📝 파이썬 - 알고리즘
📌 알고리즘
✏ 선형검색
- 선형으로 나열되어 있는 데이터를 순차적으로 스캔하면서 원하는 값을 찾는다.
datas = [3,2,5,7,9,1,0,8,6,4]
print(f'datas : {datas}')
print(f'datas length : {len(datas)}')
searchDatas = int(input('찾으려는 숫자 입력 : '))
searchResultIdx = -1
n = 0
while True:
if n == len(datas):
searchResultIdx = -1
break
elif datas[n] == searchDatas:
searchResultIdx = n
break
n+= 1
print('searchResultIdx : {}'.format(searchResultIdx))
↓
datas : [3, 2, 5, 7, 9, 1, 0, 8, 6, 4]
datas length : 10
찾으려는 숫자 입력 : 9
searchResultIdx : 4
✏ 보초법
- 마지막 인덱스에 찾으려는 값을 추가해서 찾는 과정을 간략화 한다.
datas = [3,2,5,7,9,1,0,8,6,4]
print(f'datas : {datas}')
print(f'datas length : {len(datas)}')
searchData = int(input('찾으려는 숫자 입력 : '))
searchResultIdx = -1
datas.append(searchData)
n = 0
while True:
if datas[n] == searchData:
if n != len(datas) - 1:
searchResultIdx = n
break
n+= 1
print(datas)
print('searchResultIdx : {}'.format(searchResultIdx))
↓
datas : [3, 2, 5, 7, 9, 1, 0, 8, 6, 4]
datas length : 10
찾으려는 숫자 입력 : 10
[3, 2, 5, 7, 9, 1, 0, 8, 6, 4, 10]
searchResultIdx : -1
num = [4,7,10,2,4,7,0,1,7,3,9]
searchNum = 7
num.append(searchNum)
searchNumIdx = -1
n = 0
while True:
if num[n] == searchNum:
if n != len(num)-1:
searchNumIdx = n
break
n+=1
print('searchNumIdx : {}'.format(searchNumIdx))
↓
searchNumIdx : 1
searchResultIdxs = []
for i, v in enumerate(num):
if v == searchNum and i != len(num)-1:
searchResultIdxs.append(i)
print('searchResultIdxs : {}'.format(searchResultIdxs))
↓
searchResultIdxs : [1, 5, 8]
✏ 이진검색
- 정렬되어 있는 자료구조에서 중앙값과의 크고 작음을 이용해서 데이터를 검색한다.
datas = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]
print('datas : {}'.format(datas))
print('datas length: {}'.format(len(datas)))
searchData = int(input('search data : '))
searchResultIdx = -1
staIdx = 0
endIdx = len(datas) - 1
midIdx = (staIdx + endIdx) // 2
midVal = datas[midIdx]
print(f'midIdx : {midIdx}')
print(f'midVal : {midVal}')
while searchData <= datas[len(datas) - 1] and searchData >= datas[0]:
if searchData == datas[len(datas) - 1]:
searchResultIdx = len(datas) - 1
break
if searchData > midVal:
staIdx = midIdx
midIdx = (staIdx + endIdx) // 2
midVal = datas[midIdx]
print(f'midIdx : {midIdx}')
print(f'midVal : {midVal}')
elif searchData < midVal:
endIdx = midIdx
midIdx = (staIdx + endIdx) // 2
midVal = datas[midIdx]
print(f'midIdx : {midIdx}')
print(f'midVal : {midVal}')
elif searchData == midVal:
searchResultIdx = midIdx
break
print('searchResultIdx : {}'.format(searchResultIdx))
↓
datas : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
datas length: 11
search data : 11
midIdx : 5
midVal : 6
searchResultIdx : 10
- 이진검색 실습
리스트를 오름차순으로 정렬한 후 '7'을 검색하고 위치(인덱스)를 출력하자.
datas = [4,10,22,5,0,17,7,11,9,61,88]
print(f'datas : {datas}')
print(f'datas length : {len(datas)}')
datas.sort()
print(datas)
searchData = int(input('search data : '))
searchResultIdx = -1
startIdx = 0
endIdx = len(datas) - 1
lastIdx = len(datas) - 1
midIdx = (startIdx + endIdx) // 2
midVal = datas[midIdx]
print(f'midIdx : {midIdx}')
print(f'midVal : {midIdx}')
while searchData <= datas[lastIdx] and searchData >= datas[0]:
if searchData == datas[lastIdx]:
searchResultIdx = lastIdx
break
if searchData > midVal:
startIdx = midIdx
midIdx = (startIdx + endIdx) // 2
midVal = datas[midIdx]
elif searchData < midVal:
endIdx = midIdx
midIdx = (startIdx + endIdx) // 2
midVal = datas[midIdx]
elif searchData == midVal:
searchResultIdx = midIdx
break
if searchData not in datas :
searchResultIdx= -1
print('this data is not in datas')
break
print(f'searchResultIdx : {searchResultIdx}')
↓
datas : [4, 10, 22, 5, 0, 17, 7, 11, 9, 61, 88]
datas length : 11
[0, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 17, 22, 61, 88]
search data : 13
midIdx : 5
midVal : 5
this data is not in datas
searchResultIdx : -1
↓
search data : 11
midIdx : 5
midVal : 5
searchResultIdx : 6
✏ 순위
- 수의 크고 작음을 이용해서 수의 순서를 정하는 것을 순위라고 한다.
