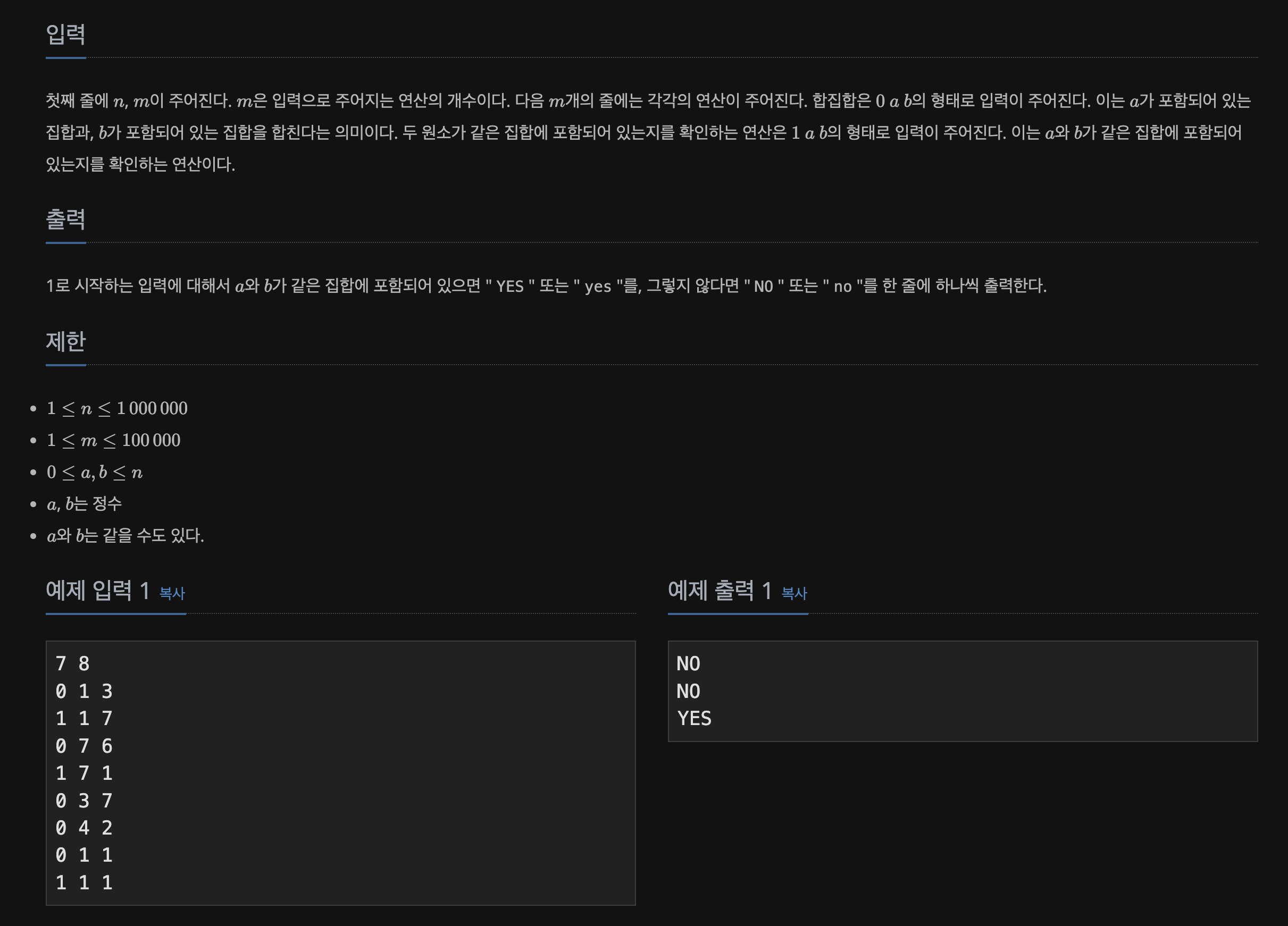
🔍 Problem
📃 Input&Output
🌁 문제 배경
가. 접근 방법
유니온 파인드로 각각의 연산을 해주면 될 것이다. 그리고 경로압축을 사용해 시간초과를 예방해야할 것이다.
나. 사용할 알고리즘 선택
유니온 파인드
📒 해결 과정
가. 입력 첫번째 줄
전체 노드들을 받고 root배열을 idx값으로 초기화한다.
그리고 두번째 파라미터만큼 연산을 한다.
