📝 자료구조
📌 연습문제
✏ 리스트
- 1부터 사용자가 입력한 숫자까지의 약수와 소수를 리스트에 각각 저장하고, 이것을 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자.
inputN = int(input('1보다 큰 정수 입력 : '))
listA = []
listB = []
for i in range(1, inputN + 1):
if inputN % i == 0:
listA.append(i)
for j in range(2, inputN + 1):
if 1 not in listB:
listB.append(1)
if j % 2 == 0:
continue
else :
listB.append(j)
print('{}의 약수 : {}'.format(inputN, listA))
print('{}의 소수 : {}'.format(inputN, listB))
↓
1보다 큰 정수 입력 : 30
30의 약수 : [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30]
30의 소수 : [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29]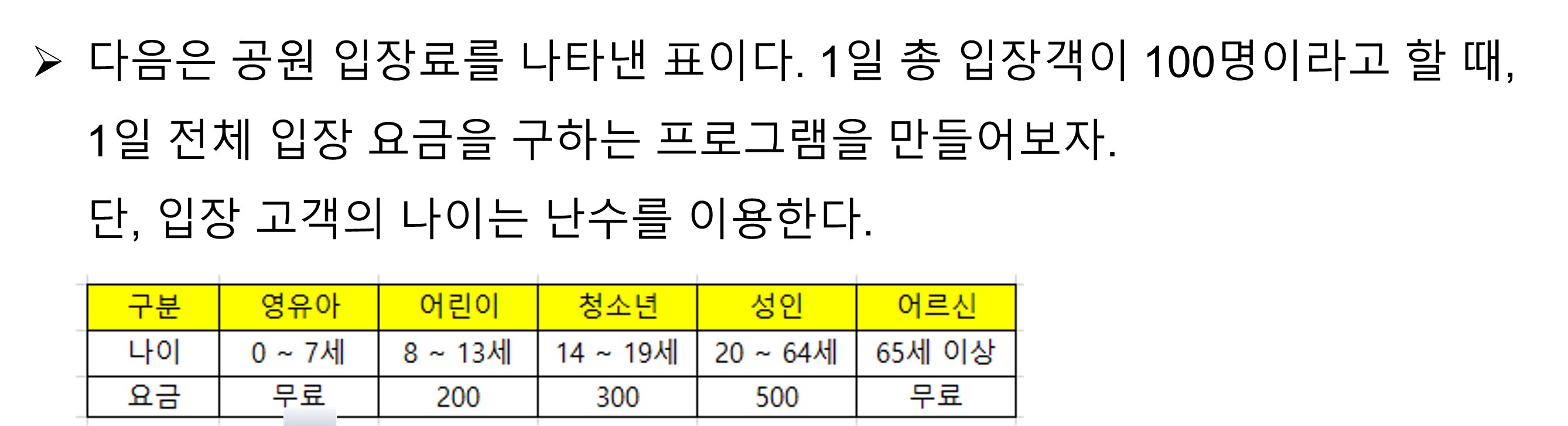
import random as rd
visitors = []
for n in range(100):
visitors.append(rd.randint(1, 100))
print(visitors)
group1, group2, group3, group4, group5 = 0,0,0,0,0
for age in visitors:
if age >= 0 and age <= 7:
group1 += 1
elif age >= 8 and age <= 13:
group2 += 1
elif age >= 14 and age <= 19:
group3 += 1
elif age >= 20 and age <= 64:
group4 += 1
else:
group5 += 1
group1Price = group1 * 0
group2Price = group2 * 200
group3Price = group3 * 300
group4Price = group4 * 500
group5Price = group5 * 0
sumPrice = group1Price+group2Price+group3Price+group4Price+group5Price
print('-'*30)
print('영유아 : {}명, 금액 : {}원'.format(group1, group1Price))
print('어린이 : {}명, 금액 : {}원'.format(group2, group2Price))
print('청소년 : {}명, 금액 : {}원'.format(group3, group3Price))
print('성인 : {}명, 금액 : {}원'.format(group4, group4Price))
print('노인 : {}명, 금액 : {}원'.format(group5, group5Price))
print('-'*30)
print('1일 요금 총합계 : {}원'.format(sumPrice))
print('-'*30)
↓
[4, 79, 39, 33, 77, 100, 66, 97, 54, 50, 78, 13, 60,
15, 74, 18, 75, 16, 83, 81, 19, 76, 100, 57, 86, 61,
57, 98, 82, 4, 12, 84, 21, 11, 46, 9, 61, 76, 59, 28,
68, 29, 21, 43, 36, 28, 44, 37, 24, 36, 83, 36, 59, 8,
15, 34, 80, 93, 4, 29, 95, 9, 64, 31, 40, 22, 32, 9,
87, 61, 27, 25, 50, 10, 47, 89, 21, 93, 60, 80, 13, 47,
77, 19, 65, 83, 100, 32, 5, 40, 51, 28, 92, 91, 49, 63,
42, 73, 85, 19]
------------------------------