import random
rdNums = random.sample(range(50,101),20)
ranks = [0 for i in range(20)]
print(rdNums)
print(ranks)
for idx, num1 in enumerate(rdNums):
for num2 in rdNums:
if num1 < num2:
ranks[idx] += 1
for idx, num in enumerate(rdNums):
print(f'num : {num}, \t rank: {ranks[idx] + 1}')
↓
[60, 84, 53, 69, 72, 66, 55, 83, 95, 59, 63, 92, 56,
78, 75, 50, 98, 51, 94, 65]
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0]
num : 60, rank: 14
num : 84, rank: 5
num : 53, rank: 18
num : 69, rank: 10
num : 72, rank: 9
num : 66, rank: 11
num : 55, rank: 17
num : 83, rank: 6
num : 95, rank: 2
num : 59, rank: 15
num : 63, rank: 13
num : 92, rank: 4
num : 56, rank: 16
num : 78, rank: 7
num : 75, rank: 8
num : 50, rank: 20
num : 98, rank: 1
num : 51, rank: 19
num : 94, rank: 3
num : 65, rank: 12
- 순위 실습
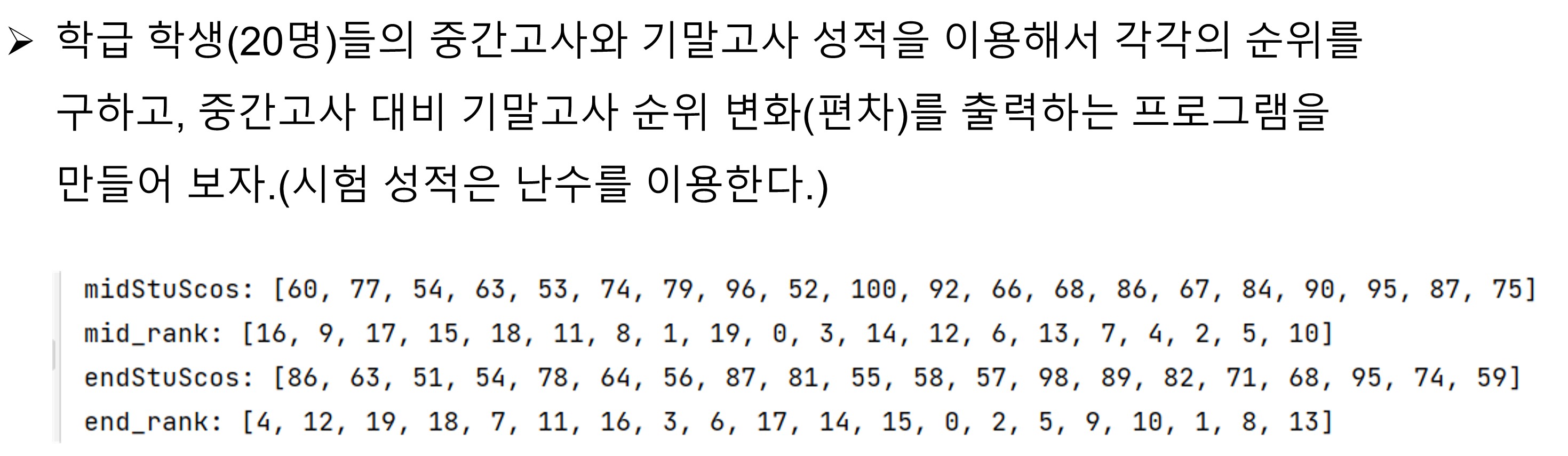
class RankMd:
def __init__(self, mss, ess):
self.midStuScos = mss
self.endStuScos = ess
self.midRanks = [0 for i in range(len(mss))]
self.endRanks = [0 for i in range(len(mss))]
self.rankDiviation = []
def setRank(self,ss, rs):
for idx, sco1 in enumerate(ss):
for sco2 in ss:
if sco1 < sco2:
rs[idx] += 1
def setMidRank(self):
self.setRank(self.midStuScos, self.midRanks)
def setEndRank(self):
self.setRank(self.endStuScos, self.endRanks)
def getMidRank(self):
return self.midRanks
def getEndRank(self):
return self.endRanks
def printRankDeviation(self):
for idx, mRank in enumerate(self.midRanks):
deviation = mRank - self.endRanks[idx]
self.rankDiviation.append(deviation)
if deviation > 0:
deviation = '↑' + str(abs(deviation))
elif deviation == 0:
deviation = '=' + str(abs(deviation))
else:
deviation = '↓' + str(abs(deviation))
print(f'mid_rank: {mRank} \t end_rank : {self.endRanks[idx]} \t Diviation : {deviation}')
import day23_04 as rk
import random
midStuScos = random.sample(range(50, 101), 20)
endStuScos = random.sample(range(50, 101), 20)
rd = rk.RankMd(midStuScos,endStuScos)
rd.setMidRank()
print(f'midStuScores : {midStuScos}')
print(f'getMidRank : {rd.getMidRank()}')
rd.setEndRank()
print(f'midStuScores : {endStuScos}')
print(f'getMidRank : {rd.getEndRank()}')
rd.printRankDeviation()
↓
midStuScores : [91, 50, 87, 70, 54, 58, 62, 83, 59, 80,
79, 75, 55, 67, 99, 95, 85, 94, 92, 66]
getMidRank : [4, 19, 5, 11, 18, 16, 14, 7, 15, 8, 9,
10, 17, 12, 0, 1, 6, 2, 3, 13]
midStuScores : [81, 76, 60, 59, 97, 78, 73, 72, 87, 51,
92, 62, 99, 91, 66, 95, 96, 79, 83, 80]
getMidRank : [8, 12, 17, 18, 1, 11, 13, 14, 6, 19, 4,
16, 0, 5, 15, 3, 2, 10, 7, 9]
mid_rank: 4 end_rank : 8 Diviation : ↓4
mid_rank: 19 end_rank : 12 Diviation : ↑7
mid_rank: 5 end_rank : 17 Diviation : ↓12
mid_rank: 11 end_rank : 18 Diviation : ↓7
mid_rank: 18 end_rank : 1 Diviation : ↑17
mid_rank: 16 end_rank : 11 Diviation : ↑5
mid_rank: 14 end_rank : 13 Diviation : ↑1
mid_rank: 7 end_rank : 14 Diviation : ↓7
mid_rank: 15 end_rank : 6 Diviation : ↑9
mid_rank: 8 end_rank : 19 Diviation : ↓11
mid_rank: 9 end_rank : 4 Diviation : ↑5
mid_rank: 10 end_rank : 16 Diviation : ↓6
mid_rank: 17 end_rank : 0 Diviation : ↑17
mid_rank: 12 end_rank : 5 Diviation : ↑7
mid_rank: 0 end_rank : 15 Diviation : ↓15
mid_rank: 1 end_rank : 3 Diviation : ↓2
mid_rank: 6 end_rank : 2 Diviation : ↑4
mid_rank: 2 end_rank : 10 Diviation : ↓8
mid_rank: 3 end_rank : 7 Diviation : ↓4
mid_rank: 13 end_rank : 9 Diviation : ↑4
✏ 버블정렬
- 처음부터 끝까지 인접하는 인덱스의 값을 순차적으로 비교하면서 큰 숫자를 가장 끝으로 옮기는 알고리즘이다.
