🔍 Problem
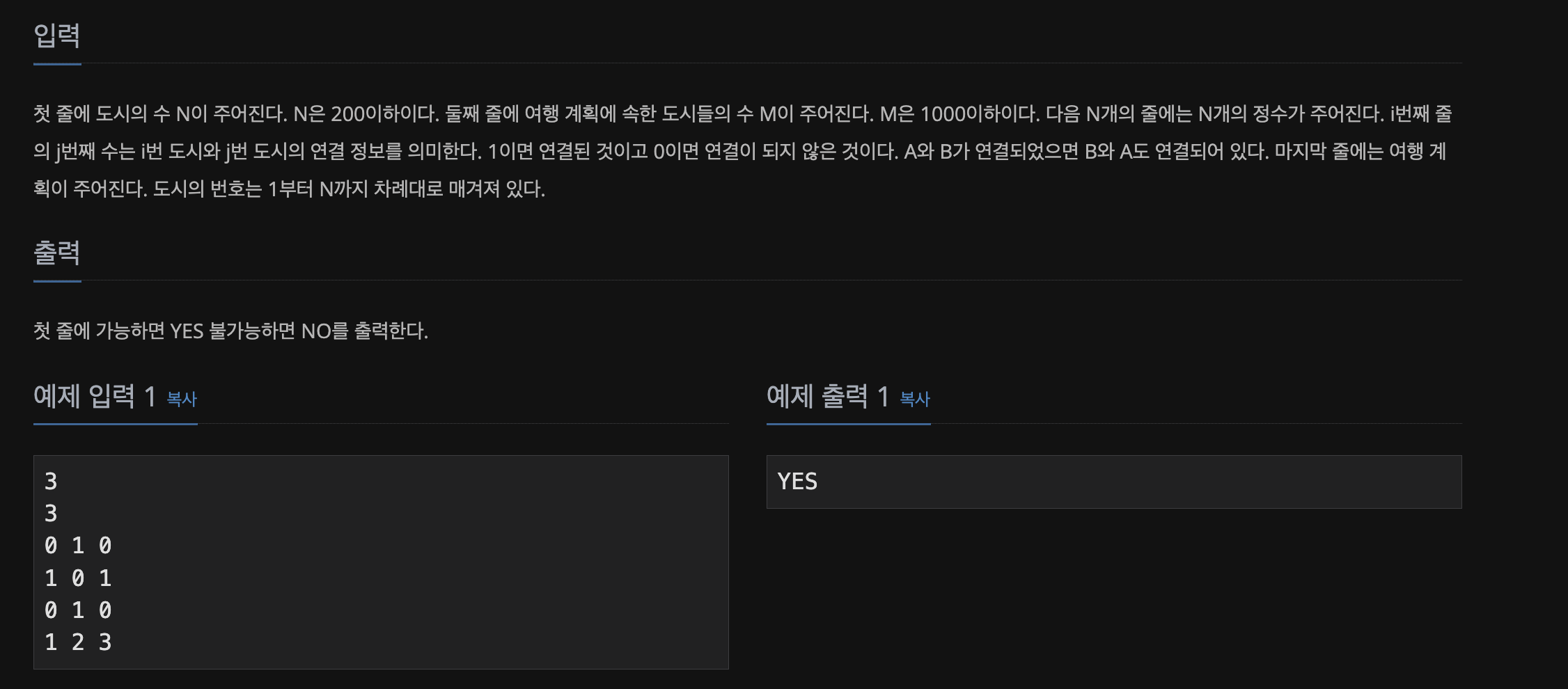
📃 Input&Output
🌁 문제 배경
가. 접근 방법
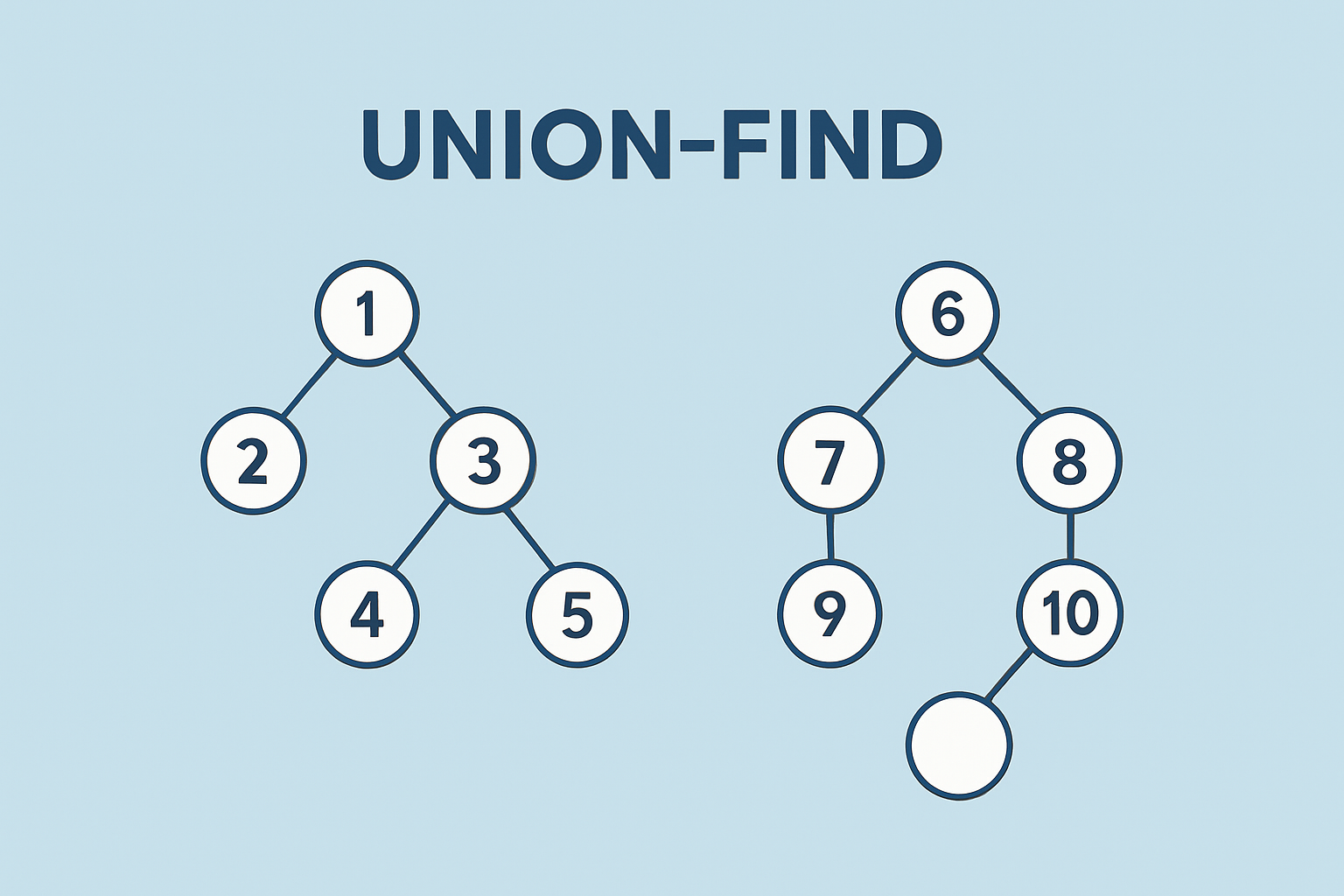
결국 사용자가 원하는 도시들을 "여행가능한지"에 대한 여부만 조사하면 되므로, 마지막 라인의 여행계획에서 모든 노드들의 Root노드들이 같으면 된다. 왜냐하면 모든 Root 노드들이 같다는 것은 서로 연결되어 있다는 것을 의미하기 때문이다.
즉, 만약 모든 노드들이 연결되어 있는 문제에 접근할 때는, 루트노드가 모두 같은지 확인하면 되고 이는 유니온 파인드를 알고리즘을 쓰면 된다!
나. 사용할 알고리즘 선택
유니온 파인애플 아니고 파인드
📒 해결 과정
- Root 배열 오름차순으로 초기화
- 노드간의 정보를 담은 입력값이 1이면 해당 노드끼리 Union
- 마지막에 여행계획 Line에서 모든 Root 노드가 동일한지 Check!!
💻 Code
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class P1976 {
static int GetRoot(int[] root, int n) {
if (root[n] == n) {
return n;
}
return root[n] = GetRoot(root, root[n]);
}
static void Union(int[] root, int a, int b) {
a = GetRoot(root, a);
b = GetRoot(root, b);
if (a < b) {
root[b] = a;
} else {
root[a] = b;
}
}
static boolean Find(int[] root, int a, int b) {
a = GetRoot(root, a);
b = GetRoot(root, b);
if (a == b) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N, M;
// int[][] mat;
int[] roots;
int tmp;
int root;
boolean flag = true;
int[] arr;
N = sc.nextInt();
M = sc.nextInt();
roots = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < N + 1; i++) {
roots[i] = i;
}
// mat = new int[N + 1][N + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < N + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < N + 1; j++) {
tmp = sc.nextInt();
if (tmp == 1) {
Union(roots, i, j);
}
}
}
root = GetRoot(roots, sc.nextInt());
for (int i = 1; i < M; i++) {
int k = sc.nextInt();
if (GetRoot(roots, k) != root) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag) {
System.out.print("YES");
} else {
System.out.print("NO");
}
}
}
🤔 느낀점
모든 노드들이 연결되어 있는지 확일할 때는 유니온 파인드를 쓰면 된다는 점을 파악하였다.