테스트 코드는 현재 웹 서비스에선 매우 중요한 요소이다
테스트 코드에서 짚고 넘어가야할 것 은 TDD와 단위 테스트(Unit-test)는 다른 것!!
🐣 TDD ≠ 단위테스트
TDD는 테스트가 주도하는 개발
- 레드 그린 사이클
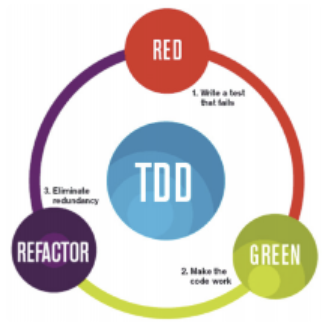
- 항상 실패하는 테스트를 먼저 작성 (Red)
- 테스트가 통과하는 프로덕션 코드를 작성(Green)
- 테스트가 통과하면 프로덕션 코드를 리팩토링(Refactor)
단위 테스트는 기능 단위의 테스트 코드를 작성
🐣 테스트 코드는 왜 작성해야 할까?
- 개발단계 초기에 문제를 발견하게 도움
- 개발자가 나중에 코드를 리팩토링하거나 라이브러리 업그레이드 등에 서 기존 기능이 올바르게 작동하지는 확인(회귀 테스트)
- 기능에 대한 불확실성을 감소
- 시스템에 대한 실제 문서를 제공, 단위 테스트 자체가 문서로 사용 가능
단위 테스트를 모를때 - 필자의 경험담
- 코드 작성
- 프로그램(Tomcat)을 실행
- Postman과 같은 API 텟트 도구로 HTTP 요청
- 요청 결과를 System.out.println()으로 눈으로 검증
- 결과가 다르면 다시 프로그램을 중지하고 코드를 수정
2~5는 매번 코드를 수정할 때마다 반복 왜?
- 테스트 코드가 없으니 눈과 손으로 직접 수정된 기능을 확인할 수 밖에 없다
- 테스트 코드를 작성하게 되면 자동검증이 가능
- 개발자가 만든 기능을 안전하게 보호
- B 기능이 추가되어 오픈했더니 기존에 잘 되던 A 기능에 문제가 발견 → 서비스의 모든 기능을 테스트 못함
→ 새로운 기능이 추가될 때, 기존 기능이 잘 작동되는 것을 보장해주는 것이 테스트 코드
- B 기능이 추가되어 오픈했더니 기존에 잘 되던 A 기능에 문제가 발견 → 서비스의 모든 기능을 테스트 못함
테스트 코드를 작성을 도와주는 프레임워크들이 있음 자바를 사용하니 JUnit을 사용!!
현재 버전은 5까지 나와서 책은 4를 사용하지만 5를 사용해보록 하겠다
오류가 나면 4로,,,
🐣 Hello Controller 테스트 코드 작성하기
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}package com.example.web;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}
@RestController- 컨트롤러를 JSON을 반환하는 컨트롤러로 만들어 줌
@GetMapping- HTTP Method인 Get의 요청을 받을 수 있는 API를 만들어 줌
package com.example.web;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@WebMvcTest(controllers = HelloController.class)
class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mvc;
@Test
public void hello가_리턴된다() throws Exception {
String hello = "hello";
mvc.perform(get("/hello"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(hello));
}
}
@WebMvcTest
- 여러 스프링 어노테이션 중, Web에 집중할 수 있는 어노테이션
- 선언할 경우
@Controller관련 어노테이션은 사용가능@Service,@Component,@Repository는 사용 불가
@Autowired- 스프링이 관리하는 빈(Bean)을 주입 받음
private MockMvc mvc
- 웹 API를 테스트할 때 사용 / 스프링 MVC 테스트의 시작점
- 이 클래스를 통해 HTTP, GET, POST 등에 대한 API 테스트를 할 수 있음
mvc.perform(get("/hello"))
- MockMvc를 통해 /hello 주소로 HTTP GET 요청
.andExpect(Status().isOk))
- mvc.perform의 결과를 검증