nums = [10,2,7,21,0]
print(f'not sorted nums : {nums}')
length = len(nums) -1
for i in range(length):
for j in range(length-i):
if nums[j] > nums[j+1] :
nums[j], nums[j+1] = nums[j+1], nums[j]
print(nums)
print(f'sorted nums : {nums}')
↓
not sorted nums : [10, 2, 7, 21, 0]
[2, 10, 7, 21, 0]
[2, 7, 10, 21, 0]
[2, 7, 10, 21, 0]
[2, 7, 10, 0, 21]
[2, 7, 10, 0, 21]
[2, 7, 10, 0, 21]
[2, 7, 0, 10, 21]
[2, 7, 0, 10, 21]
[2, 0, 7, 10, 21]
[0, 2, 7, 10, 21]
sorted nums : [0, 2, 7, 10, 21]
- 버블정렬 실습

import copy
def bubbleSort(ns, deepCopy = True):
if deepCopy :
cns = copy.copy(ns)
else :
cns = ns
length = len(cns) - 1
for i in range(length):
for j in range(length-i):
if cns[j] > cns[j+1]:
cns[j], cns[j + 1] = cns[j + 1], cns[j]
return cns
import bubbleMod as bm
import random as rd
students = []
for i in range(20):
students.append(rd.randint(170,185))
print(students)
sortedStudents = bm.bubbleSort(students)
print(students)
print(sortedStudents)
↓
[175, 175, 176, 174, 182, 173, 173, 178, 178, 177, 184,
177, 176, 176, 183, 175, 179, 183, 183, 180]
[173, 173, 174, 175, 175, 175, 176, 176, 176, 177, 177,
178, 178, 179, 180, 182, 183, 183, 183, 184]
✏ 삽입정렬
- 정렬되어 있는 자료 배열과 비교해서, 정렬 위치를 찾는다.
nums = [5,10,2,1,0]
for i1 in range(1, len(nums)):
i2 = i1 -1
cNum = nums[i1]
while nums[i2] > cNum and i2 >= 0:
nums[i2 + 1] = nums[i2]
i2 -= 1
nums[i2+1] = cNum
print(nums)
↓
[5, 10, 2, 1, 0]
[2, 5, 10, 1, 0]
[1, 2, 5, 10, 0]
[0, 1, 2, 5, 10]
- 삽입정렬 실습

import copy
def getInsert(ns, deepCopy = True, asc=False, desc=False):
if deepCopy :
cns = copy.copy(ns)
else :
cms = ns
if asc==True:
for i1 in range(1, len(cns)):
i2 = i1 - 1
cNum = cns[i1]
while cns[i2] > cNum and i2 >= 0:
cns[i2+1] = cns[i2]
i2 -= 1
cns[i2+1] = cNum
elif desc==True:
for i1 in range(1, len(cns)):
i2 = i1 - 1
cNum = cns[i1]
while cns[i2] < cNum and i2 >= 0:
cns[i2 + 1] = cns[i2]
i2 -= 1
cns[i2 + 1] = cNum
minNum = min(cns)
maxNum = max(cns)
print(f'min number : {minNum}')
print(f'max number : {maxNum}')
return cns
import insertMod as im
import random as rd
nums = []
for i in range(100):
nums.append(rd.randint(1, 1000))
print(nums)
resultAsc = im.getInsert(nums, asc=True)
resultDesc = im.getInsert(nums, desc=True)
print(f'sorted number by ASC : {resultAsc}')
print(f'sorted number by DESC : {resultDesc}')
print(f'min number : {min(resultAsc)}')
print(f'max number : {max(resultAsc)}')
↓
[42, 57, 642, 199, 375, 931, 922, 797, 888, 495, 990,
535, 921, 626, 988, 120, 552, 166, 350, 533, 351, 970,
736, 497, 8, 456, 189, 183, 804, 999, 974, 937, 58,
584, 687, 616, 811, 924, 139, 354, 118, 241, 811, 849,
923, 316, 479, 93, 655, 5, 918, 437, 359, 748, 620, 13,
201, 352, 21, 34, 156, 973, 126, 820, 125, 473, 320,
791, 304, 124, 871, 734, 267, 276, 999, 821, 475, 707,
639, 706, 169, 677, 924, 159, 737, 471, 586, 344, 284,
140, 324, 526, 388, 243, 964, 431, 755, 680, 776, 345]
sorted number by ASC : [5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 42, 57, 58,
93, 118, 120, 124, 125, 126, 139, 140, 156, 159, 166,
169, 183, 189, 199, 201, 241, 243, 267, 276, 284, 304,
316, 320, 324, 344, 345, 350, 351, 352, 354, 359, 375,
388, 431, 437, 456, 471, 473, 475, 479, 495, 497, 526,
533, 535, 552, 584, 586, 616, 620, 626, 639, 642, 655,
677, 680, 687, 706, 707, 734, 736, 737, 748, 755, 776,
791, 797, 804, 811, 811, 820, 821, 849, 871, 888, 918,
921, 922, 923, 924, 924, 931, 937, 964, 970, 973, 974,
988, 990, 999, 999]
sorted number by DESC : [999, 999, 990, 988, 974, 973,
970, 964, 937, 931, 924, 924, 923, 922, 921, 918, 888,
871, 849, 821, 820, 811, 811, 804, 797, 791, 776, 755,
748, 737, 736, 734, 707, 706, 687, 680, 677, 655, 642,
639, 626, 620, 616, 586, 584, 552, 535, 533, 526, 497,
495, 479, 475, 473, 471, 456, 437, 431, 388, 375, 359,
354, 352, 351, 350, 345, 344, 324, 320, 316, 304, 284,
276, 267, 243, 241, 201, 199, 189, 183, 169, 166, 159,
156, 140, 139, 126, 125, 124, 120, 118, 93, 58, 57, 42,
34, 21, 13, 8, 5]
min number : 5
max number : 999
✏ 선택정렬
- 주어진 리스트 중에 최소값을 찾아, 그 값을 맨 앞에 위치한 값과 교체하는 방식으로 자료를 정렬하는 알고리즘이다.
