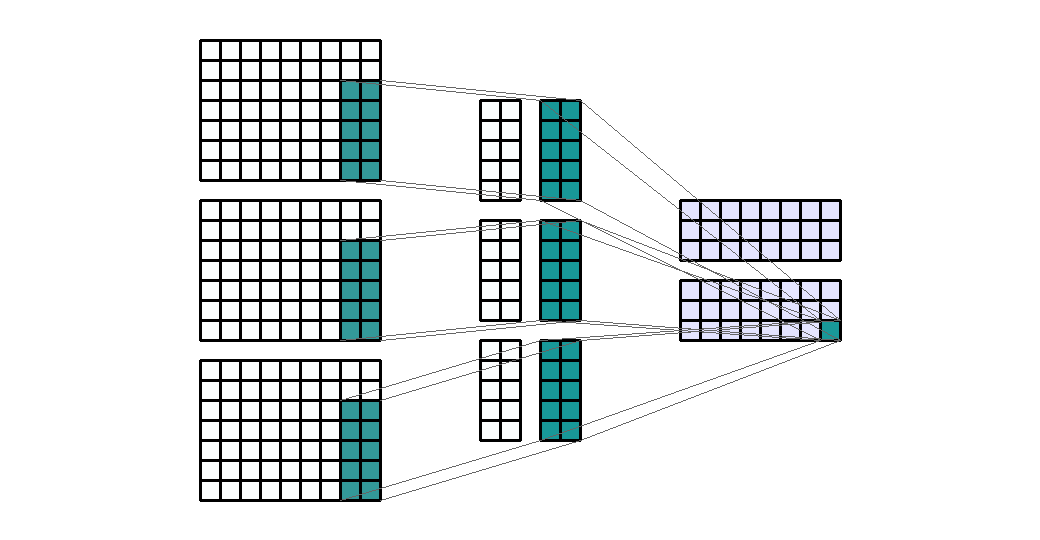
Input Shape: (7, 9, 3) Output Shape : (3, 8, 2) K : (5, 2) P : (0, 0) S : (1, 1) Filter : 2
(출처 - https://miro.medium.com/max/1100/1*EnIGiVTcIMQm9ujkOHPc5A.gif)
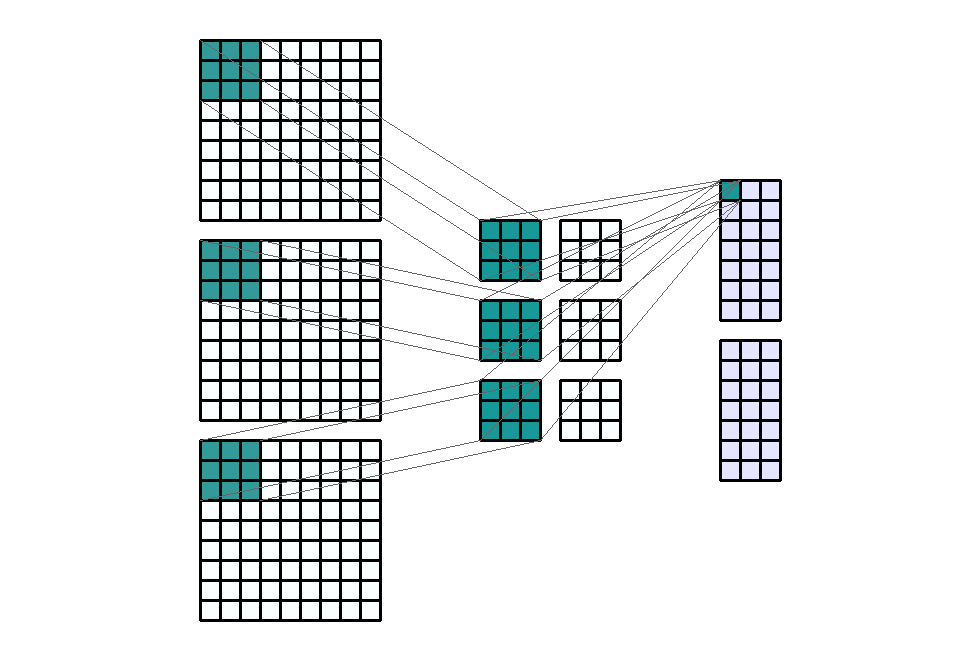