영유아 : 4명, 금액 : 0원
어린이 : 9명, 금액 : 1800원
청소년 : 7명, 금액 : 2100원
성인 : 46명, 금액 : 23000원
노인 : 34명, 금액 : 0원
------------------------------
1일 요금 총합계 : 26900원
------------------------------
Process finished with exit code 0
- 리스트 입력 후 오름차순, 내림차순 나타내기
listA = []
for i in range(5):
setName = input('친구 이름 입력 : ')
listA.append(setName)
print('친구 : {}'.format(listA))
listA.sort()
print('친구(오름차순) : {}'.format(listA))
listA.sort(reverse=True)
print('친구(내림차순): {}'.format(listA))
↓
친구 이름 입력 : 짱구
친구 이름 입력 : 짱아
친구 이름 입력 : 철수
친구 이름 입력 : 맹구
친구 이름 입력 : 유리
친구 : ['짱구', '짱아', '철수', '맹구', '유리']
친구(오름차순) : ['맹구', '유리', '짱구', '짱아', '철수']
친구(내림차순): ['철수', '짱아', '짱구', '유리', '맹구']- 4개의 숫자 중 서로 다른 숫자 2개를 선택해서 만들 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어 보자.
import math
numbers = [1,3,8,9]
result = []
for i in numbers:
for j in numbers:
if i == j:
continue
else:
result.append([i,j])
print(f'결과 : {result}')
pernutation = math.factorial(len(numbers)) / math.factorial(len(numbers) - 2)
print('경우의 수 : {}'.format(pernutation))
↓
결과 : [[1, 3], [1, 8], [1, 9], [3, 1], [3, 8], [3, 9],
[8, 1], [8, 3], [8, 9], [9, 1], [9, 3], [9, 8]]
경우의 수 : 12.0✏ 튜플

scores = (3.7, 4.2),(2.9, 4.3),(4.1, 4.2)
total = 0
for i in scores:
for j in i:
total += j
total = round(total, 1)
avg = round(total / 6, 1)
print('3학년 총 학점 : {}'.format(total))
print('3학년 평균 : {}'.format(avg))
targetScore = round((4.0 * 8) - total, 1)
print(f'4학년 목표 학점 : {targetScore}')
minScore = round(targetScore / 2, 1)
print('4학년 한학기 최소 학점 : {}'.format(minScore))
scores = list(scores)
scores.append(minScore)
scores =tuple(scores)
print(scores)
↓
3학년 총 학점 : 23.4
3학년 평균 : 3.9
4학년 목표 학점 : 8.6
4학년 한학기 최소 학점 : 4.3
((3.7, 4.2), (2.9, 4.3), (4.1, 4.2), 4.3)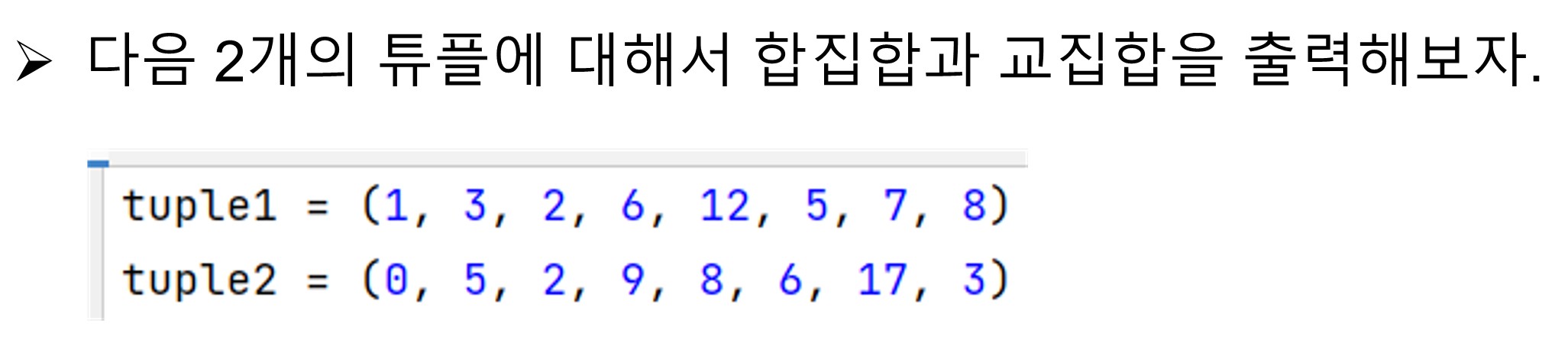
tuple1 = (1,3,2,6,12,5,7,8)
tuple2 = (0,5,2,9,8,6,17,3)
tuple1 = list(tuple1)
tuple2 = list(tuple2)
union = []
intersection = []
for num in tuple1:
if num in tuple2:
union.append(num)
else:
intersection.append(num)
intersection.extend(tuple2)