nums = [4,2,5,1,3]
print(nums)
for i in range(len(nums) - 1):
minIdx = i
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)):
if nums[minIdx] > nums[j]:
minIdx = j
# tempNum = nums[i]
# nums[i] = nums[minIdx]
# nums[minIdx] = tempNum
nums[i],nums[minIdx] = nums[minIdx],nums[i]
print(nums)
↓
[4, 2, 5, 1, 3]
[1, 2, 5, 4, 3]
[1, 2, 5, 4, 3]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
- 선택정렬 실습

import random
scores = random.sample(range(50, 101),20)
print(f'scores : {scores}')
def printScores(ns,asc=True):
if asc:
for i in range(len(ns)-1):
minIdx = i
for j in range(i+1,len(ns)):
if ns[minIdx] > ns[j]:
minIdx = j
ns[i], ns[minIdx] = ns[minIdx], ns[i]
else:
for i in range(len(ns) - 1):
minIdx = i
for j in range(i + 1, len(ns)):
if ns[minIdx] < ns[j]:
minIdx = j
ns[i], ns[minIdx] = ns[minIdx], ns[i]
return ns
printAsc = printScores(scores)
print(f'scores by ASC : {printAsc}')
printDesc = printScores(scores, asc=False)
print(f'scores by Desc : {printDesc}')
↓
scores : [66, 71, 85, 53, 59, 78, 88, 82, 90, 68, 86,
76, 81, 69, 92, 50, 67, 94, 56, 75]
scores by ASC : [50, 53, 56, 59, 66, 67, 68, 69, 71,
75, 76, 78, 81, 82, 85, 86, 88, 90, 92, 94]
scores by Desc : [94, 92, 90, 88, 86, 85, 82, 81, 78,
76, 75, 71, 69, 68, 67, 66, 59, 56, 53, 50]
✏ 최댓값
class Maxalgorithm:
def __init__(self, ns):
self.nums = ns
self.maxNum = 0
def getMaxNum(self):
self.maxNum = self.nums[0]
for n in self.nums:
if self.maxNum < n:
self.maxNum = n
return self.maxNum
nums = [-2,-4,5,7,10,0,8,20,-11]
ma = Maxalgorithm(nums)
result = ma.getMaxNum()
print(nums)
print('maxNum : {}'.format(result))
↓
[-2, -4, 5, 7, 10, 0, 8, 20, -11]
maxNum : 20
class MaxAlgorithm :
def __init__(self, ns):
self.chars = ns
self.maxChar = 0
def getMaxChar(self):
self.maxChar = self.chars[0]
for c in self.chars:
if ord(self.maxChar) < ord(c):
self.maxChar = c
return self.maxChar
chars = ['c','x','Q','A','e','P','p']
ma = MaxAlgorithm(chars)
print('chars : {}'.format(chars))
print('maxChar : {}'.format(ma.getMaxChar()))
↓
char : ['c', 'x', 'Q', 'A', 'e', 'P', 'p']
maxChar : x
✏ 최솟값
class MinAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, ns):
self.nums = ns
self.minNum = 0
def getMinNum(self):
self.minNum = self.nums[0]
for n in self.nums:
if self.minNum > n:
self.minNum = n
return self.minNum
nums = [-2,-4,5,7,10,-100,8,20,-11]
ma = MinAlgorithm(nums)
minNum = ma.getMinNum()
print(f'nums : {nums}')
print(f'minNum : {minNum}')
↓
nums : [-2, -4, 5, 7, 10, -100, 8, 20, -11]
minNum : -100
- 최솟값 실습
- 리스트에서 아스키코드가 가장 작은 값을 찾는 알고리즘을 만들어보자.
class MinChar:
def __init__(self, cs):
self.chars = cs
self.minChar = 0
def getMinChar(self):
self.minChar = self.chars[0]
for c in self.chars:
if ord(self.minChar) > ord(c):
self.minChar = c
return self.minChar
chars = ['c','x','Q','A','e','P','p']
mc = MinChar(chars)
minChar = mc.getMinChar()
print(f'chars : {chars}')
print(f'minChar : {minChar}')
↓
chars : ['c', 'x', 'Q', 'A', 'e', 'P', 'p']
minChar : A
✏ 최빈값
- 데이터에서 빈도수가 가장 많은 데이터를 최빈값이라고 한다.
class MAxAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, ns):
self.nums = ns
self.maxNum = 0
self.maxNumIdx = 0
def setMaxIdxAndNum(self):
self.maxNum = self.nums[0]
self.maxNumIdx = 0
for i, n in enumerate(self.nums):
if self.maxNum < n :
self.maxNum = n
self.maxNumIdx = i
def getMaxNum(self):
return self.maxNum
def getMaxNumIdx(self):
return self.maxNumIdx
nums = [1,3,7,6,7,7,7,12,12,17]
ma = MAxAlgorithm(nums)
ma.setMaxIdxAndNum()
maxNum = ma.getMaxNum()
print(f'maxNum : {maxNum}')
indexes = [0 for i in range(maxNum + 1)]
print(f'indexes length : {len(indexes)}')
for n in nums:
indexes[n] = indexes[n] + 1
print(f'indexes : {indexes}')
maxAlo = MAxAlgorithm(indexes)
maxAlo.setMaxIdxAndNum()
maxNum = maxAlo.getMaxNum()
maxNumIdx = maxAlo.getMaxNumIdx()
print(f'maxNum : {maxNum}')
print(f'maxNumIdx : {maxNumIdx}')
print(f'즉, {maxNumIdx}의 빈도수가 {maxNum}로 가장 높다.')
↓
maxNum : 17
indexes length : 18
indexes : [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
maxNum : 4
maxNumIdx : 7
즉, 7의 빈도수가 4로 가장 높다.
class MaxAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, ns):
self.nums = ns
self.MaxNum = 0
self.MaxNumIdx = 0
def setMaxNumIdxAndNum(self):
self.MaxNum = self.nums[0]
self.MaxNumIdx = 0
for i, n in enumerate(self.nums):
if self.MaxNum < n :
self.MaxNum = n
self.MaxNumIdx = i
def getMaxNum(self):
return self.MaxNum
def getMaxNumIdx(self):
return self.MaxNumIdx
import random as rd
import lowestMod as lm
scores = []
for i in range(100):
scores.append(rd.randint(14, 20)*5)
print(f'scores : {scores}')
maxAlo = lm.MaxAlgorithm(scores)
maxAlo.setMaxNumIdxAndNum()
maxNum = maxAlo.getMaxNum()
print(f'maxNum : {maxNum}')
indexes = [0 for i in range(len(scores)+1)]
for n in scores:
indexes[n] = indexes[n] + 1
n = 1
while True :
maxAlo = lm.MaxAlgorithm(indexes)
maxAlo.setMaxNumIdxAndNum()
maxNum = maxAlo.getMaxNum()
maxNumIdx = maxAlo.getMaxNumIdx()
if maxNum == 0:
break
print(f'{n}. {maxNumIdx} 빈도수 : {maxNum} \t', end='')
print('+' * maxNum)
indexes[maxNumIdx] = 0
n += 1
↓
scores : [100, 90, 90, 85, 100, 85, 80, 95, 100, 90,
75, 80, 100, 100, 95, 75, 75, 100, 100, 80, 100, 75,
70, 85, 80, 70, 75, 75, 85, 80, 90, 75, 75, 75, 75,
100, 75, 70, 90, 75, 90, 100, 95, 85, 90, 85, 75, 75,
95, 70, 90, 80, 70, 90, 70, 70, 100, 95, 70, 70, 85,
80, 100, 75, 75, 75, 85, 70, 85, 100, 75, 70, 75, 100,
90, 70, 95, 85, 85, 80, 75, 100, 70, 90, 85, 80, 70,
95, 95, 90, 80, 85, 95, 80, 80, 95, 95, 70, 85, 85]
maxNum : 100
1. 75 빈도수 : 20 ++++++++++++++++++++
2. 70 빈도수 : 15 +++++++++++++++
3. 85 빈도수 : 15 +++++++++++++++
4. 100 빈도수 : 15 +++++++++++++++
5. 80 빈도수 : 12 ++++++++++++
6. 90 빈도수 : 12 ++++++++++++
7. 95 빈도수 : 11 +++++++++++
✏ 근삿값
- 특정 값(참값)에 가장 가까운 값을 근삿값이라고 한다.
import random
nums = random.sample(range(0, 50), 20)
print(f'nums : {nums}')
inputNum = int(input('input number: '))
print(f'inputNum : {inputNum}')
nearNum = 0
minNum = 50
for n in nums:
absNum = abs(n - inputNum)
if absNum < minNum:
minNum = absNum
nearNum = n
print(f'nearNum: {nearNum}')
↓
nums : [37, 25, 39, 5, 19, 13, 40, 2, 10, 34, 28, 31, 38, 12, 43, 11, 0, 35, 23, 30]
input number: 44
inputNum : 44
nearNum: 43
def getNearNum(an):
baseScores = [95, 85, 65, 55]
nearNum = 0
minNum = 100
for n in baseScores:
absNum = abs(n - an)
if absNum < minNum:
minNum = absNum
nearNum = n
if nearNum == 95 :
return 'A'
elif nearNum == 85 :
return 'B'
elif nearNum == 75 :
return 'C'
elif nearNum == 65 :
return 'D'
elif nearNum <= 55 :
return 'F'
import near
korScore = int(input('input kor score : '))
engScore = int(input('input eng score : '))
matScore = int(input('input mat score : '))
sciScore = int(input('input sci score : '))
hisScore = int(input('input his score : '))
scores = [korScore,engScore,matScore,sciScore,hisScore]
totalScore = 0
avgScore = 0
for n in scores:
totalScore += n
avgScore = totalScore / len(scores)
print(f'totalScore : {totalScore}')
print(f'avgScore : {avgScore}')
grade = near.getNearNum(avgScore)
print(f'grade : {grade}')
↓
input kor score : 77
input eng score : 88
input mat score : 97
input sci score : 88
input his score : 79
totalScore : 429
avgScore : 85.8
grade : B
✏ 평균
- 여러 수나 양의 중간값을 갖는 수를 평균이라고 한다.
