linked list가 다음과 같이 구성되어있다고 생각하자!
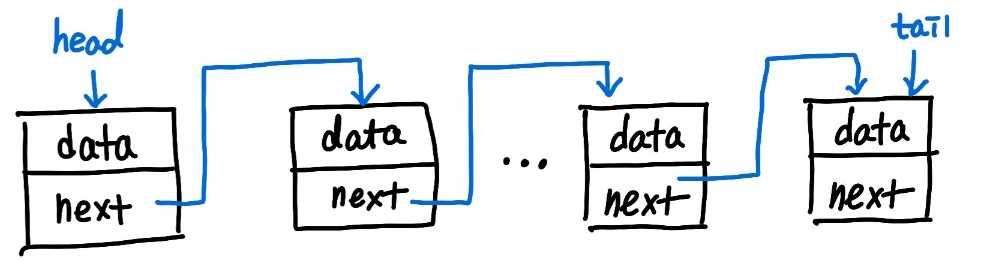
- Node 하나를 나타내는 Element
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
typedef struct Element{
Element* next;
void *data;
} Element;
// head, tail
Element* head = nullptr;
Element* tail = nullptr;delete operation
지우고 싶은 원소의 위치가 다음과 같은 경우로 나뉠 수 있다.
-
head일 때
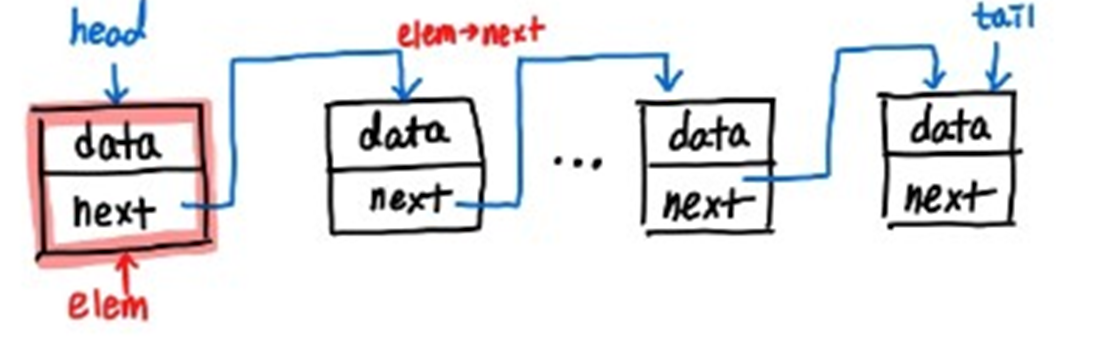
-
tail일 때!
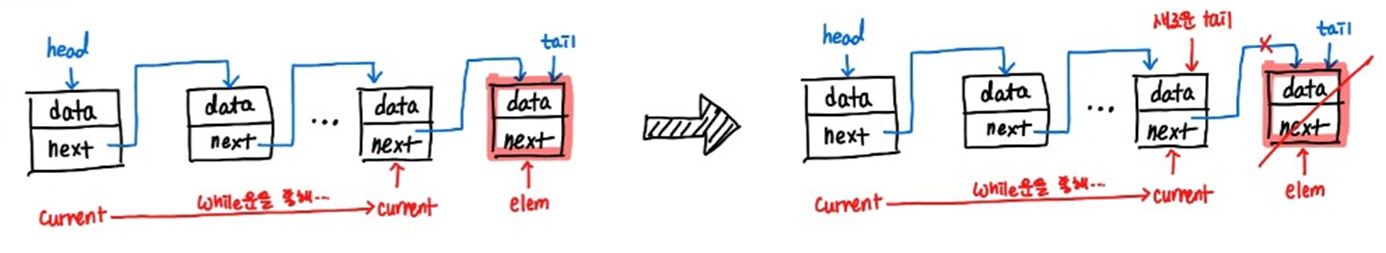
- 중간에 있는 위치일 때!
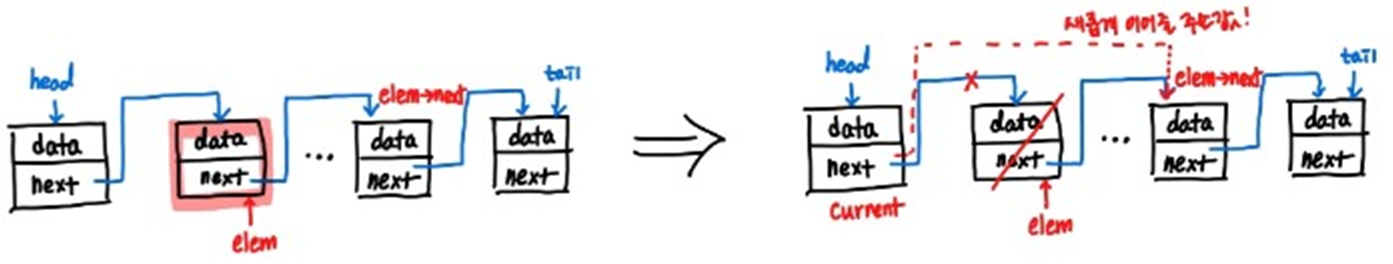
Implementation
해당 조건들에 따라서 코드로 표현해보면 다음과 같다.
bool deleteElement(Element* elem){
// empty-element list일 때
if (!elem){return false;} //nullptr
if (head==nullptr){return false;}
// elem이 head일때
if (elem == head)
{
head = elem->next;
// one-element list 일때
if (head==nullptr){tail=nullptr;} // list becomes empty
delete elem;
return true;
}
// elem이 middle일 때
Element *current = head;
while(current->next && current->next != elem)
{
current = current->next;
}
if (current->next == nullptr) return false; // elem이 list에 없을 때!