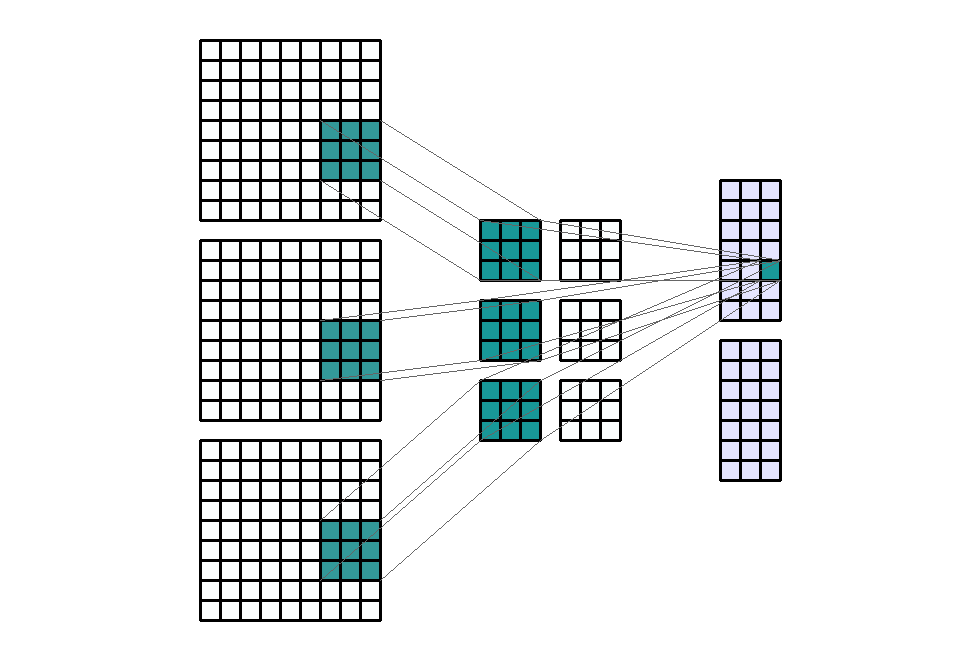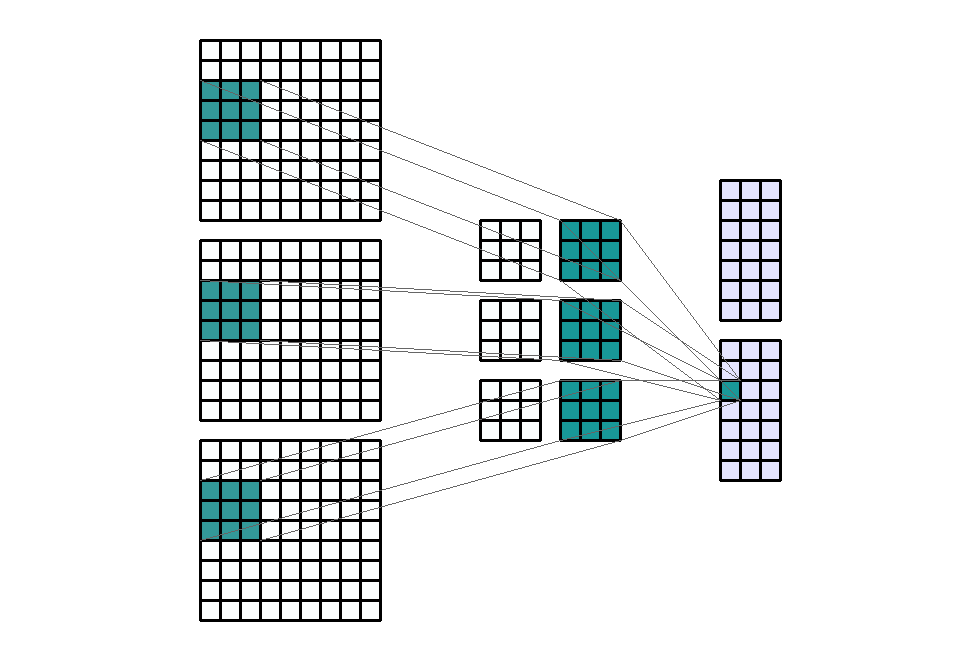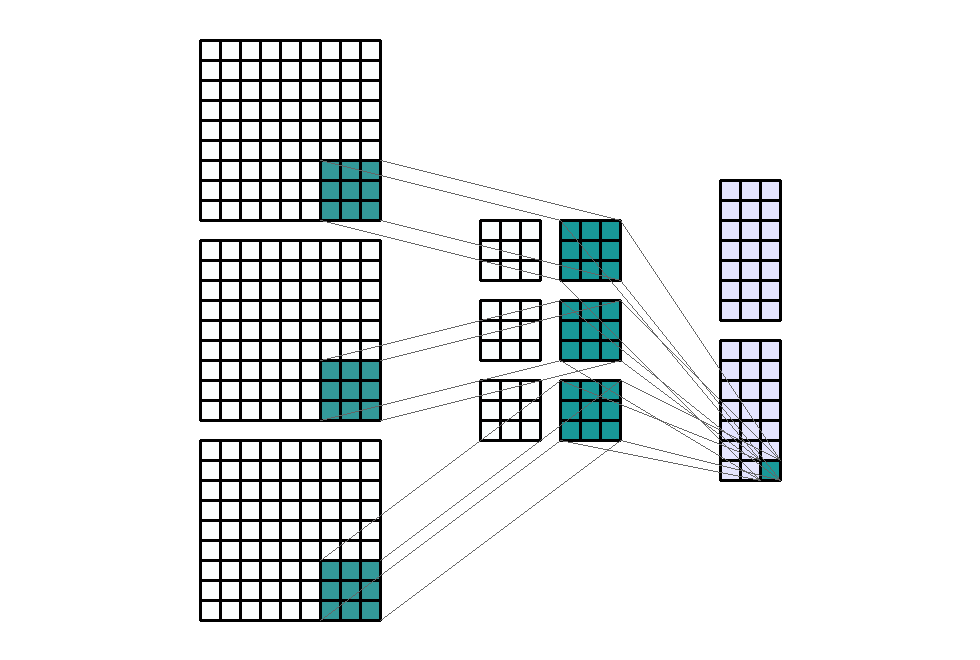
Input Shape: (9, 9, 3) Output Shape : (7, 3, 2) K : (3, 3, 2) P : (0, 0) S : (1, 3) Filter : 2
(출처 - https://miro.medium.com/max/1100/1*o9-Rq3QUC8IzTMfAJIbhLA.gif)
