Queue란?
Queue란 컴퓨터의 기본 자료구조 중 하나로 먼저 들어온 데이터가 먼저 나가는 구조로 되어 있는 FIFO(First In First Out) 형식의 자료구조 이다.
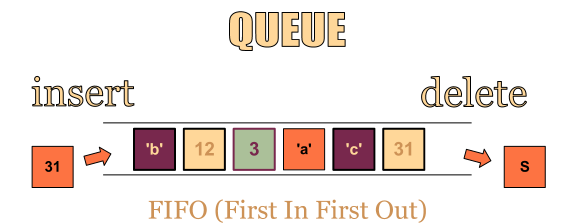
Queue의 간단 예시
- 줄을 서서 놀이기구를 차례대로 타는 사람들
- 드라이브 스루
FIFO구조이기 때문에 먼저 들어온 것이 먼저 나간다.
(Stack은 LIFO로 늦게 들어온게 먼저 나간다.)
Queue 특징
가장 최근 들어온 자료가 가장 먼저 나가는 FIFO(First-In First-Out) 선입선출 형태를 갖는다.
Queue는 한쪽에서는 데이터가 추가되고 한쪽에서는 데이터가 삭제되는 구조를 가지고 있다.
Queue의 용어
- 삽입(Enqueue) 이 일어나는 곳을 Rear
- 삭제(Dequeue) 가 일어나는 곳을 Front
장점
- 데이터가 입력된 시간 순서대로 처리해야 할 필요가 있는 상황에 유리하다.
- 데이터 접근 삽입 삭제가 빠르다.
단점
-
크기가 제한적이다.
-
중간에 위치한 데이터에 대한 접근이 불가능 하다.
Queue 연산
add(item): item을 리스트의 끝부분에 추가한다.
remove(): 리스트의 첫 번째 항목을 제거한다.
peek(): 큐에서 가장 위에 있는 항목을 반환한다.
isEmpty(): 큐가 비어 있을 때에 true를 반환한다.
Queue 구현
// Queue 인터페이스를 LinkedList로 구현
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// add(item): item을 리스트의 끝부분에 추가한다.
queue.add("Apple");
queue.add("Banana");
queue.add("Cherry");
// 현재 큐의 상태 출력
System.out.println("Queue after additions: " + queue);
// peek(): 큐에서 가장 위에 있는 항목을 반환한다.
System.out.println("Peek: " + queue.peek());
// isEmpty(): 큐가 비어 있을 때에 true를 반환한다.
System.out.println("Is the queue empty? " + queue.isEmpty());
// remove(): 리스트의 첫 번째 항목을 제거한다.
queue.remove();
System.out.println("Queue after removing one element: " + queue);
// 다시 peek()와 isEmpty()를 사용하여 상태 확인
System.out.println("Peek after removing: " + queue.peek());
System.out.println("Is the queue empty now? " + queue.isEmpty());
// 모든 요소를 제거하여 큐가 비게 만들기
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
System.out.println("Queue after removing all elements: " + queue);
System.out.println("Is the queue empty after removing all elements? " + queue.isEmpty());Queue의 종류
1. Linear Queue(선형 큐)
- 기본적인 큐의 형태
- 막대 모양으로 된 Queue로, 크기가 제한되어 있고 빈 공간을 사용하려면 모든 자료를 꺼내거나 자료를 한칸 씩 옮겨야 한다는 단점이 있다.
우리가 지금까지 알아본 Queue가 선형 Queue이다.
2. Circular Queue (원형 큐)
- 선형 큐의 문제점을 보완한 큐
- 배열의 마지막 인덱스에서 다음 인덱스로 넘어갈 때
(index+1) % 배열의 사이즈를 통해 0으로 순환되는 구조를 가진다.
public class CircularQueue {
private int[] queue;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int size;
private int capacity;
public CircularQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.queue = new int[capacity];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = 0;
this.size = 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public void enqueue(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue is full");
return;
}
queue[rear] = item;
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
size++;
}
public int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return -1;
}
int item = queue[front];
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
size--;
return item;
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return -1;
}
return queue[front];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularQueue cq = new CircularQueue(5);
cq.enqueue(1);
cq.enqueue(2);
cq.enqueue(3);
cq.enqueue(4);
cq.enqueue(5);
System.out.println("Dequeued: " + cq.dequeue());
System.out.println("Peek: " + cq.peek());
cq.enqueue(6);
while (!cq.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Dequeued: " + cq.dequeue());
}
}
}3. Priority Queue (우선순위 큐)
- 우선순위 큐는 마치 매직패스를 들고 있으면 가장 먼저 놀이기구를 탈 수 있는 것 처럼 들어간 순서에 상관 없이 우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼 저 나오는 큐
- 우선순위가 높은 데이터를 먼저 Dequeue 하는 특성을 위해 내부의
heap이라는 완전 이진트리 자료구조를 통해 우선순위를 유지한다.
class Element {
int value;
int priority;
public Element(int value, int priority) {
this.value = value;
this.priority = priority;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public int getPriority() {
return priority;
}
}
class ElementComparator implements Comparator<Element> {
@Override
public int compare(Element e1, Element e2) {
// 우선순위가 높은 것이 먼저 나오도록 정렬 (우선순위가 낮은 수가 높은 우선순위)
return Integer.compare(e1.getPriority(), e2.getPriority());
}
}
public class PriorityQueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Element> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new ElementComparator());
pq.add(new Element(10, 3));
pq.add(new Element(20, 1));
pq.add(new Element(30, 2));
pq.add(new Element(40, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Element element = pq.poll();
System.out.println("Value: " + element.getValue() + ", Priority: " + element.getPriority());
}
}
}
