GPU Architecture and Memory
GPU Architecture

GPU Memory

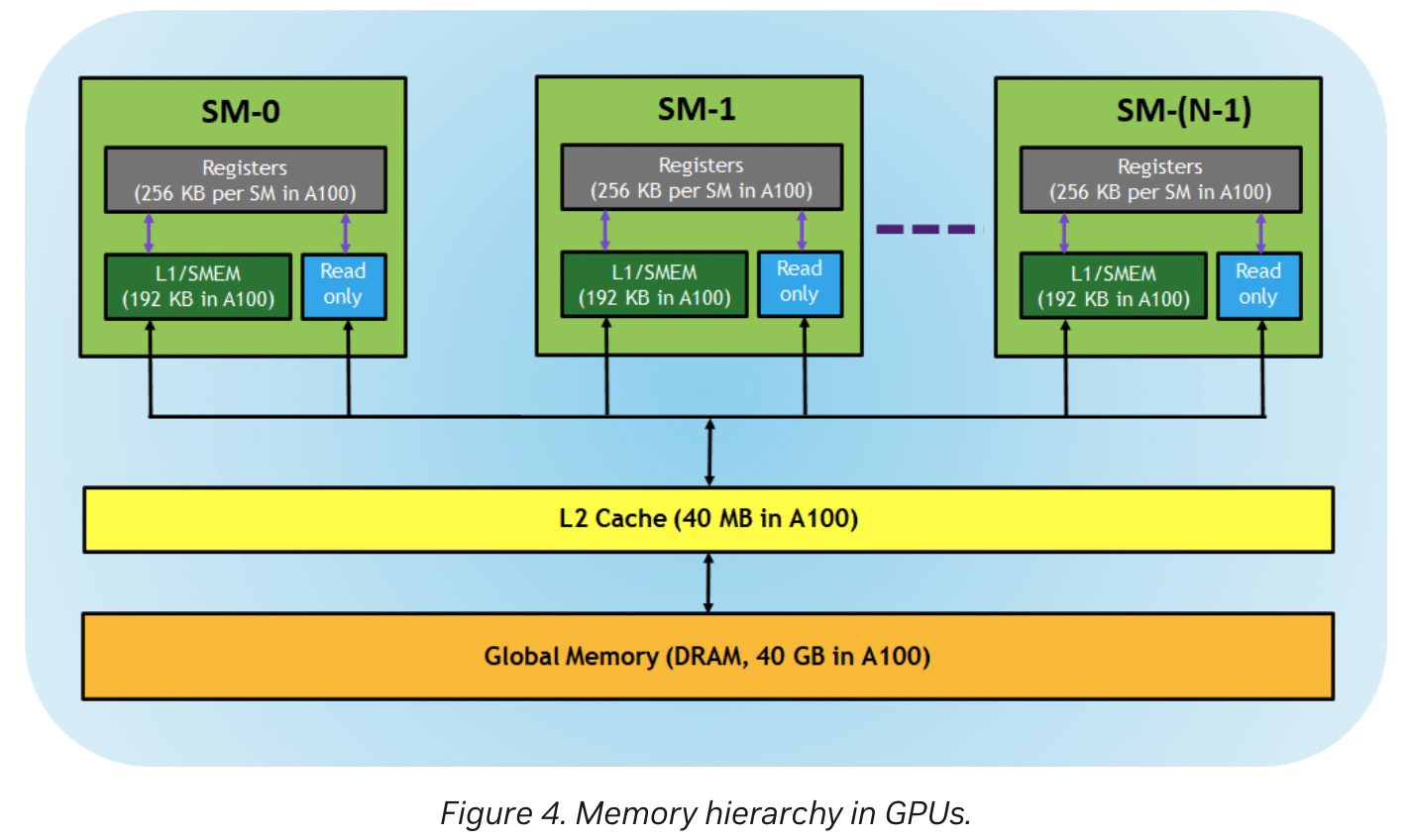
- Registers: These are private to each thread, which means that registers assigned to a thread are not visible to other threads. The compiler makes decisions about register utilization.
- L1/Shared memory (SMEM): Every SM has a fast, on-chip scratchpad memory that can be used as L1 cache and shared memory. All threads in a CUDA block can share shared memory, and all CUDA blocks running on a given SM can share the physical memory resource provided by the SM.
- Read-only memory: Each SM has an instruction cache, constant memory, texture memory, and RO cache, which is read-only to kernel code.
- L2 cache: The L2 cache is shared across all SMs, so every thread in every CUDA block can access this memory. The NVIDIA A100 GPU has increased the L2 cache size to 40 MB as compared to 6 MB in V100 GPUs.
- Global memory: This is the framebuffer size of the GPU and DRAM sitting in the GPU.
https://cvw.cac.cornell.edu/gpu-architecture/gpu-memory/memory_levels
https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/performance/dl-performance-gpu-background/index.html#gpu-arch
https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-best-practices-guide/index.html#device-memory-spaces__memory-spaces-cuda-device
https://timdettmers.com/2023/01/30/which-gpu-for-deep-learning/#comments
