Chater 3. Register
3-1. Introduction to register
3-1-1. What is register?
Register is just variable that computer use3-1-2. ARM architecture and Register
- Memory Architecture
- Register is fastest memory device in computer
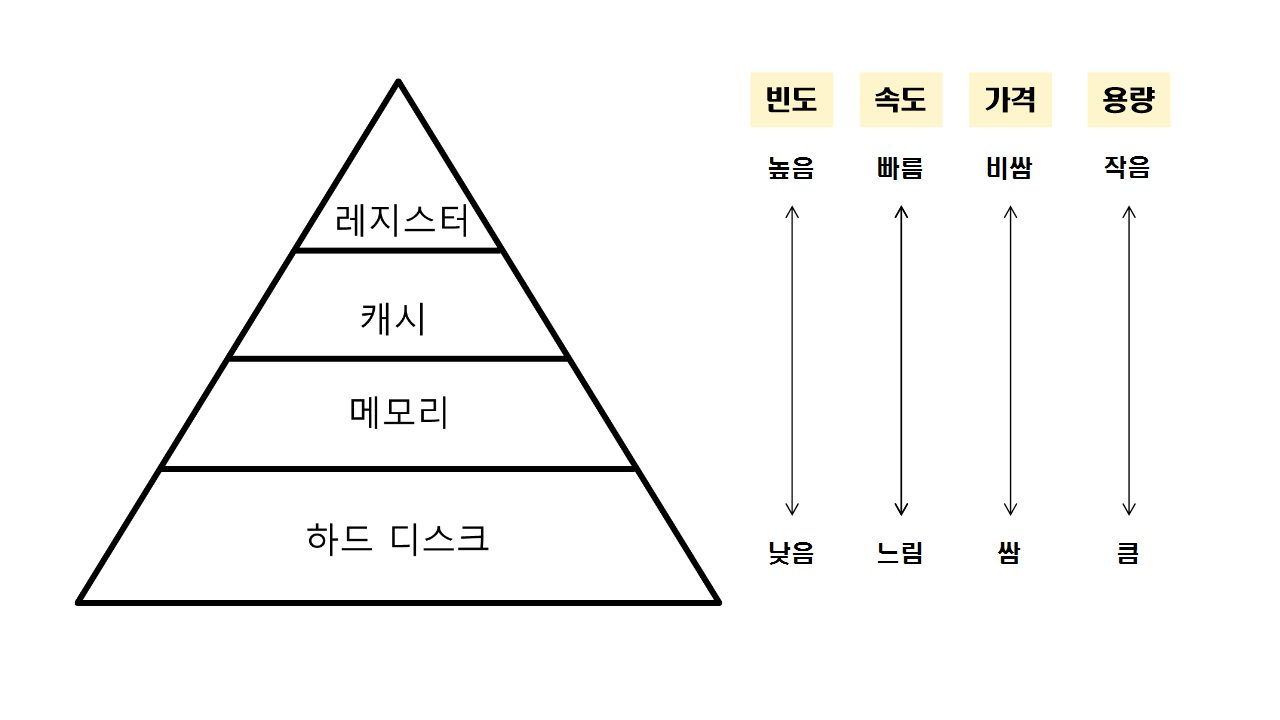
cf) compiler prefer to use register than memory when compile at higher optimization level
3-2. ARMv7 Register
3-2-1. General Register
-
ARMv& have 16 general registers that software can use(R0-R15)
- 32-bits register
- R0~R14 registers are used to data process
- R15 register is special register used as PC
- CPSR reigster save processor status. SPSR is copy of CPSR(so, it save previous status of processor)
-
Special Registers: R13, R14, PC(R15)
- R13: Stack Pointer
- R14: Link Regsier. save instruction address when call subroutine(function) to return from subroutine. in RISC-V we could as ra(return address)
- R15: Program Counter
-
Banked Register
- e.g.) R13_svc, R14_svc, R13_irq, R14_irq
- ARM sperate some register(usually special register) by processor's authorization mode(supervisor mode, irq mode, fiq mode)
- e.g) when you run follow code in supervisor mode
SUB, SP, SP, #4 - this code adjust SP(R13) register. but in supervisor mode, it also R13_svc register. in irq mode, it adjust R13 and R13_irq
-
Why we need banked register?
- for simple execute mode exchange.
- We don't need to save special register in stack when we change execute mode
3-2-2. CPSR, SPSR
-
CPSR(Current Processor Status Register)
- organized with 32-bits and each bits contain information about processor status
- condition flag: bit[31:28], usally used for branch instruction
- 31, Negative(N) : 음수
- 30, Zero(Z) : 0
- 29, C(Carry) : 자리올림
- 28, V(oVerflow) : 오버플로
- mask bits: bit[8:6], active, inactive interrupt or exception(0 is active, 1 is inactive)
- 8, A: Asynchronous abort
- 7, I: IRQ
- 6, F: FIQ
- Mode bits(CPSR.M): bit[4:0], express execute level of processor by bits encoding
-
SPSR(Saved Processor Status Register)
- back up CPSR before exception occured
- copy CPSR information instantly when exception occur
- exception handler use this information(mostly, want to restore status before exception occured)
- How to use banked SPSR register?
- usually used for efficient mode exchange- if IRQ exception occur when processor in svc(supervisor) mode
- set SPSR_irq.M as svc mode to record previous mode and set R14_irq
- set CPSR.M to irq mode.(1, 2 occur simultaneously)
- run exception handler(back up SPSR_irq and R14_irq in stack. idk why this process needed)
- restore previous svc mode using SPSR_irq and R14_irq
3.3 ARMv8
3-3-1. General Register
-
ARMv& have 62 general registers that software can use(X0-X30, W0-W30)
- almost same as v7 registers
- but, ARMv8 have two type of register → 32-bits(W), 64-bits(X)
- normally, v8 use X for data processing
-
Special Registers: X30
- X30: Link Regsie(ra)
- SP, PC: unlike v7, v8 have individual register for SP and PC
- total 4 SP for each mode(EL0~3) but PC register is only one
- XZR/WZR
- SPSR
- ELR(Exception Link Register): Return address after handle exception
- only 3 for EL1, EL2, EL3. EL0 doesn't need
3-3-2. PSTATE, SPSR
-
PSTATE
- Very similar to CPSR in v7. but slightly different.
- condition flag: bit[31:28], same as CPSR
- mask bits(PSTATE.<D,A,I,F>): bit[8:6], active, inactive interrupt or exception(0 is active, 1 is inactive)
- 9, D: Debug
- 8, A: System Error
- 7, I: IRQ
- 6, F: FIQ
- Mode bits(CPSR.M): bit[3:2], express execute level of processor by bits encoding → EL0~3
- SS/IL: For debugging
- IL: Illegal Instruction mode(manual exception trigger)
- SS: Single Step mode
- Instruction for set PSTATE
MSR SPSel, #i_1 PSTATE.SP = i→MSR DAIFSet, #i_4 PSTATE.DAIF |= i→MSR DAIFClr, #i_4 PSTATE.DAIF &= ~i→
-
SPSR(Saved Processor Status Register)
- back up CPSR before exception occured
- copy PSTATE information instantly when exception occur
- exception handler use this information(mostly, want to restore status before exception occured)
3-3-4. System Register
- Register for editting specific system configuration
- System register list
- SCTLR_ELx(System Control Register): MMU, Cache
3-3-5. Instruction for System Register
- MRS: read system register
MRS X0, TTBR1_EL1: read TTBR1 and save that value in X0 register
- MSR: write system register
MSR TTBR1_EL1, X0: set TTBR1 as X0 register's value
