문제
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
You can return the answer in any order.
- Input : 정수 배열
nums, 특정 두 수의 합target - Output :
nums안의 특정 두 수의 합이target인 두 수의 index ([index1, index2])- 반드시 단 한 개의 정답이 존재한다.
index1,index2의 위치가 서로 바뀌어도 상관없다.
문제 해결 방법
-
방법 1. 이중 반복문 사용
- 반복문을 이중으로 순회하면서 두 원소를 비교
- 두 원소의 합이
target일 경우[index1, index2]를 반환 - Time complexity :
- Space complexity:
-
방법 2. 정렬 후 two pointer 사용
- 우선
nums를 오름차순으로 정렬함 - 양 옆에서 시작해서 두 수의 합이
target보다 크면 오른쪽 포인터를 한 칸 왼쪽으로,target보다 작으면 왼쪽 포인터를 한 칸 오른쪽으로 이동- 자세한 내용은 유사 문제 참고
- 두 원소를 찾은 후, 해당 원소들을 기존의
nums에서 index를 찾는다. - Time complexity :
- Space complexity:
- 우선
-
방법 3. Map 자료구조 사용
- [num - index]로 구성하는 Map을 이용
i (0 <= i < nums.length)를 순회하면서target - num[i]를 key로 하는 value가 없을 때,(nums[i], i)형식으로 Map에 넣음target - num[i]를 key로 하는 value가 있을 때, 두 index를[index1, index2]으로 반환함
- Time complexity :
- Space complexity:
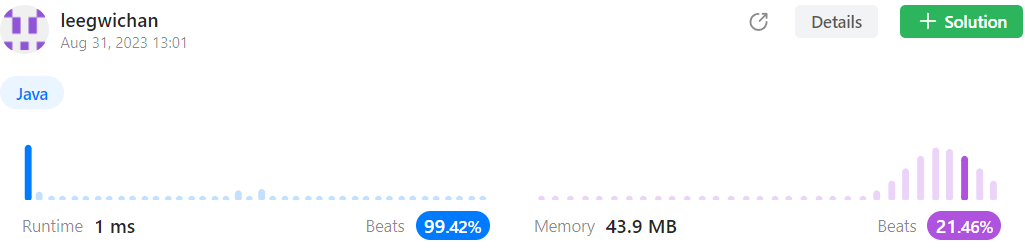
답안 1 (이중 반복문)
- Time complexity :
- Space complexity:
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return new int[]{i, j};
}
}
}
return null;
}
}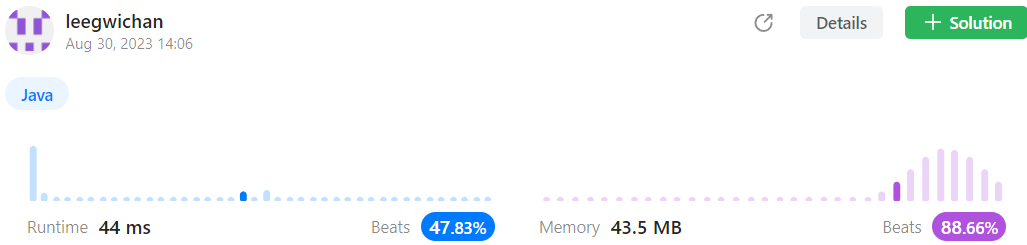
답안 2 (정렬 후 two pointer 사용)
- Time complexity :
- Space complexity:
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] sortedNums = Arrays.copyOf(nums, nums.length);
Arrays.sort(sortedNums);
int front = 0;
int behind = nums.length - 1;
while (front < behind) {
int sum = sortedNums[front] + sortedNums[behind];
if (sum > target) {
behind--;
} else if (sum < target) {
front++;
} else {
int fIndex = findIndexFromFront(sortedNums[front], nums);
int bIndex = findIndexFromBehind(sortedNums[behind], nums);
return new int[]{fIndex, bIndex};
}
}
return new int[0];
}
// 찾는 두 수가 같은 경우일 것을 대비해 하나는 앞에서부터, 하나는 뒤에서부터 찾는다.
private int findIndexFromFront(int element, int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] == element) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
private int findIndexFromBehind(int element, int[] array) {
for (int i = array.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (array[i] == element) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}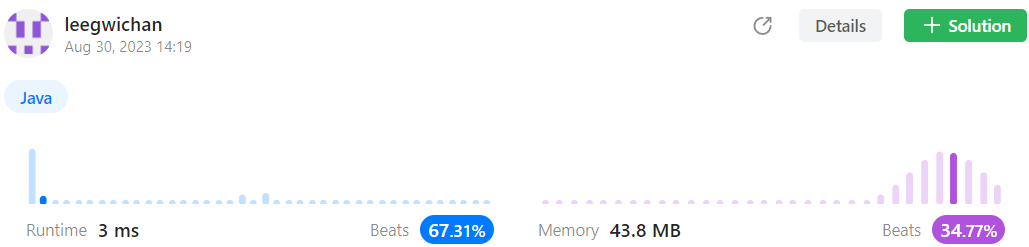
답안 3 (Map 자료구조 사용)
- Time complexity :
- Space complexity:
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> numToIndex = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int complement = target - nums[i];
if (numToIndex.containsKey(complement)) {
return new int[]{numToIndex.get(complement), i};
}
numToIndex.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0]; // 해가 없는 경우
}
}