import random
nums = random.sample(range(0, 100), 10)
print(nums)
total = 0
for n in nums:
total += n
avgNum = total / len(nums)
print(avgNum)
↓
[71, 35, 15, 83, 97, 1, 2, 96, 39, 20]
45.9
- 평균 실습
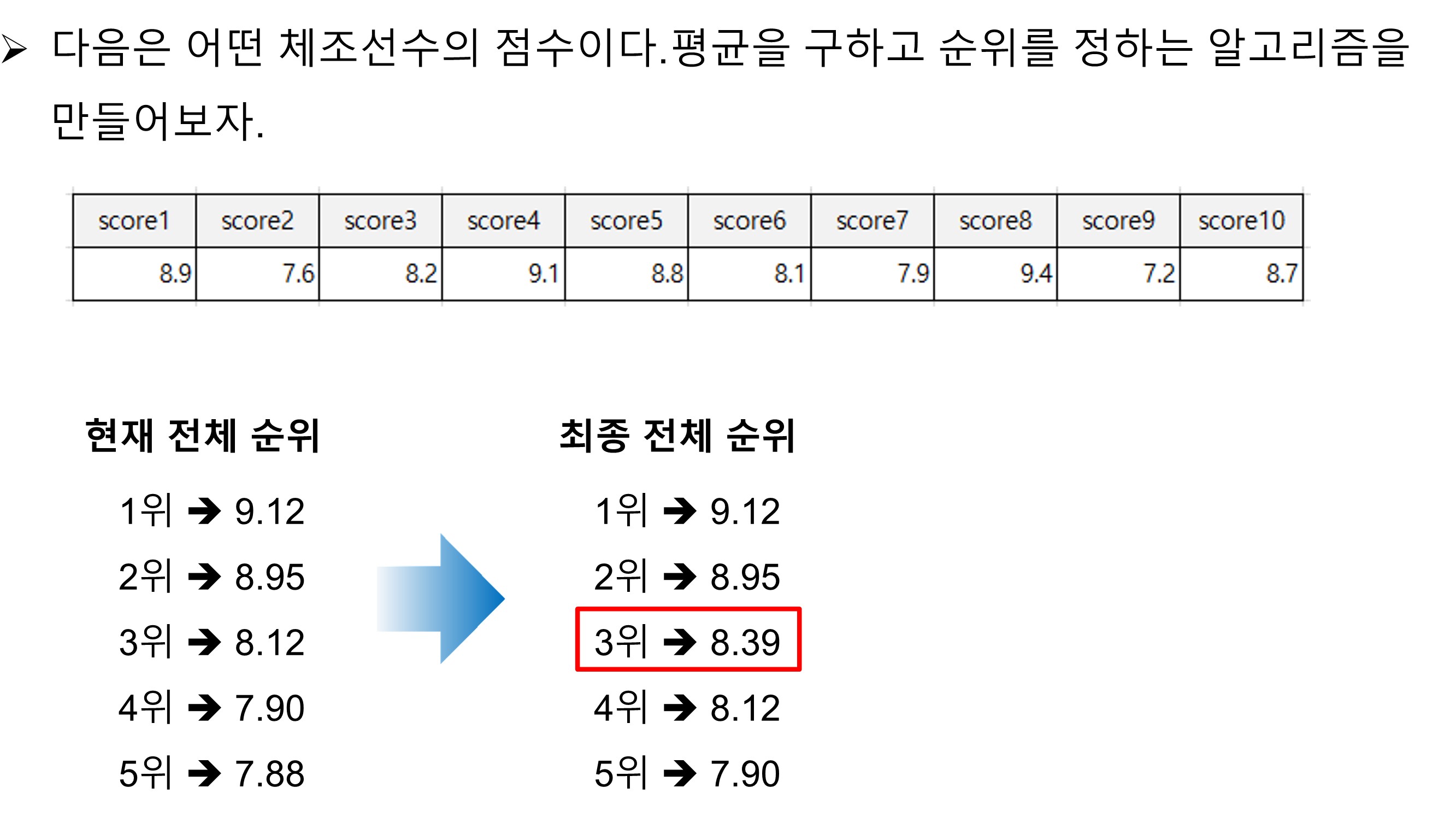
class Top5Players :
def __init__(self, cs, ns):
self.currentScores = cs
self.newScore = ns
def setAlignScore(self):
nearIdx = 0
nearScore = 0
minNum = 10.0
for i, s in enumerate(self.currentScores):
absNum = abs(self.newScore - s)
if absNum < minNum:
minNum = absNum
nearIdx = i
nearScore = s
if self.newScore >= self.currentScores[nearIdx]:
for i in range(len(self.currentScores)-1, nearIdx, -1):
self.currentScores[i] = self.currentScores[i-1]
self.currentScores[nearIdx] = self.newScore
else:
for i in range(len(self.currentScores)-1, nearIdx+1, -1):
self.currentScores[i] = self.currentScores[i-1]
self.currentScores[nearIdx] = self.newScore
def getFinalTo5Players(self):
return self.currentScores
import random
import avgNear as nr
scores = [8.9, 7.6, 8.2, 9.1, 8.8, 8.1, 7.9, 9.4, 7.2, 8.7]
total = 0
top5PlayerScores = [9.12, 8.95, 8.12, 7.9, 7.88]
for n in scores:
total += n
print(total)
avgScore = round(total / len(scores),2)
print(avgScore)
tp = nr.Top5Players(top5PlayerScores, avgScore)
tp.setAlignScore()
top5PlayerScores = tp.getFinalTo5Players()
print(f'top5PlayerScores : {top5PlayerScores}')
↓
83.9
8.39
top5PlayerScores : [9.12, 8.95, 8.39, 8.12, 7.9]
✏ 재귀 알고리즘
- 나 자신을 다시 호출하는 것을 재귀라고 한다.
