Linked List
❓ Linked List(연결 리스트)란?
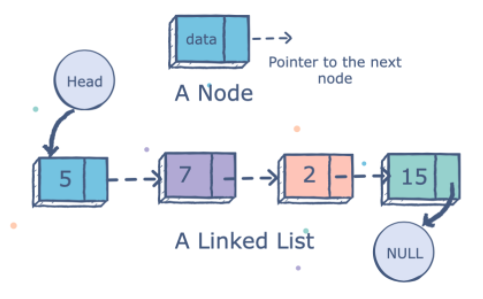
Linked List는 자료들을 반드시 연속적으로 배열시키지는 않고 임의의 기억공간에 기억시키되, 자료 항목의 순서에 따라 노드의 포인터 부분을 이용하여 서로 연결시킨 자료 구조이다.
✍️ Linked List 특징
- 노드의 삽입, 삭제 작업이 용이하다.
- 기억공간이 연속적으로 놓여 있지 않아도 저장이 가능하다.
- 연결을 위한 링크(포인터) 부분이 필요하기 때문에 순차 리스트에 비해 기억공간 이용 효율이 좋지 않다.
- 연결을 위한 포인터를 찾는 시간이 필요하기 때문에 접근 속도가 느리다.
- 중간 노드 연결이 끊어지면 그 다음 노드를 찾기 힘들다.
- 희소 행렬 을 링크드 리스트로 표현하면 기억장소가 절약된다.
- 트리를 표현할 때 가장 적합한 자료 구조이다.
✍️ Linked List의 종류
-
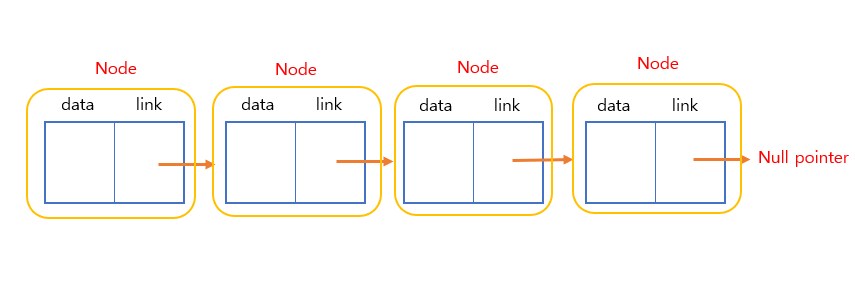
Singly Linked List (단일 연결 리스트)
-
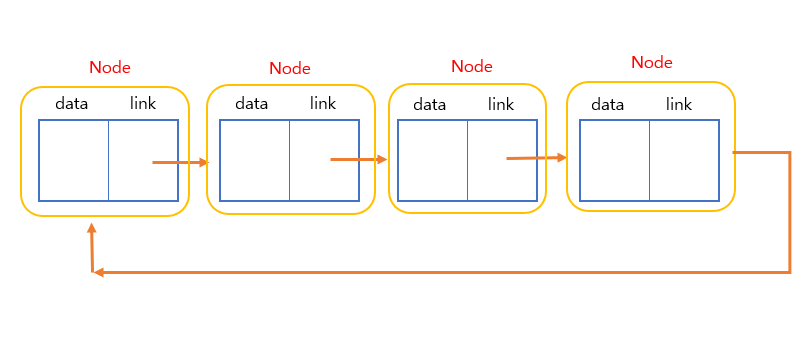
Circular Linked List (원형 연결 리스트)
: 마지막 노드가 다시 처음 노드를 가리킴.
-
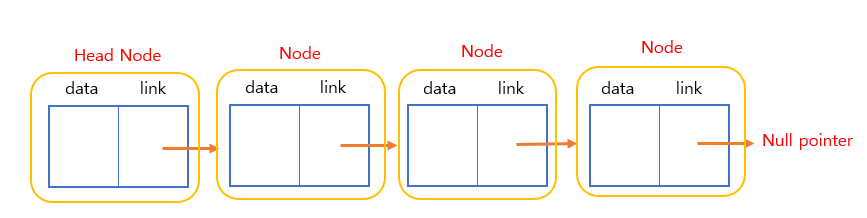
List with a header node
: 노드 맨앞에 head node 를 넣어 삽입, 삭제 등 연산에서 이점을 만듬.
-
Doubly Linked List (양방향 연결 리스트)
: 노드를 연결하는 link가 앞 뒤로 존재해서 앞 뒤 노드들 간의 관계를 바로 확인할 수 있다.

-
Doubly Circularly Linked List (원형 이중 연결 리스트)
: 이중 연결리스트의 구조에서 가장 처음과 마지막 노드가 서로 연결 되어있는 구조 (시작 위치를 알기 위해 연결리스트의 맨 앞에 NULL 노드를 추가)

🥸 그럼 JavaScript에서 Linked List 구현해보자
class Node {
constructor(data, next = null) {
//data와 next를 넣고 next의 디폴트는 null로 지정 왜냐하면 linkedlist의 tail(마지막은) null로 끝나기때문
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null; //처음에 데이터가 없다면 head는 null이다.
this.size = 0; //리스트의 크기를 찾기위해 사용 디폴트는 0으로 지정.