// elem이 tail일 때
if (elem == tail)
{
tail = current;
}
current->next=elem->next;
delete elem;
return true;
}
insertAfter
넣고 싶은 원소의 위치가 다음과 같은 경우로 나뉠 수 있다.
-
head에 넣을 때
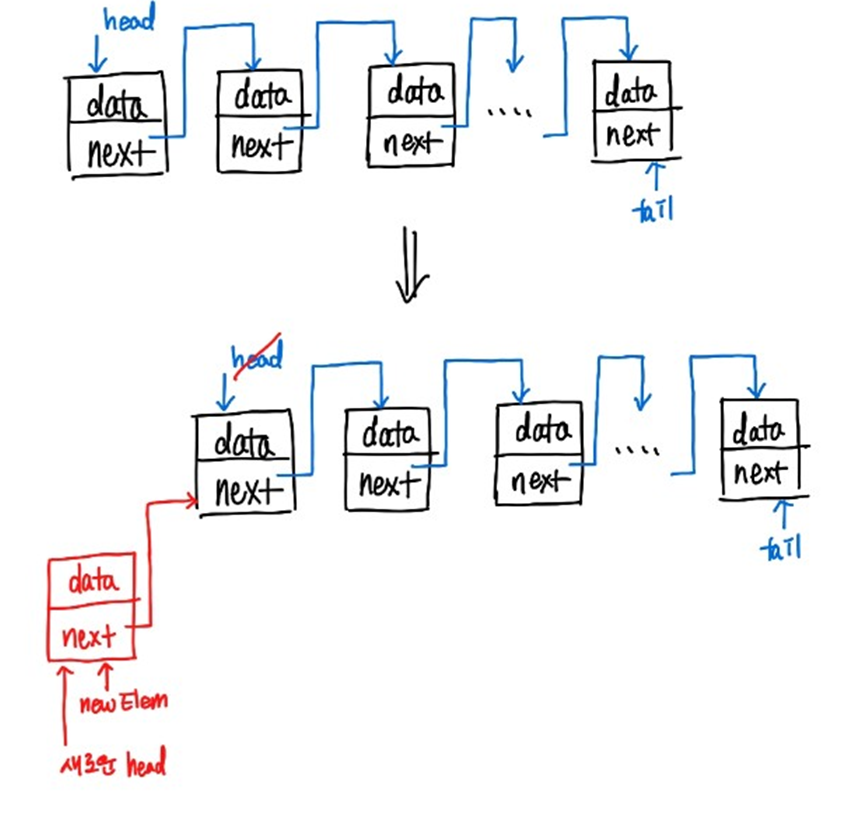
- empty list였을 때,,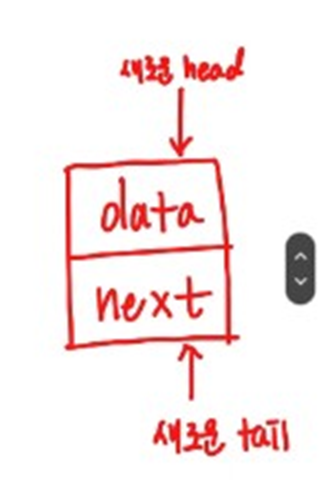
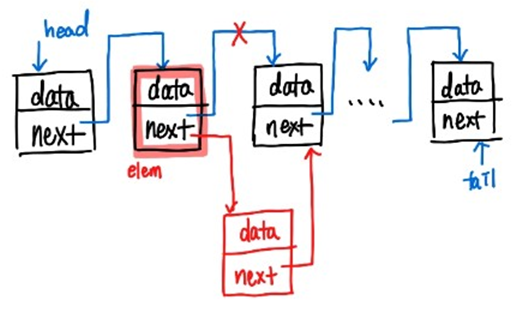
-
중간의 원소 사이의 위치일 때
- tail에 넣었을 때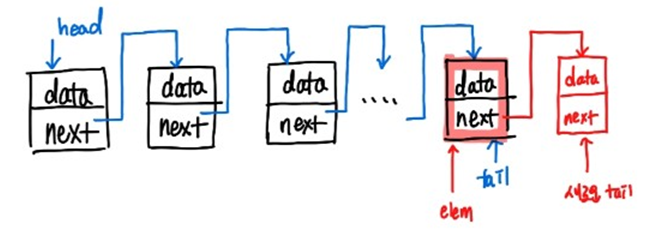
Implementation
bool insertAfter(Element *elem, int data)
{
Element* newElem = new Element();
Element* curPos = head;
// Allocating memory for new data
int* newData = new int(data);
if (!newData) return false; // Memory allocation failed
// 일단 data node에 넣어주기
if (!newElem){delete newData; return false;}
newElem->data = newData;
// if inserting at the beginning
if (!elem)
{
newElem->next=head;
head=newElem;
// if empty list
if (!tail)
{
tail=newElem;
}
return true;
}
// in the middle
while (curPos)
{
if (curPos==elem)
{
newElem->next = curPos->next;
curPos->next = newElem;
// if inserted at the end
if (newElem->next==nullptr){
tail=newElem;
}
return true;
}
curPos=curPos->next;
}
delete newElem; // free element and return false
return false;
}