- HTTP Header의 Status를 검증 → 우리가 흔히 아는 200, 404, 500등의 상태 검증
- 여기선 Ok 즉, 200인지를 검증
.andExpect(content().string(hello))
- 응답 본문의 내용을 검증
- Controller에서 "hello"를 리턴하기 때문에 이 값이 맞나 검증
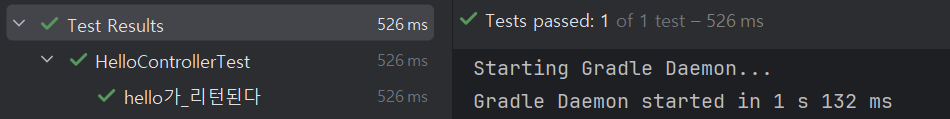
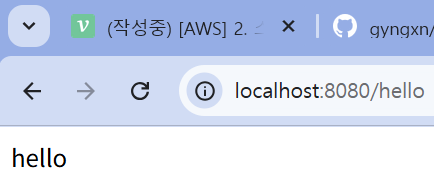
Test 와 Web 다 성공~
🐣 롬복 소개 및 설치
롬복 소개
롬복은 자바 개발할 때 자주 사용하는 코드 Getter, Setter, 기본 생성자, toString을 어노테이션으로 자동 생성
롬복 설치
build.gradle에서 dependenicies안에
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok' 작성
Preferences → build, Execution, Development → Complier → Annotation processor 에서 Enable annotation processing 반드시 체크하자
🐣 Hello Controller 코드를 롬복으로 전환하기
package com.example.web.dto;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class HelloResponseDto {
private final String name;
private final int amount;
}
@Getter
- 선언된 모든 필드의 get 메소드를 생성
@RequiredArgsConstructor
- 선언된 모든 final 필드가 포함된 생성자를 생성
- final이 없는 필드는 생성자에 포함 X
package com.example.web.dto;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
class HelloResponseDtoTest {
@Test
public void 롬복_기능_테스트() {
//given
String name = "test";
int amount = 1000;
//when
HelloResponseDto dto = new HelloResponseDto(name, amount);
//then
assertThat(dto.getName()).isEqualTo(name);
assertThat(dto.getAmount()).isEqualTo(amount);
}
}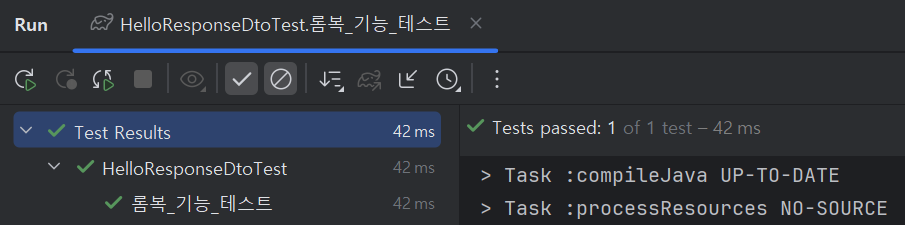
깔끔하게 성공
HelloController에서도 ResponseDto를 사용하게 해보자
@GetMapping("/hello/dto")
public HelloResponseDto hellodto(@RequestParam("name") String name,
@RequestParam("amount") int amount) {
return new HelloResponseDto(name, amount);
}@Test
public void 롬복_기능_테스트() throws Exception{
String name = "hello";
int amount = 1000;
mvc.perform(
get("/hello/dto")
.param("name",name)
.param("amount", String.valueOf(amount)))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.name", is(name)))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.amount", is(amount)));
}
param
- API 테스트할 때 사용될 요청 파라미터를 설정 / 단, 값은 String만 허용
jsonPath
- JSON 응답값을 필드별로 검증할 수 있는 메서드 / $을 기준으로 필드명을 명시
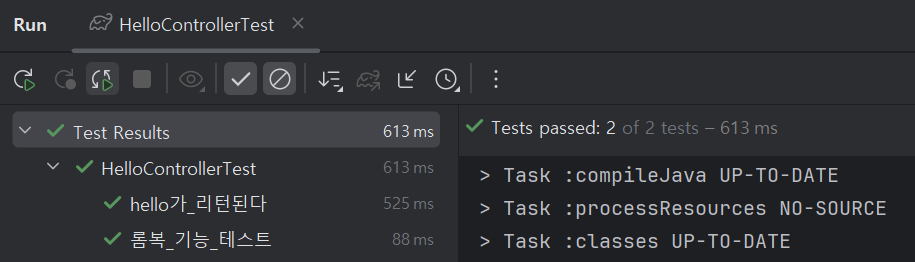
이것또한 깔끔히 성공~
