1. 개념
Redux에서 특정 기능들을 제공하는 package
Redux 코드에서 계속 반복되는 함수생성, switch 분기처리 등 이에 소요되는 반복도를 줄이고 코드를 간결하기위해 redux에서 제공하는 일종의 package(라이브러리)이다.
2-1. createAction
action 전달 시 객체를 전달하거나, 별도 함수를 통해 전달하는 구조를
단순한 action 함수 선언만을 통해 가능하게 해주는 기능
- 함수선언과 type의 즉시 선언
import {createStore} from 'redux'
const ADD = "ADD"
const DELETE = "DELETE"
const addFunc = text => {
return {
type : ADD,
text : text,
id : Date.now()
}
}
const deleteFunc = id => {
return {
type : DELETE,
id : id
}
}위 코드를 createAction을 통해 type을 바로 선언하면서 코드를 1차적으로 간결화할 수 있다.
const addFunc = createAction("ADD")
const deleteFunc = createAction("DELETE")
const reducer = (state=[], action) => {
switch(action.type){
case addFunc.type:
return [...state, {text : action.text, id : action.id}]
case deleteFunc.type:
return state.filter(deletedList => deletedList.id !== action.id)
default :
return state
}
}위 코드처럼 createAction을 통해 하나의 함수를 선언하면서 type까지 같이 선언해주고, 이를 case 문에 활용하여 코드를 간결하게 작성할 수 있다.
모든 data들은 payload에 일괄적으로 저장
위에서 새롭게 정의한 addFunc, deleteFunc 부분만 고치면 logic이 정상적으로 작동하지 않는다.
createAction toolkit을 활용할 경우 data를 받아오는 방식도 바꿔줘야 한다.
function Home({doList, addFunc}) {
//console.log(props)
const [text, setText] = useState("")
function onChange(e) {
setText(e.target.value)
}
function onSubmit(e){
e.preventDefault()
addFunc(text) //call dispatch logic by specific function
setText("")
}
return(
<div>
<h1>TO DO LIST</h1>
<form onSubmit={onSubmit}>
<input type="text" value = {text} onChange={onChange}/>
<button>LIST ADD</button>
</form>
<ul>{doList.map(doListToView => <Dolistview key={doListToView.id} {...doListToView} />)}</ul>
</div>
)
}
function mapStateToProps(state) {
//console.log(state, ownProps)
return {doList : state}
}
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch){
return {
addFunc : (text) => dispatch(actionTrigger.addFunc(text))
//you can only use dispatch(action) structure, when you give dispatch with action aruguments.
}
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps) (Home)Home 화면에서 문자열을 입력하고, 이후 LIST ADD 버튼을 클릭하였을 때(혹은 엔터키) text에 저장된 내용이 addFunc 인자에 전달되면서 dispatch가 다시 호출되는 방식으로 입력되었다.
이 기존 방식에서 유의할 점은 이제는 addFunc을 통해 전달받은 {type : ~, text : ~} 객체가 없다는 점인데, 다시 말해 직접적으로 전달해주는 text 값이 없는 상태라 할 수 있다.
CreateAction을 이용하면, 자신이 받은 인자는 payload에 일괄 저장하여 전달한다.
const reducer = (state=[], action) => {
switch(action.type){
case addFunc.type:
return [...state, {text : action.payload, id : action.id}]
case deleteFunc.type:
return state.filter(deletedList => deletedList.id !== action.id)
default :
return state
}
}submit 이벤트가 실행되었을 때
- 이벤트가 실행되면서 addFunc를 호출.
- 호출하면서 text 인자를 전달하고, 최종적으로 dispatch를 통해 action 인자를 전달.
dispatch를 통해 전달된 action 인자가 createAction으로 정의되어 있는 경우, 반드시 payload라는 저장소에 일괄적으로 저장되어 호출된다.
case addFunc.type:
return [...state, {text : action.payload, id : action.id}]※ remind ) list add 시 state 배열에 객체가 추가되어, 새로운 객체가 return 된다.
즉 함수의 return 형태를 객체로 안맞추어도 되고, 단순히 action의 payload로부터 data를 받아 쓰기만 하면 된다.
switch(action.type){
case addFunc.type:
console.log(action)
return [...state, {text : action.payload, id : Date.now()}]
case deleteFunc.type:
return state.filter(deletedList => deletedList.id !== action.payload)
default :
return state
}마찬가지 원리로 id값 또한 동일하게 적용된다.
※ remind ) createAction을 통해 dispatch되는 action을 통해 return되는 모든 data들은 payload에 일괄 저장
위 코드에서 리스트를 삭제하는 deletefunc의 구조를 살펴보도록 한다.
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch, ownProps){
//console.log(ownProps)
return {
deleteFunc : () => dispatch(actionTrigger.deleteFunc(ownProps.id))
//you can only use dispatch(action) structure, when you give dispatch with action aruguments.
}
}삭제하면서 dispatch 되는 시점에 createAction에 저장되는 인자값인 id가 payload에 저장되는 것이다(※ state 배열은 별도, dispatch를 통해 action이 전달되는 시점을 봐야한다).
case deleteFunc.type:
return state.filter(deletedList => deletedList.id !== action.payload)따라서 같은 원리로 id값을 action.id가 아닌, action.payload로 바꿔준다.
2-2. (참조)
createAction으로 선언된 함수들을 log 출력해본다.
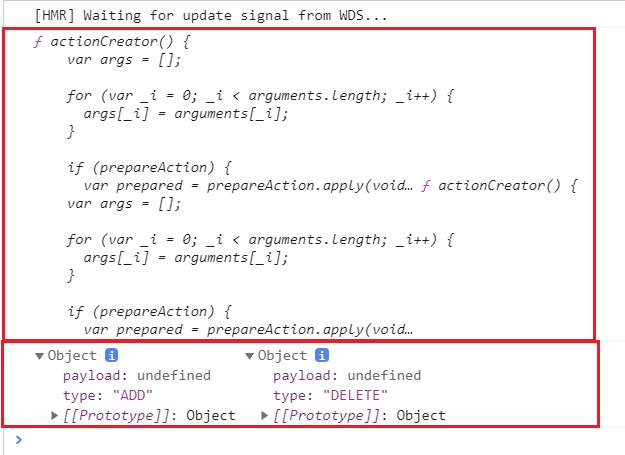
- console.log(addFunc, deleteFunc) → 하나의 함수임을 보여준다.
- console.log(addFunc(), deleteFunc()) → 함수 내부에 type이 선언되어있고, 이와 함께 payload도 같이 내장되어 있음을 보여준다.
payload는 state 자체가 아닌, dispatch 되면서 전달되는 인자를 저장하는 곳이다.
- dispatch하면서 함수를 호출하는 과정에서 함수에 전달된 인자가 payload에 저장된다.
- payload는 현재 저장되어 있는 state와는 별도로, dispatch 되는 시점에서 전달되는 인자이다.
2-3. 참조링크
redux toolkit 관련 공식문서
https://redux-toolkit.js.org/introduction/getting-started
다음 항목에서 계속