tuple1 = tuple(tuple1)
tuple2 = tuple(tuple2)
union.sort()
union = tuple(union)
intersection.sort()
intersection = tuple(intersection)
print('tuple1 : {}'.format(tuple1))
print('tuple2 : {}'.format(tuple2))
print('합집합 : {}'.format(intersection))
print('교집합 : {}'.format(union))
↓
tuple1 : (1, 3, 2, 6, 12, 5, 7, 8)
tuple2 : (0, 5, 2, 9, 8, 6, 17, 3)
합집합 : (0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, 17)
교집합 : (2, 3, 5, 6, 8)- 다음 튜플의 과일 개수에 대해서 오름차순 및 내림차순으로 정렬해보자.
fruits = (
{'수박':8},
{'포도':13},
{'참외':12},
{'사과':17},
{'자두':19},
{'자몽':15}
)
fruits = list(fruits)
cIdx = 0; nIdx = 1
eIdx = len(fruits) - 1
flag = True
while flag:
curDic = fruits[cIdx]
nexDic = fruits[nIdx]
curDicCnt = list(curDic.values())[0]
nexDicCnt = list(nexDic.values())[0]
if nexDicCnt < curDicCnt :
fruits.insert(cIdx, fruits.pop(nIdx))
nIdx = cIdx + 1
continue
nIdx += 1
if nIdx > eIdx:
cIdx += 1
nIdx = cIdx + 1
if cIdx == eIdx:
flag = False
print(tuple(fruits))
↓
({'수박': 8}, {'참외': 12}, {'포도': 13}, {'자몽': 15},
{'사과': 17}, {'자두': 19})✏ 딕셔너리
- 과목별 점수를 딕셔너리에 저장하고 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자.
subject = ['kor','eng','mat','sci','his']
scores = {}
for s in subject:
score = int(input(f'{s} 점수 입력 :'))
scores[s] = score
print(scores)
↓
kor 점수 입력 :80
eng 점수 입력 :70
mat 점수 입력 :55
sci 점수 입력 :77
his 점수 입력 :80
{'kor': 80, 'eng': 70, 'mat': 55, 'sci': 77, 'his': 80}- 삼각형부터 십각형까지의 내각의 합과 내각을 딕셔너리에 저장하는 프로그램을 만들어보자.
- n각형의 내각의 합 : 180 x (n-2)
dic = {}
for n in range(3, 11):
hap = 100 * (n - 2)
ang = int(hap / n)
dic[n] = [hap, ang]
print(dic)
↓
{3: [100, 33], 4: [200, 50], 5: [300, 60],
6: [400, 66], 7: [500, 71], 8: [600, 75],
9: [700, 77], 10: [800, 80]}
- 다음 문구를 공백으로 구분하여 리스트에 저장한 후, 인덱스와 단어를 이용해서 딕셔너리에 저장해 보자.
aboutPython = '파이썬은 1991년 프로그래머인 귀도 반 로섬이 발표한 고급 프로그래밍 언어이다.'
spiotList = aboutPython.split()
print(spiotList)
dic = {}
for idx, value in enumerate(spiotList) :
dic[idx] = value
print(dic)
↓
['파이썬은', '1991년', '프로그래머인', '귀도', '반',
'로섬이', '발표한', '고급', '프로그래밍', '언어이다.']
