시작
React 에서 사용되는 1.글로벌 상태관리 방법과 내부저장소 2.Storage 에 대해서 공부 해 보도록 하겠습니다.
1. 글로벌 상태관리
함수형 컴포넌트에서 useContext 와 useReducer 를 사용해서 useState 보다 더 다양하게 사용될수 있는 글로벌 상태 관리에 대해서 보도록 하겠습니다.
name , age 를 관리하는 user 라는 state 를 만들어 보겠습니다.
UserContextProvider.js
import {useContext, useReducer, createContext} from "react";
const userContext = createContext(null);
const UserContextProvider = ({children}) => {
// reducer 함수 ( 제어 함수 ) , action.type 에 따라서 action 을 선택
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'up' :
return { name : state.name , age : state.age + 1};
case 'down' :
return { name : state.name , age : state.age - 1};
default :
return state;
// action 이 없으면 그대로 state 반환
}
}
const [user , dispatcher] = useReducer(reducer, { name : 'hello', age: 10});
/* const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer 함수 , 초기 state 값 ) */
const ageUp = () => {
dispatcher({type :'up'});
}
const ageDown = () => {
dispatcher({type :'down'});
}
return (
<userContext.Provider value={ {user,ageUp,ageDown}}>
{children}
</userContext.Provider>
);
}
/* Custom Hooks 사용 */
export function useUserContext() {
const context = useContext(userContext);
if(!context) {
throw new Error('UserContextProvider 를 찾을 수 없음.');
}
return context;
}
export default UserContextProvider;action.type 에 따라서 state 를 변화 시킬 reducer 함수를 만들어 줍니다. dispatcher 를 통해서 action 이 들어 오게 되면 각 action.type 에 맞게 state 가 변화 됩니다.
다음 , useReducer 를 통해서 user 라는 state 를 만들어 주겠습니다. useReducer( reduce 함수 , 초기 state 값 ) 형태를 취하게 됩니다.
그리고 dispatcher 를 통해서 state 를 변화시켜줄 함수를 생성 하겠습니다.
const ageUp = () => { dispatcher({type :'up'}); }
그다음 Provider 를 통해서 return 을 해주도록 하겠습니다 !
Custom Hooks 을 사용하여 userContext 를 손쉽게 사용하도록 해주겠습니다.
그후 Context 를 사용할 범위를 선택해서 <UserContextProvider> 로 묶어주시면 됩니다.
const App = () => {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<UserContextProvider>
<div className="App">
<Navbar/>
<Switch>
<Route path="/" exact component={Home} />
<Route path="/page" component={Page}/>
<Route component={NotFound}/>
</Switch>
</div>
</UserContextProvider>
</BrowserRouter>
);
}
export default App;정상적으로 동작하는지 확인 해 봅시다.
Home 에서 user를 불러와서 ageUp 함수를 실행 후, Page 에서 age 를 확인 해 봅시다.
Home.js
const Home = () => {
const history = useHistory();
const context = useUserContext();
useEffect(()=> {
context.ageUp();
},[])
useEffect(()=> {
console.log(context.user);
},[context.user]);
const onClick = () => {
history.push("/page");
}
return (
<div>
<h1>Home</h1>
<button onClick={onClick}>Page 이동</button>
</div>
);
}
export default Home;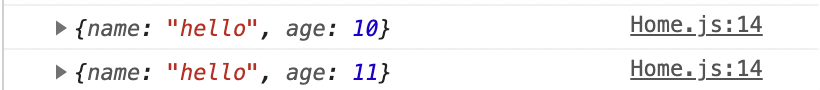
Home 화면 에서는 ageUp 이 실행되 정상적으로 age 의 값이 1 증가 한것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
이제 , Page 화면에서도 확인 해 봅시다.
page.js
const Page = () => {
const context = useUserContext();
console.log(context.user);
return (
<div>
<h1>Page</h1>
</div>
)
}
export default Page;
age 의 값이 11인 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
이런식으로 context 와 reducer 를 통해서 글로벌 상태관리가 가능합니다.
상황에 맞게 useState 와 고려해서 사용하시면 되겠습니다.
2. Stroage
이번에는 HTML5 에 추가된 저장소 기능을 보겠습니다.
LocalStorage
SessionStorage
두 가지 저장소가 존재 합니다, 두 저장소 모두 어플리케이션 전역에서 접근이 가능합니다.
두 저장소 모두key-value 형식으로 데이터를 저장합니다.
데이터는 문자열 형식으로만 사용 가능하기 때문에 서로 다른 타입의 데이터를 사용할 때에는 JSON 형태로 사용하면 됩니다.
사용법
window.localStorage.setItem('key', value);
window.localStorage.getItem('key');
window.localStorage.removeItem('key');
window.localStorage.clear();
window.localStorage.setItem("key", JSON.stringify(value));일반적으로 setItem('key',value), getItem('key') 를 사용하여 데이터를 저장하고 가져옵니다.
차이점
LocalStorage 은 동일 브라우저 안에서 영구적으로 데이터가 저장됩니다, SessionStorage는 브라우저를 종료하게 되면 데이터가 사라지게 됩니다,
같은 브라우저의 탭을 닫는것도 동일하게 작용합니다 !