def recusion(num):
if num > 0:
print('*' * num)
return recusion(num-1)
else:
return 1
recusion(10)
↓
**********
*********
********
*******
******
*****
****
***
**
*
def factorial(num):
if num > 0:
return num * factorial(num-1)
else:
return 1
print(f'factorial(10) : {factorial(10)}')
↓
factorial(10) : 3628800
- 재귀 알고리즘 실습

def greatestCommonDevide(n1,n2):
maxNum = 0
for i in range(1, (n1+1)):
if n1 % i == 0and n2 % i == 0:
maxNum = i
return maxNum
print(f'maxNum : {greatestCommonDevide(82,32)}')
print(f'maxNum : {greatestCommonDevide(96,40)}')
↓
maxNum : 2
maxNum : 8
def gcd(n1, n2):
if n1 % n2 == 0:
return n2
else:
return gcd(n2, n1 % n2)
print(f'maxNum : {gcd(82,32)}')
print(f'maxNum : {gcd(96,40)}')
↓
maxNum : 2
maxNum : 8
✏ 하노이의 탑
- 퍼즐 게임의 일종으로 세 개의 기둥을 이용해서 원판을 다른 기둥으로 옮기면 되고, 제약 조건은 다음과 같다.
- 한 번에 한개의 원판만 옮길 수 있다.
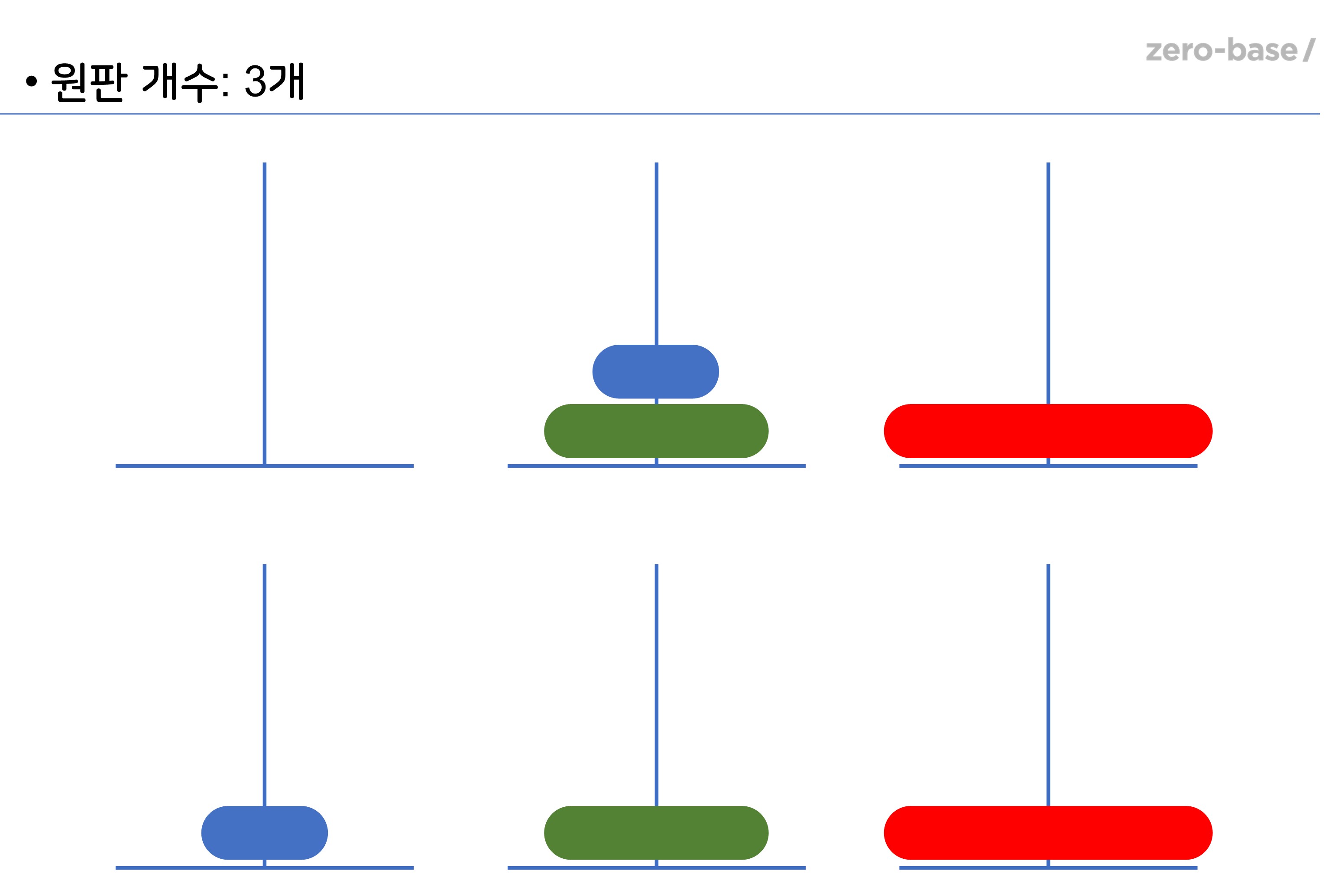
# 원판 개수, 출발 기둥, 도착 기둥, 경유 기둥
def moveDisc(discCnt, fromBar, toBar, viaBar):
if discCnt == 1:
print(f'{discCnt}disc를 {fromBar}에서 {toBar}(으)로 이동!')
else:
# (discCnt - 1)개들을 경유 기둥으로 이동
moveDisc(discCnt - 1, fromBar, viaBar, toBar)
# discCnt를 목적 기둥으로 이동
print(f'{discCnt}disc를 {fromBar}에서 {toBar}(으)로 이동!')
# (discCnt-1)개들을 도착 기둥으로 이동
moveDisc(discCnt-1, viaBar, toBar, fromBar)
moveDisc(3,1,3,2)
↓
1disc를 1에서 3(으)로 이동!
