이론
📖 유클리드 호제법
두 수의 최대공약수를 구하는 알고리즘.
📍 최대공약수
#최대공약수
def gcd(a,b):
while b!=0:
r=a%b
a=b
b=r
return a
📍 최소공배수
def gcd(a,b):
while b!=0:
r=a%b
a=b
b=r
return a
# 먼저 gcd() 함수 구현 후,
def lcm(a,b):
return int(a*b/gcd(a,b))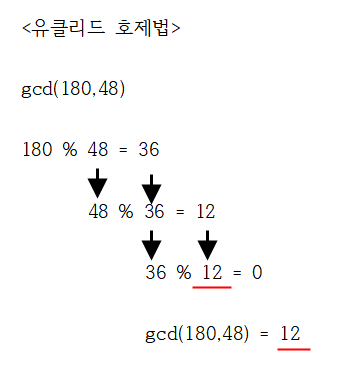
위의 유클리드 호제법을 이용하여 코드를 작성하면,
def gcd(a,b):
if b==0:
return a
else:
return gcd(b,a%b)
문제풀이
📖 백준 1033 (🔗백준 1033 문제)
✏ 각 재료의 비율을 그래프로 구현.
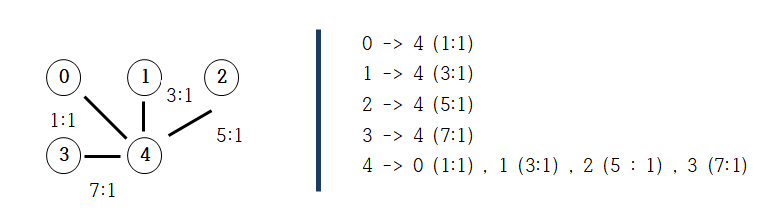
이를 바탕으로 인접리스트 작성 시, 튜플형태로 비율까지 포함시킨다.
for i in range(n-1):
a,b,p,q=map(int,input().split())
arr[a].append((b,p,q))
arr[b].append((a,q,p))✏ 데이터를 저장할 때마다, 비율과 관련된 수들의 최소공배수를 업데이트 시킨다.
위에서 작성한 반복문 안에 최소공배수를 업데이트시키는 코드를 추가하면, 아래와 같다.
#인접리스트 작성, lcm(최소공배수) 업데이트
for i in range(n-1):
a,b,p,q=map(int,input().split())
arr[a].append((b,p,q))
arr[b].append((a,q,p))
total_lcm*=lcm(p,q)✏ 최대공약수, 최소공배수는 유클리드 호제법을 이용하여 따로 작성해놓는다.
✏ 임의의 시작점에서 DFS로 탐색을 수행하면서 각 노드의 값을 이전 노드의 값과의 비율 계산을 통해 계산하고 저장한다.
cf)
0을 임의의 점으로 선정할 때,
4 -> 0번 노드값 1/1 = 105
1 -> 4번 노드값 1/3 = 35
2 -> 4번 노드값 1/5 = 21
3 -> 4번 노드값 1/7 = 15
✏ 각 노드의 값을 모든 노드의 최대공약수로 나눈다.
📝 코드
# 유클리드 호제법, DFS
import sys
input=sys.stdin.readline
n=int(input())
arr=[[] for i in range(n)]
visit=[0]*n
total_lcm=1
ingredient=[0]*n
def gcd(a,b):
while b!=0:
r=a%b
a=b
b=r
return a
def lcm(a,b):
return int(a*b//gcd(a,b))
def dfs(a):
visit[a]=True
for i in arr[a]:
next=i[0]
if not visit[next]:
#다음 노드 값=현재노드값*비율
ingredient[next]=ingredient[a]*i[2]//i[1]
#재귀
dfs(next)
#인접리스트 작성, lcm(최소공배수) 업데이트
for i in range(n-1):
a,b,p,q=map(int,input().split())
arr[a].append((b,p,q))
arr[b].append((a,q,p))
total_lcm*=lcm(p,q)
#0번 노드에 최소공배수 저장, 0번부터 dfs탐색 시작.
ingredient[0]=total_lcm
dfs(0)
total_gcd=ingredient[0]
for i in range(1,n):
total_gcd=gcd(total_gcd,ingredient[i])
for i in ingredient:
print(i//total_gcd,end=" ")
◼ 참고사항
- Do it! 알고리즘 코딩테스트
- 백준
