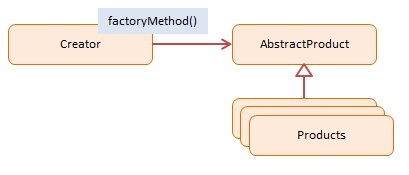
특징
- 객체 생성을 위한 디자인 패턴중 하나이다. (생성 패턴)
- 객체 생성에 필요한 과정을 템플릿처럼 정해 놓고 각 과정에 대한 다양한 구현이 가능하다.
- 실제 생성하고자 하는 클래스의 객체를 유연하게 정할 수 있다.
- 객체 생성에 대한 인터페이스와 구현을 분리시킴으로써 시스템의 확장과 유지보수성을 높여 준다.
- 하나의 interface를 통해서 여러가지 다른 종류의 object를 찍어낸다.
- 동적 환경에 최적화 된 패턴이다.
⚙ object의 타입이나 속성을 컴파일 하는 시점에 모른다고 했을 때 팩토리 factory method 패턴을 사용해서 런타임이나 생성주기안에서 다이나믹하게 생성 할 수 있도록 도와준다.
e.g.
API 데이터 페칭하고 결과에 따라 동적으로 무언가를 구현해야 할 때,
특히 반복적으로 무언가를 만들어내야 할 때 사용된다.
중요 포인트
- 새로운 object를 생성하고 리턴하는 일을 위임해서 한다.
- 속성, 매개함수를 공유하는 다른 타입의 오브젝트를 생성한다.
코드로 이해하기
data.ts
export interface Data {
type: string;
attr: { name: string; size: number };
}
export const data: Data[] = [
{ type: "Nike", attrs: { name: "a", size: 250 } },
{ type: "Nike", attrs: { name: "b", size: 240 } },
{ type: "Puma", attrs: { name: "c", size: 230 } },
{ type: "Adidas", attrs: { name: "d", size: 220 } },
{ type: "Nike", attrs: { name: "e", size: 260 } },
];index.ts
import { Data } from "./data";
interface Attrs {
name?: string;
size?: number;
brand?: string;
}
class Shoe {
private _attrs: Attrs;
constructor(attrs?: Attrs) {
this._attrs = attrs || {};
}
getName() {
return this._attrs?.name;
}
getSize() {
return this._attrs?.size;
}
getBrand() {
return Object.getPrototypeOf(this).constructor.name;
}
}
// Shoe라는 base class를 상속받는다.
class Nike extends Shoe {}
class Adidas extends Shoe {}
class Puma extends Shoe {}
// factory class
class ShoeFactory {
// 조건을 담당하는 object
typeMap: { [key: string]: typeof Shoe } = {
nike: Nike,
puma: Puma,
adidas: Adidas,
};
// create
// 액션 함수, 객체 생성을 담당한다.
// typeMap 객체를 활용해서 어떤 타입의 class를 생성할 지 선택한 후에 Brand라는 변수에 저장하고 Brand 변수를 생성자 함수로 호출한다.
create(props: Data) {
try {
const Brand = this.typeMap[props?.type?.toLowerCase()];
return new Brand(props.attrs);
} catch (e) {
console.error("error creating new shoes", e);
}
}
}
// test
const factory = new ShoeFactory();
const nike1 = factory.create({
type: "Nike",
attrs: { name: "kkk", size: 260 },
});
console.log(nike1);결과
Nike class가 생성되었고 instance를 반환받았다.

상속된 함수들 test
console.log(nike1?.getBrand());
console.log(nike1?.getSize());결과

map 함수 이용한 test
const items = data.map((item) => factory.create(item));
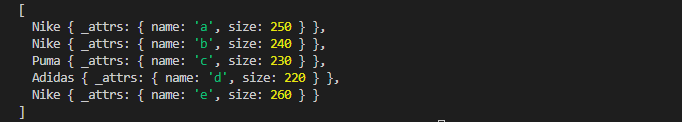
console.log(items);결과
data를 바탕으로 각자 다른 타입의 class가 생성된 것을 볼 수 있다.
정리
- 팩토리 패턴은 생성자 카테고리에 속하는 패턴 중 가장 기본이 되는 패턴이다.
- class객체 생성 처리를 팩토리 interface or 팩토리 class를 통해서 위임하여 처리한다.
- 팩토리 class는 조건로직이 필요하다. 그래서 조건 로직에 따라 어떤 객체를 생성할 지 결정를 하게된다.
- 팩토리 패턴의 특성상 class간의 의존도가 낮다. 그래서 확장이 쉽다. -> 추후 유지보수 용이하다.
참고 자료
