스택이란?
스택(Stack)은 "쌓다"라는 의미로데이터를 하나씩 쌓아 올린 형태의 자료구조로, 한쪽 끝에서만 자료를 넣고 뺄 수 있는 LIFO(Last In First Out) 형식의 자료 구조이다.
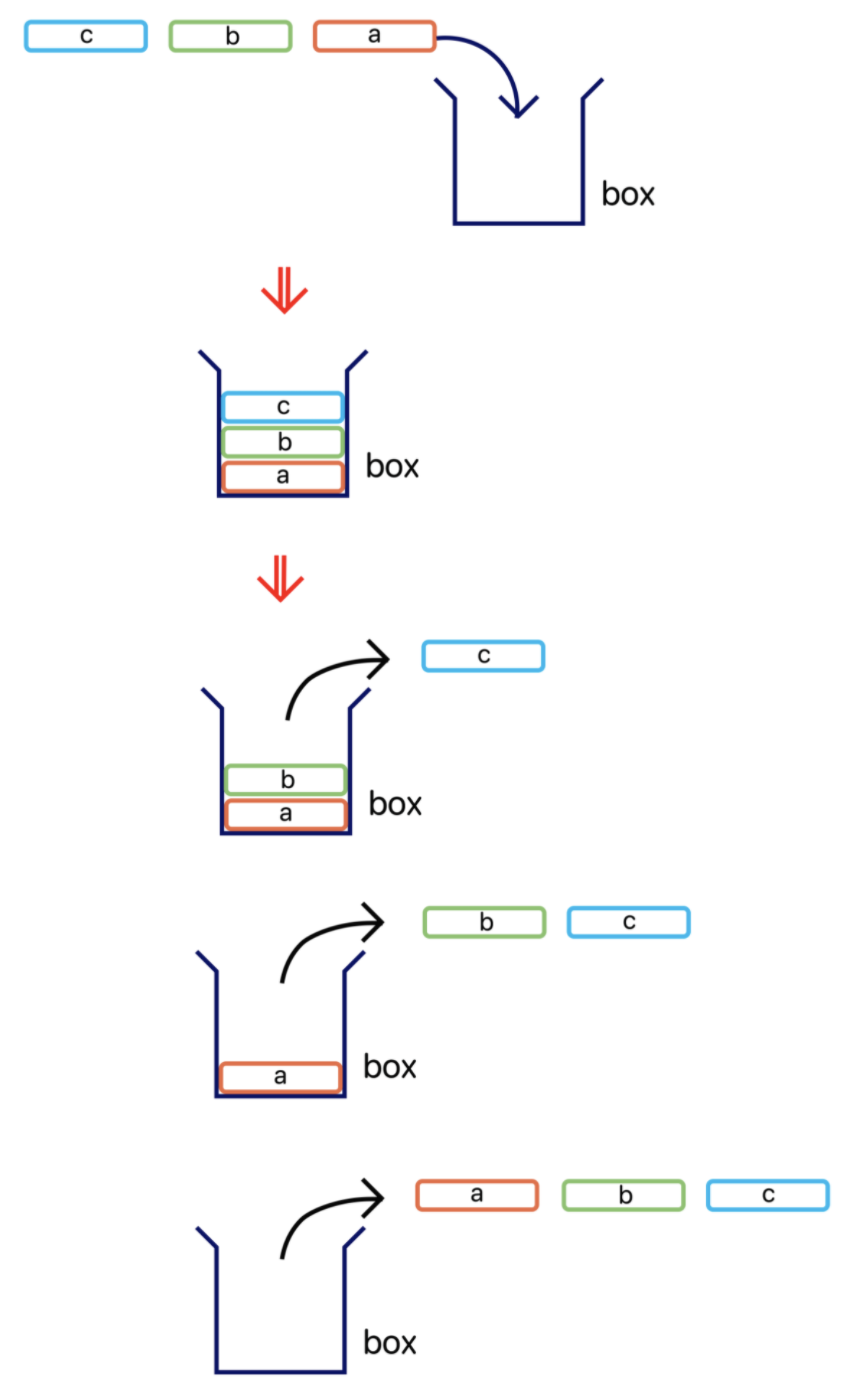
스택 메서드
-
pop() : 스택(Stack)의 가장 윗부분에 있는 자료를 제거한다.
-
push(item) : 스택(Stack)의 가장 윗부분에 item을 추가한다.
-
peek() : 스택(Stack) 가장 윗 부분에 있는 데이터를 반환한다.(제거하지 않음)
-
search(item) : 스택(Stack)에서 item이 있는 인덱스 위치를 반환한다.
-
sEmpty(): 스택이 비어 있을 때에 true를 반환한다.
스택 구현
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CustomStack<T> {
private List<T> stack;
public CustomStack() {
stack = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 스택(Stack)의 가장 윗부분에 있는 자료를 제거한다.
public T pop() {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Stack is empty");
}
return stack.remove(stack.size() - 1);
}
// 스택(Stack)의 가장 윗부분에 item을 추가한다.
public void push(T item) {
stack.add(item);
}
// 스택(Stack) 가장 윗 부분에 있는 데이터를 반환한다.
public T peek() {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Stack is empty");
}
return stack.get(stack.size() - 1);
}
// 스택(Stack)에서 item이 있는 인덱스 위치를 반환한다.
public int search(T item) {
int index = stack.lastIndexOf(item);
if (index == -1) {
return -1; // item이 스택에 없을 경우 -1 반환
}
return stack.size() - 1 - index;
}
// 스택이 비어 있을 때에 true를 반환한다.
public boolean isEmpty() {
return stack.isEmpty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CustomStack<Integer> stack = new CustomStack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
System.out.println("Peek: " + stack.peek()); // 출력: Peek: 3
System.out.println("Pop: " + stack.pop()); // 출력: Pop: 3
System.out.println("Search 2: " + stack.search(2)); // 출력: Search 2: 0
System.out.println("IsEmpty: " + stack.isEmpty()); // 출력: IsEmpty: false
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
System.out.println("IsEmpty after popping all elements: " + stack.isEmpty()); // 출력: IsEmpty after popping all elements: true
}
}스택 사용 사례
재귀 알고리즘을 사용하는 경우 스택이 유용하다.
재귀 알고리즘
- 재귀적으로 함수를 호출해야 하는 경우에 임시 데이터를 스택에 넣어준다.
- 재귀함수를 빠져 나와 퇴각 검색(backtrack)을 할 때는 스택에 넣어 두었던 임시 데이터를 빼 줘야 한다.
- 스택은 이런 일련의 행위를 직관적으로 가능하게 해 준다.
- 또한 스택은 재귀 알고리즘을 반복적 형태(iterative)를 통해서 구현할 수 있게 해준다.
웹 브라우저 방문기록 (뒤로가기)
실행 취소 (undo)
역순 문자열 만들기
- 수식의 괄호 검사 (연산자 우선순위 표현을 위한 괄호 검사)
Ex) 올바른 괄호 문자열(VPS, Valid Parenthesis String) 판단하기

