
코딩 테스트 준비를 하다가 시간 초과를 마주하는 경험은 다들 한 번씩 있을 것이다.
본인도 백준에서 수 정렬하기 2라는 문제를 풀다가 시간 초과를 마주했고, 시간 초과를 해결했던 방법에 대해 이야기하며 I/O에 대해서 간단하게 설명해 보겠다.
문제 풀이 과정
수를 정렬하는 프로그램을 짜는 것이고 시간 제한도 2초로 넉넉했기 때문에 Javascript의 sort를 이용하여 정렬해 준 후 각 iteration마다 console.log를 통해 출력을 해주었다.
const fs = require("fs");
const filePath = process.platform === "linux" ? "/dev/stdin" : "./input.txt";
const input = fs.readFileSync(filePath).toString().trim().split("\n");
input
.splice(1)
.map(Number)
.sort((a, b) => a - b)
.forEach((num) => console.log(num));하지만 위 코드에서 정렬해야 하는 수의 개수가 최대인 1,000,000이 들어오게 되면 시간 초과가 발생하게 된다.
시간 초과를 해결하기 위해 여러 글을 보던 중 iteration마다 매번 출력하는 것이 아닌, 배열을 join 하라는 글을 발견했다. 아래는 수정된 코드이다.
const fs = require("fs");
const filePath = process.platform === "linux" ? "/dev/stdin" : "./input.txt";
const input = fs.readFileSync(filePath).toString().trim().split("\n");
console.log(
input
.slice(1)
.map(Number)
.sort((a, b) => a - b)
.join("\n")
);성능 비교
성능 차이가 궁금하여 console.time을 이용하여 매 반복문마다 console.log를 실행하는 것과 join 연산을 이용했을 때의 시간 차이를 측정해 보았다.
const largeArray = Array.from({ length: 1000000 }, (_, idx) => idx);
console.time("join");
const joinOperation = [];
for (const number of largeArray) joinOperation.push(number);
console.log(joinOperation.join("\n"));
console.timeEnd("join");
console.time("console.log");
for (const number of largeArray) console.log(number);
console.timeEnd("console.log");1,000,000 크기의 배열을 생성 후 join 연산을 사용한 경우와 매 반복문마다 console.log를 실행하는 것의 시간을 측정해 보았다.
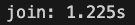

사진에서 볼 수 있듯이 join 연산을 이용한 것이
약 3초 정도 더 빠른 것을 확인할 수 있다.
I/O System
위의 결과를 알아보기 전에 I/O의 개념과 동기 I/O, 비동기 I/O에 대해 알아보겠다.
I/O
I/O는 Input(입력)과 Output(출력)의 약자로 컴퓨터가 외부 세계와 데이터를 주고받는 모든 작업을 의미한다.
- 입력(Input): 키보드로 글자를 입력하거나 파일에서 데이터를 읽는 것
- 출력(Output): 화면에 결과를 출력하거나 파일에 데이터를 저장하는 것
즉, I/O는 컴퓨터가 외부 장치(키보드, 디스크, 네트워크 등)와 소통하는 과정이라고 생각하면 된다.
I/O는 컴퓨터 내부(CPU와 메모리)에서 이루어지는 작업보다 느리다. 이는 외부 장치와 소통하는 데 시간이 걸리기 때문이다.
동기 I/O (Synchronous I/O)
동기 I/O는 이전의 요청이 완료될 때까지 프로그램이 멈추는 방식이다.
Node.js에서는 이벤트 루프가 차단되어 다른 작업을 수행할 수 없다.
아래 코드는 동기 I/O의 예시이다.
const fs = require("fs");
const filePath = "./example.txt";
console.log("Starting file read...");
const data = fs.readFileSync(filePath);
console.log("File content:", data);
console.log(
"This message is logged immediately, while the file is still being read."
);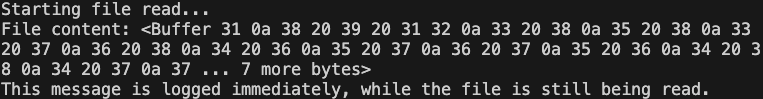
example.txt 파일을 모두 읽어와야만 “This message~” 부분이 출력 되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
비동기 I/O (Asynchronous I/O)
비동기 I/O는 요청을 보내고 응답을 기다리는 동안 다른 코드를 실행하는 것을 의미한다.
Node.js에서는 요청이 완료되면 콜백 함수나 이벤트 핸들러를 통해 결과를 처리한다. 이 방식은 non-blocking으로 이벤트 루프가 멈추지 않고 다른 작업을 병렬로 처리할 수 있게 한다.
아래 코드는 비동기 I/O의 예시이다.
const fs = require("fs");
const filePath = "./example.txt";
async function readFileAsync() {
const data = await fs.readFileSync(filePath);
console.log("File content:", data);
}
console.log("Starting file read...");
readFileAsync();
console.log(
"This message is logged immediately, while the file is still being read."
);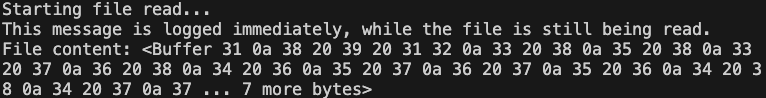
“This message~” 부분의 출력을 blocking 하지 않고 example.txt
파일을 읽어오는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
결론
Node.js에서 console.log는 동기 I/O에 해당한다. 따라서 반복적인 console.log 호출은 다음 작업을 blocking 할 뿐 아니라, I/O System에 많이 접근하기 때문에 비용이 많이 드는 작업(느린 작업)이라는 것을 알 수 있었다.
또한 정답 출력 시 하나의 배열에 정답을 모은 후 join 연산을 이용하여 한 번에 출력을 하는 것이 성능 측면에서 더 유리하다는 것을 알 수 있었다.

좋은 정보 감사합니다..~~