나. 입력 두번째 줄 부터
1) oper (첫번째 파라미터)
0일 경우: Union연산을 실행한다.static void Union(int[] root, int a, int b) { a = GetRoot(root, a); b = GetRoot(root, b); if (a < b) { root[b] = a; } else { root[a] = b; } }
1일 경우: Find연산을 실행한다.static boolean Find(int[] root, int a, int b) { a = GetRoot(root, a); b = GetRoot(root, b); if (a == b) { return true; } return false; }
2) a (두번째 파라미터)
첫번째 노드 값
3) b (세번째 파라미터)
두번째 노드값
💻 Code
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class P1717 {
static int GetRoot(int[] root, int n) {
if (root[n] == n) {
return n;
}
return root[n] = GetRoot(root, root[n]);
}
static void Union(int[] root, int a, int b) {
a = GetRoot(root, a);
b = GetRoot(root, b);
if (a < b) {
root[b] = a;
} else {
root[a] = b;
}
}
static boolean Find(int[] root, int a, int b) {
a = GetRoot(root, a);
b = GetRoot(root, b);
if (a == b) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer st;
int N, M;
int[] root;
int op, a, b; // op : 연산자
boolean ck;
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
root = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) {
root[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
op = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (op == 0) {
Union(root, a, b);
} else if (op == 1) {
ck = Find(root, a, b);
if (ck) {
bw.write("YES\n");
} else {
bw.write("NO\n");
}
}
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
}
🎸 기타
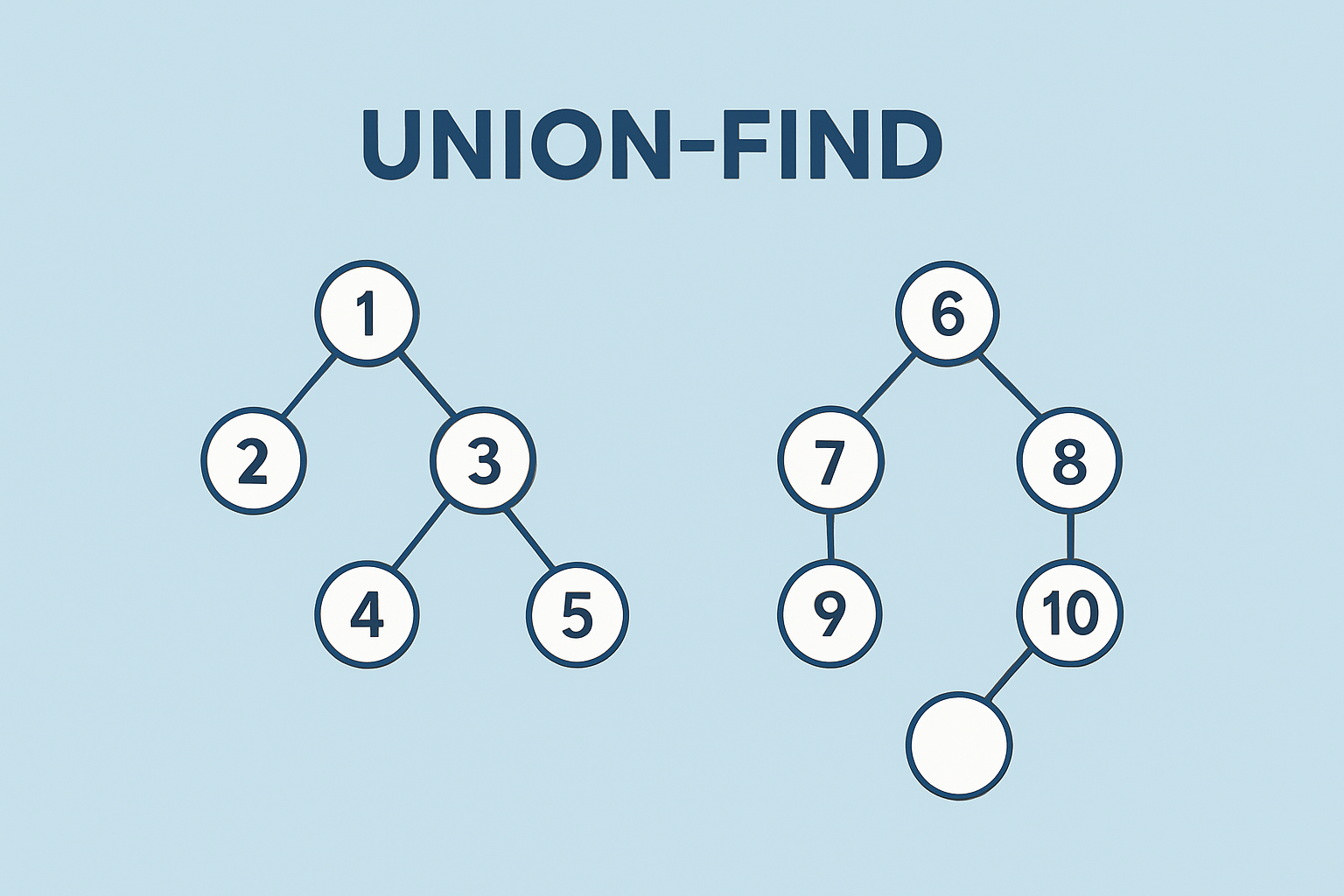
가. 유니온 파인드 경로 압축
유니온 파인드 경로압축 문제 해결 예시 1
🤔 느낀점
경로압축을 함으로써 시간복잡도를 다음과 같이 줄일 수 있었다.
O(N) -> O(logN)