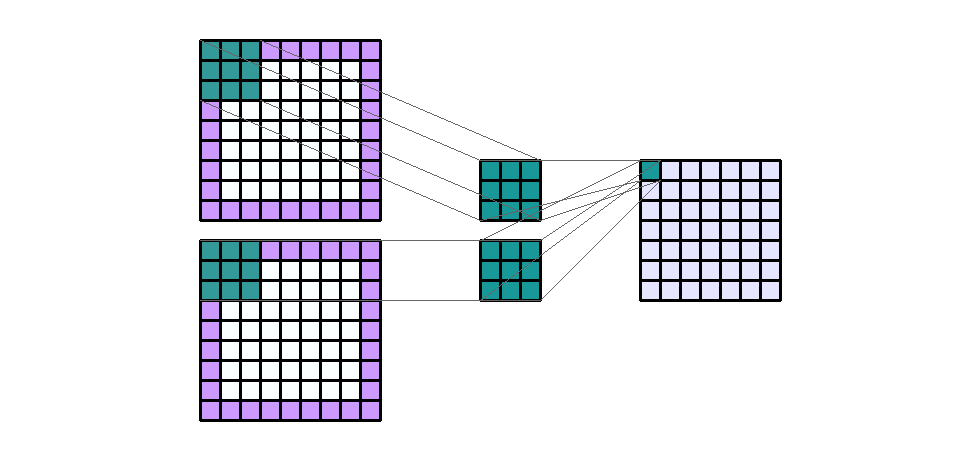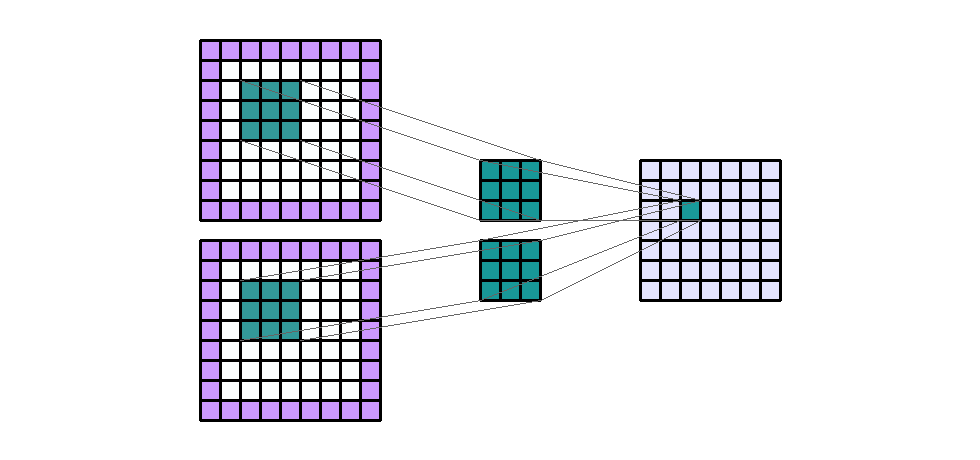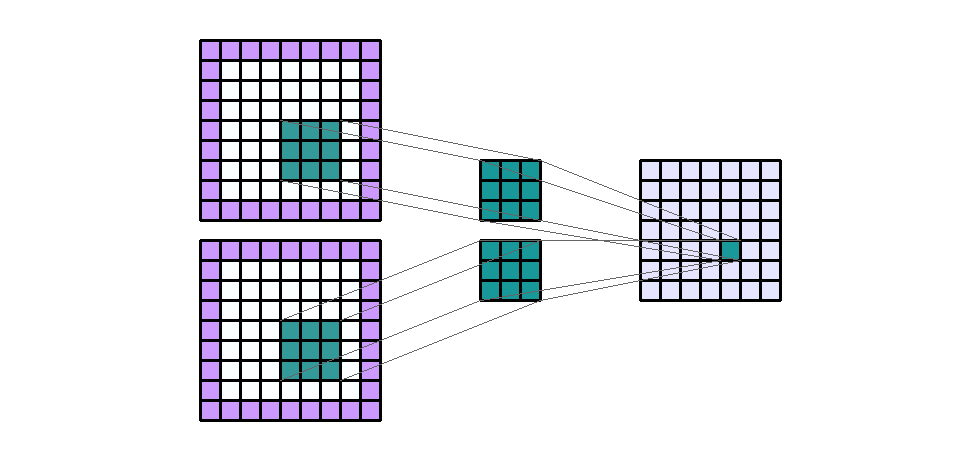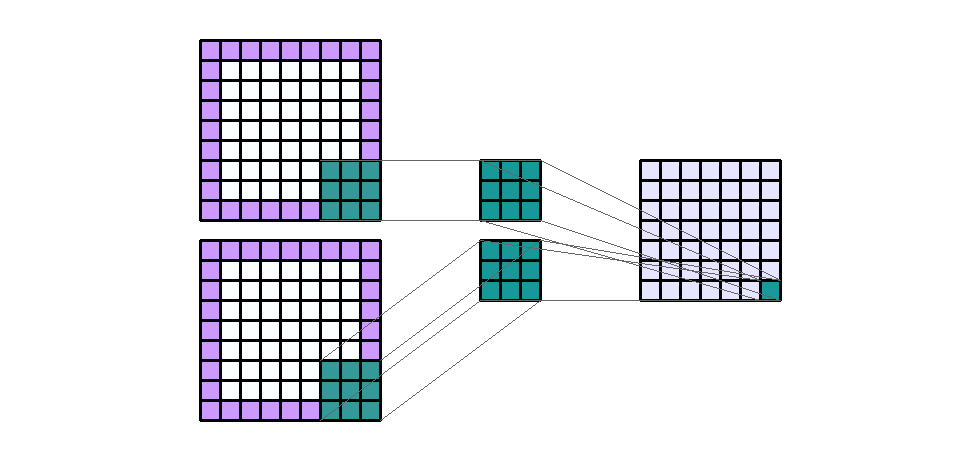
Input Shape : (7, 7, 2) Output Shape : (7, 7, 1) K : (3, 3) P : (1, 1) S : (1, 1) Filter : 1
(출처 - https://miro.medium.com/max/1100/1*EnIGiVTcIMQm9ujkOHPc5A.gif)
-
CNN Layer의 입/출력, 파라미터 계산
- 파라미터 계산식
- Output Channel은 Filters 값
- 파라미터 계산식
-
Pooling Layer 계산
-
BatchNormalization 파라미터 계산
- 현재 gamma, beta, mean, standard deviation 총 4개의 파라미터를 구하도록 구현되어 있음.
