1. 공통 함수
std::fixed가 있다.
#include <iostream>
int main(){
double pi = 3.14;
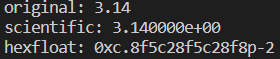
std::cout << "original: " << pi << std::endl;
std::cout << std::fixed << std::scientific <<
"scientific: " << pi << std::endl;
std::cout << std::fixed << std::hexfloat <<
"hexfloat: " << pi << std::endl;
return 0;
}
std::cout << std::fixed << how_to_fixstd::fixed는 출력할 때 특정 동작으로 출력하라고 지시해준다. 위 예시는 특정 동작을 scientific(유효숫자와 10의 거듭제곱으로 표현) 혹은 hexfloat(16진법 소수점)으로 지시한 코드이다.
바로 밑에서 볼 std::setw(), std::setprecision()으로도 지시할 수 있다.
2.std::basic_ios 클래스
2-1 ignore
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main(){
int num;
std::string str;
std::cin >> num;
std::getline(std::cin, str);
std::cout << num << str << std::endl;
return 0;
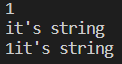
}위 코드에서 1을 입력하고 엔터키를 누르면 1만 출력하고 출력을 멈춘다. str에 \n이 들어갔기 때문이다. 이를 방지하기 위해 입력 버퍼에서 한 글자를 지운다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main(){
int num;
std::string str;
std::cin >> num;
std::cin.ignore(); // 입력 버퍼 맨 앞 글자 무시(지움)
std::getline(std::cin, str);
std::cout << num << str << std::endl;
return 0;
}
2-2 fail, clear
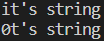
만약 위 코드에서 it's string 먼저 입력했다면 어떻게 될까?
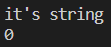
getline 함수는 실행되지 않고 num, str 어디에도 값이 입력되지 않았다. cin에 잘못된 값이 입력됐고, 이에 입력 버퍼의 상태 플래그가 입력 받지 않음으로 변경됐기 때문이다.
num의 올바른 입력 여부와 상관 없이 str를 입력 받기 위해 std::cin.fail()과 std::cin.clear()를 사용한다.
- std::cin.fail(): 입력이 실패하면 1을, 성공하면 0을 return
- std::cin.clear(): 입력 버퍼의 상태 플래그를 입력 받음으로 변경
따라서 위 코드를 다음과 같이 바꾸면
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main(){
int num;
std::string str;
std::cin >> num;
if(std::cin.fail()){ // 입력 버퍼에 입력 실패 시
std::cin.clear(); // 입력 버퍼를 다시 입력 받을 상태로
}
std::cin.ignore(); // 입력 버퍼 맨 앞 글자 무시(지움)
std::getline(std::cin, str);
std::cout << num << str << std::endl;
return 0;
}
2-3 tie()
다른 예제는 감이 안와서 cppreference 예제를 가지고 왔다.
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
std::ofstream os("test.txt");
std::ifstream is("test.txt");
std::string value("0");
os << "Hello";
is >> value;
std::cout << "Result before tie(): " << std::quoted(value) << "\n";
is.clear();
is.tie(&os);
is >> value;
std::cout << "Result after tie(): " << std::quoted(value) << "\n";
}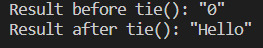
os와 is 모두 test.txt 파일 내부 데이터 흐름을 나타내는 파일 스트림이다. 두 스트림은 독자적으로 동작한다.
os >> "Hello";
test.txt에 값을 넣어도 출력을 보면 value는 0이다.
is.tie(&os);
is와 os는 서로 tie됐기 때문에 value는 "Hello"로 초기화 됐다.
3. std::ios_base 클래스
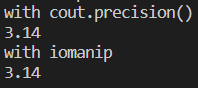
3-1 std::cout.precision()
std::cout.precision(n)은 소수점 이하 n-1자리까지 표현함을 의미한다. std::setprecision(n)과 같은 동작을 하며, 차이는 <iomanip> 헤더의 include 유무이다.
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
int main() {
double pi = 3.141592653589793238;
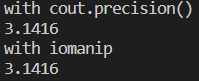
std::cout << "with cout.precision()" << std::endl;
std::cout.precision(5);
std::cout << pi << std::endl;
std::cout.precision(0);
std::cout << "with iomanip" << std::endl;
std::cout << std::setprecision(5);
std::cout << pi << std::endl;
return 0;
}
3-2 std::cout.width()
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
int main() {
double pi = 3.141592653589793238;
std::cout << "with cout.width()" << std::endl;
std::cout.width(10);
std::cout << pi << std::endl;
std::cout.width(0);
std::cout << "with iomanip" << std::endl;
std::cout << std::setw(10);
std::cout << pi << std::endl;
return 0;
}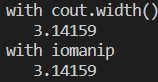
설정 값인 10으로 맞춰서 출력된다. 이때 오른쪽 정렬로 출력되어 나머지는 스페이스로 채워진다.
3-3 std::ios::sync_with_stdio()
sync_with_stdio()
이름에서 볼 수 있듯이, C의 표준 입출력인 stdio와 C++의 표준 입출력을 동기화할 지 여부를 결정한다. 좀 더 구체적으로 보기 위해 C와 C++의 입출력을 표로 그렸다.(chatGPT)

둘 다 버퍼를 사용하는 방법으로 입/출력을 진행하므로 이때 버퍼를 동기화할지 여부이다.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cout << "a\n";
std::printf("b\n");
std::cout << "c\n";
}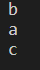
다음과 같이 동기화를 끊어놨기 때문에 C의 함수인 std::printf가 먼저 실행된다.(경우에 따라서는 나중에 실행되기도 한다.)
다음 포스팅은 <sstream> 내용을 올릴 예정이다.