2disc를 1에서 2(으)로 이동!
1disc를 3에서 2(으)로 이동!
3disc를 1에서 3(으)로 이동!
1disc를 2에서 1(으)로 이동!
2disc를 2에서 3(으)로 이동!
1disc를 1에서 3(으)로 이동!
✏ 병합정렬
- 자료구조를 분할하고 각각의 분할된 자료구조를 정렬한 후 다시 병합하여 정렬한다.
def mSort(ns):
if len(ns) < 2:
return ns
midIdx = len(ns) // 2
leftNums = mSort(ns[0:midIdx])
rightNums = mSort(ns[midIdx:len(ns)])
mergeNums = []
leftIdx = 0; rightIdx = 0
while leftIdx < len(leftNums) and rightIdx < len(rightNums):
if leftNums[leftIdx] < rightNums[rightIdx]:
mergeNums.append(leftNums[leftIdx])
leftIdx += 1
else:
mergeNums.append(rightNums[rightIdx])
rightIdx += 1
mergeNums = mergeNums + leftNums[leftIdx:]
mergeNums = mergeNums + rightNums[rightIdx:]
return mergeNums
nums = [8, 1, 4, 3, 2, 5, 10, 6]
print(f'mSort : {mSort(nums)}')
↓
mSort : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10]
- 병합정렬 실습

def mSort(ns,asc=True):
if len(ns) < 2 :
return ns
midIdx = len(ns) // 2
leftNums = mSort(ns[0:midIdx], asc=asc)
rightNums = mSort(ns[midIdx: len(ns)], asc=asc)
mergeNums = []
leftIdx = 0; rightIdx = 0
while leftIdx < len(leftNums) and rightIdx < len(rightNums):
if asc:
if leftNums[leftIdx] < rightNums[rightIdx]:
mergeNums.append(leftNums[leftIdx])
leftIdx += 1
else:
mergeNums.append(rightNums[rightIdx])
rightIdx += 1
else:
if leftNums[leftIdx] > rightNums[rightIdx]:
mergeNums.append(leftNums[leftIdx])
leftIdx += 1
else:
mergeNums.append(rightNums[rightIdx])
rightIdx += 1
mergeNums += leftNums[leftIdx:]
mergeNums += rightNums[rightIdx:]
return mergeNums
↓
not sorted rNums : [14, 56, 50, 59, 33, 65, 93, 13, 6, 77]
sorted rNums : [6, 13, 14, 33, 50, 56, 59, 65, 77, 93]
sorted rNums : [93, 77, 65, 59, 56, 50, 33, 14, 13, 6]
import random
def mSort(ns, sort=True):
if len(ns) < 2:
return ns
midIdx = len(ns) // 2
leftNums = mSort(ns[0:midIdx])
rightNums = mSort(ns[midIdx:len(ns)])
leftIdx = 0; rightIdx = 0
mergeNums = []
while leftIdx < len(leftNums) and rightIdx < len(rightNums):
if leftNums[leftIdx] < rightNums[rightIdx]:
mergeNums.append(leftNums[leftIdx])
leftIdx += 1
else:
mergeNums.append(rightNums[rightIdx])
rightIdx += 1
mergeNums += leftNums[leftIdx:]
mergeNums += rightNums[rightIdx:]
if sort:
return mergeNums
else:
mergeNums.sort(reverse=True)
return mergeNums
nums = random.sample(range(1, 101), 10)
print(f'nums : {nums}')
print(f'mSort : {mSort(nums)}')
print(f'mSort : {mSort(nums, sort=False)}')
↓
not sorted nums : [40, 24, 12, 83, 79, 59, 20, 68, 98, 5]
mSort by ASC : [5, 12, 20, 24, 40, 59, 68, 79, 83, 98]
mSort by DESC : [98, 83, 79, 68, 59, 40, 24, 20, 12, 5]
✏ 퀵정렬
- 기준 값보다 작은 값과 큰 값으로 분리한 후 다시 합친다.
def qSort(ns):
if len(ns) < 2:
return ns
midIdx = len(ns) // 2
midVal = ns[midIdx]
smallNums = []; sameNums = []; bigNums = []
for n in ns :
if n < midVal:
smallNums.append(n)
elif n == midVal:
sameNums.append(n)
else:
bigNums.append(n)
return qSort(smallNums) + sameNums + qSort(bigNums)
nums = [8, 1, 4, 3, 2, 5, 4, 10, 6, 8]
print(f'not sorted nums : {nums}')
print(f'qSort(nums) : {qSort(nums)}')
↓
not sorted nums : [8, 1, 4, 3, 2, 5, 4, 10, 6, 8]
qSort(nums) : [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 8, 10]
- 퀵 정렬 실습

import random as rd
def qSort(ns, asc=True):
if len(ns) < 2:
return ns
midIdx = len(ns) // 2
midVal = ns[midIdx]
smallNums = []; sameNums = []; bigNums = []
for n in ns:
if n < midVal:
smallNums.append(n)
elif n == midVal:
sameNums.append(n)
else:
bigNums.append(n)
if asc:
return qSort(smallNums, asc=asc) + sameNums + qSort(bigNums,asc=asc)
else:
return qSort(bigNums, asc=asc) + sameNums + qSort(smallNums, asc=asc)
nums = rd.sample(range(1, 101), 10)
print(f'not sorted nums : {nums}')
print(f'sorted nums by ASC : {qSort(nums)}')
print(f'sorted nums by DESC : {qSort(nums, asc=False)}')
↓
not sorted nums : [5, 96, 21, 94, 60, 85, 49, 37, 1, 79]
sorted nums by ASC : [1, 5, 21, 37, 49, 60, 79, 85, 94, 96]
sorted nums by DESC : [96, 94, 85, 79, 60, 49, 37, 21, 5, 1]