{0: '파이썬은', 1: '1991년', 2: '프로그래머인', 3: '귀도',
4: '반', 5: '로섬이', 6: '발표한', 7: '고급',
8: '프로그래밍', 9: '언어이다.'}- 딕셔너리를 이용해서 5명의 회원을 가입 받고 전체 회원 정보를 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어 보자.
userDic = {}
for n in range(5):
userId = input('ID 입력 : ')
userPw = input('PW 입력 : ')
userDic[userId] = userPw
for idx in userDic:
print('아이디 : {}, 비밀번호 : {}'.format(idx, userDic[idx]))
↓
ID 입력 : asdf1234
PW 입력 : 1234
ID 입력 : qwer1234
PW 입력 : 4321
ID 입력 : zxc1234
PW 입력 : 1111
ID 입력 : dsa1234
PW 입력 : 2222
ID 입력 : ewq1234
PW 입력 : 3333
아이디 : asdf1234, 비밀번호 : 1234
아이디 : qwer1234, 비밀번호 : 4321
아이디 : zxc1234, 비밀번호 : 1111
아이디 : dsa1234, 비밀번호 : 2222
아이디 : ewq1234, 비밀번호 : 3333 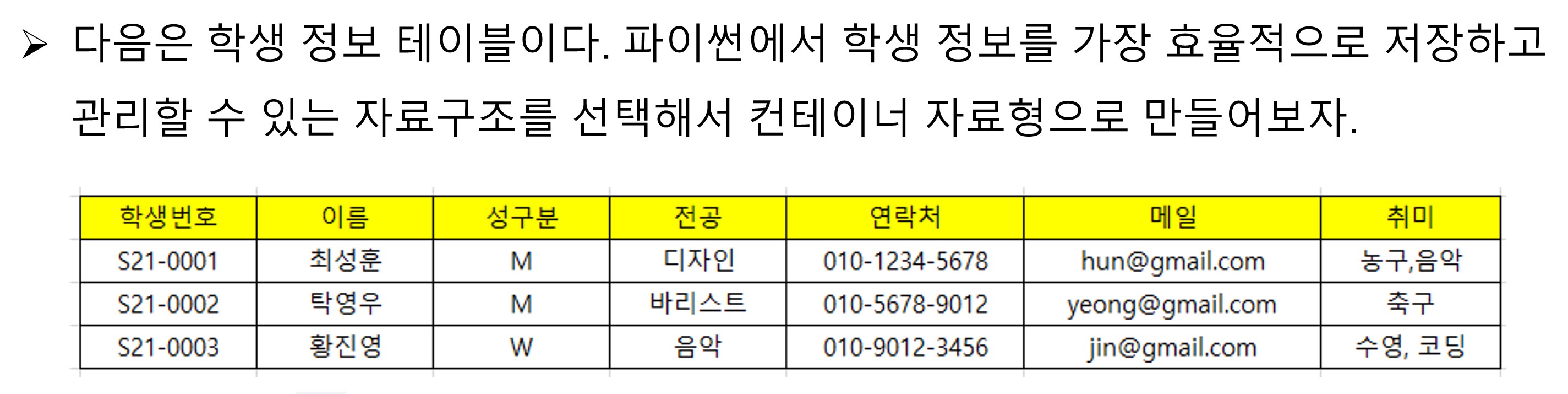
students = {'S21-0001':{'이름':'최성훈',
'성구분':'M',
'전공':'디자인',
'연락처':'010-1234-5678',
'메일':'hun@gmail.com',
'취미':['농구', '음악']},
'S21-0002': {'이름': '탁영우',
'성구분': 'M',
'전공': '바리스타',
'연락처': '010-5678-9012',
'메일': 'yeong@gmail.com',
'취미': ['축구']},
'S21-0003': {'이름': '황진영',
'성구분': 'W',
'전공': '음악',
'연락처': '010-9012-3456',
'메일': 'jin@gmail.com',
'취미': ['수영', '코딩']}
}
getStuCnt = input('학생번호 입력 : ')
# print('{} dic : {}'.format(getStuCnt, students[getStuCnt]))
def printStudent(str):
if getStuCnt in students.keys():
for w in students.keys():
if getStuCnt == w:
student = students[w]
for i in student.keys():
print(f'{i} : {student[i]}')
else :
print('학생번호를 확인하세요.')
printStudent(getStuCnt)
↓
학생번호 입력 : S21-0003
이름 : 황진영
성구분 : W
전공 : 음악
연락처 : 010-9012-3456
메일 : jin@gmail.com
취미 : ['수영', '코딩']📢 오늘의 한마디
오늘 자료구조 연습문제를 풀어봤다.
이제는 연습문제를 보고 먼저 풀어 본 뒤 강의를 들으며 다시 코드 정리를 할 수 있는 부분이 이전 강의들 보다 많아져서 스스로에게 조금은 뿌듯한 감정이 들었다.
계속해서 실습에 집중하며 실력을 키워 나가야겠다.

