책 Programming Interviews Exposed
Linked List Flattening/Unflattening
Problem.
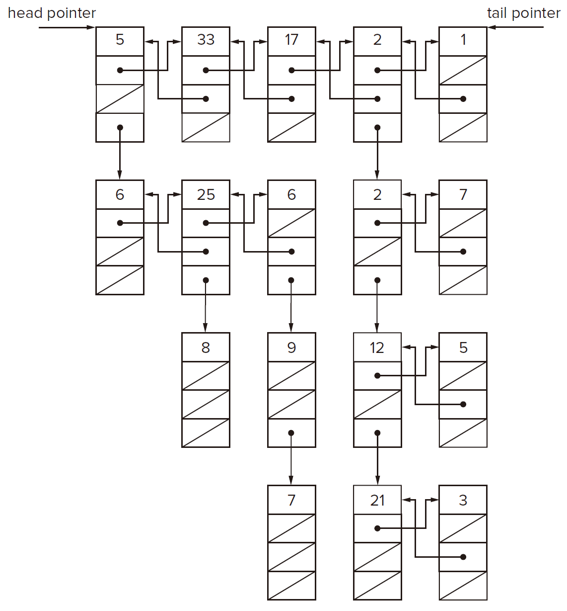
There is a standard doubly linked list. Now imagine that in addition to the next and previous pointers, each element has a child pointer, which may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure, as shown in Figure.
1. Flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list.
2. Unflatten the list created by the previous problem and restore the data structure to its original condition.
Figure
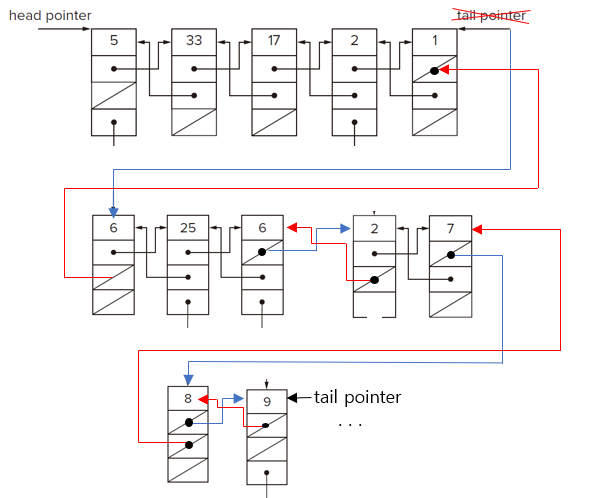
Result of flattened linked list
Code implementation
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
typedef struct Node{
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
struct Node *child;
int value;
} Node;
void flattenList(Node *head, Node **tail){
Node *curNode = head;
while (curNode){
/* The current node has a child*/
if (curNode->child)
{
append(curNode->child, tail);
}
curNode=curNode->next;
}
}
/* Appends the child list to the end of the tail and updates ;
* the tail.
*/
void append(Node *child, Node **tail){
Node *curNode;
/*Append the child list to the end*/
(*tail)->next = child;
child->prev=*tail;
/* find new tail which is the end of the child list */
for(curNode=child; curNode->next; curNode=curNode->next)
; /* Body intentionally empty */
*tail = curNode;
}
/* unflattenList wraps the recursive function and updates the tail pointer. */
void unflattenList(Node *start, Node **tail){
Node *curNode;
exploreAndSeparate(start);
// separation completed
/*update tail pointer*/
for(curNode = start; curNode->next; curNode = curNode->next)
; /* Body intentionally empty */
*tail = curNode;
}
/* exploreAndSeparate actually does the recursion and separation */
void exploreAndSeparate(Node *childListStart)
{
Node *curNode = childListStart;
while(curNode)
{
if(curNode->child)
{
/*terminates the child list before the child*/
curNode->child->prev->next=nullptr;
/* starts the child list beginning with the child */
curNode->child->prev=nullptr;
exploreAndSeparate(curNode->child);
}
curNode=curNode->next;
}
}