}
// Insert first node - 첫번째 삽입
insertFirst(data) {
this.head = new Node(data, this.head) //head에 새로운 node가 들어가고 기존의 해드는 next로 밀려난다.
this.size++;
}
// Insert last node - 마지막 삽입
insertLast(data) {
let node = new Node(data);
let current;
// if empty, make head
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.head;
while (current.next) { //this.head에 next가 있다면 즉, next가 null이아니라면
current = current.next; // current는 current.next가 되고
}
current.next = node; //결국 current.next가 새로넣은 node가 된다?
}
this.size++; //length 는 1증가
}
// Insert at index - 중간 삽입
insertAt(data, index) {
// If index is out of range ~ 인덱스가 size 범위 넘어서면 아무것도 리턴 하지 않는다.
if (index > 0 && index > this.size) {
return;
}
// If first index
if (index === 0) {
this.head = new Node(data, this.head) //즉, index 0에 삽입시 해당 노드를 넣고 다 한칸식 뒤로 미룸
this.size++
return;
}
const node = new Node(data);
let current, previous;
// Set current first
current = this.head;
let count = 0;
while (count < index) {
previous = current; //node before index
count++;
current = current.next; //node after index
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
this.size++;
}
// Get at index
getAt(index) {
let current = this.head;
let count = 0;
while (current) {
//해당 data의 값을 가져오기 위해 index와 값이 같아질때까지 loop한다.
if (count == index) {
console.log(current.data);
}
count++;
current = current.next;
}
return null;
}
// Remove at index
removeAt(index) {
if (index > 0 && index > this.size) {
return;
}
let current = this.head; //current는 현재 첫번째 노드임
let previous;
let count = 0;
// Remove first
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
} else {
//loop를 통해 해당 index의 연결고리를 끊는다.
while (count < index) {
count++;
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.size--;
}
// Clear list ~ 메모리자체에는 데이터가 남아있겠지만 보여주기 위해서 func 만들었다.
clearList() {
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
}
// Print list data ~ data값만 따로
printListData() {
let current = this.head; // 현재 노드를 나타냄
while (current) {
console.log(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
}
}
const linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.insertFirst(100);
linkedList.insertFirst(200);
linkedList.insertFirst(300);
linkedList.insertLast(400);
linkedList.insertAt(500, 1)
linkedList.removeAt(2)
linkedList.printListData();
linkedList.getAt(2);
//linkedList.clearList();
console.log(linkedList)Array
❓ Array(배열)란?
배열은 특정 크기만큼 연속된 메모리 공간에 데이터를 저장하는 자료구조이다. 만약 int형 데이터 3개를 저장할 수 있는 배열을 생각해보자. 그렇다면 아래의 그림처럼 연속된 공간에 메모리를 확보하여 데이터를 이곳에 저장할 수 있게 된다. 연속된 공간에 데이터들이 나열되어 있기 때문에 처음 주소만 알면 다른 위치도 쉽게 알 수 있을 것이다.
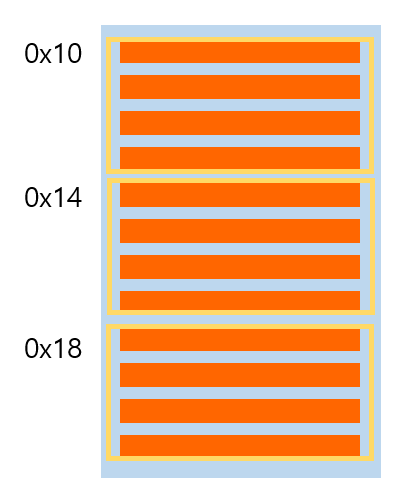
하지만 데이터를 빈번하게 데이터를 추가하거나 삭제할 때는 효율적이지 못하다. 만약 데이터를 중간에 추가하려고 한다. 그렇다면 추가하려고 하는 자리를 비우고 뒤에 있는 데이터를 한 칸씩 뒤로 밀어 야하기 때문이다. 따라서 데이터를 추가하거나 삭제할 때 배열은 좋은 선택이 되지 못한다.
🤔 Array vs Linked List
- Array는 연속된 메모리 공간에 존재하고 Linked List는 메모리 상에서 떨어져 있는 데이터들이 앞의 데이터와 뒤의 데이터를 기억하는 형태로 존재한다.
- Array에 저장되어 있는 데이터를 조회할 때는 O(1)로 가능하지만 Linked List는 O(N)이 소요된다.
- Array에 데이터 추가 및 삭제할 때는 O(N)이 소요되지만 Linked List는 O(1)로 가능하다.
- 추가적으로 Array는 컴파일 과정에서 메모리가 할당되는 정적 메모리 할당인 반면 Linked List는 런타임 환경에서 메모리가 할당되는 동적 메모리 할당이다.
- 또한 배열은 Stack 영역에 메모리 할당이 되고, Linked List는 Heap 영역에 할당이 된다.