- https://github.com/keras-team/keras/issues/1523
- gamma : 스케일링(scaling) 파라미터, beta : shift 파라미터.
- mean, standard deviation은 Non-trainable params.
-
모델
IMAGE_SIZE = 32
input_tensor = Input(shape=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3), name='input')
x = Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same', name='conv2d_1')(input_tensor)
x = BatchNormalization(name='bn_1')(x)
x = Activation('relu', name='activation_1')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2)(x)
x = Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=3, padding='same', name='conv2d_2')(x)
x = BatchNormalization(name='bn_2')(x)
x = Activation('relu', name='activation_2')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2)(x)
x = Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding='same', name='conv2d_3')(x)
x = BatchNormalization(name='bn_3')(x)
x = Activation('relu', name='activation_3')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2)(x)
x = Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding='same', name='conv2d_4')(x)
x = BatchNormalization(name='bn_4')(x)
x = Activation('relu', name='activation_4')(x)
x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
x = Dropout(rate=0.5)(x)
x = Dense(50, activation='relu', name='fc')(x)
x = Dropout(rate=0.5)(x)
output = Dense(10, activation='softmax', name='output')(x)
model = Model(inputs=input_tensor, outputs=output)- 계산 결과
| Layer | Input Shape | Output Shape | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convolution Layer 1 | (32+21-3)/1+1 = 32, (32+21-3)/1+1 = 32, 3 | 32, 32, 64 | 133*64+64=1792 |
| Batch Normalization Layer 1 | 32, 32, 64 | 32, 32, 64 | 64*4 = 256 |
| MaxPooling Layer 1 | 32, 32, 64 | 32/2=16, 32/2=16, 64 | 0 |
| Convolution Layer 2 | (16+21-3)/1+1 = 16, (16+21-3)/1+1 = 16, 128 | 16, 16, 128 | 6433*128+128=73856 |
| Batch Normalization Layer 2 | 16, 16, 128 | 16, 16, 128 | 128*4 = 512 |
| MaxPooling Layer 2 | 16, 16, 128 | 16/2 = 8,16/2 = 8,128 | 0 |
| Convolution Layer 3 | (8+21-3)/2+1 = 4, (8+21-3)/2+1 = 4, 256 | 4, 4, 256 | 12833*256+256=295168 |
| Batch Normalization Layer 3 | 4, 4, 256 | 4, 4, 256 | 256*4 = 1024 |
| MaxPooling Layer 3 | 4, 4, 256 | 4/2=2, 4/2=2, 256 | 0 |
| Convolution Layer 4 | (2+21-3)/2+1 = 1,(2+21-3)/2+1 = 1,512 | 1, 1, 512 | 25633*512+512=1180160 |
| Batch Normalization Layer 4 | 1, 1, 512 | 1, 1, 512 | 512*4 = 2048 |
| Dropout Layer 1 | None, 512 | None, 512 | 0 |
| Fully Connected Layer 1 | None, 50 | None, 50 | 512*50+50=25650 |
| Dropout Layer 2 | None, 50 | None, 50 | 0 |
| Output | None, 50 | None, 10 | 50*10+10 = 510 |
ref. https://towardsdatascience.com/conv2d-to-finally-understand-what-happens-in-the-forward-pass-1bbaafb0b148
ref. http://taewan.kim/post/cnn/
