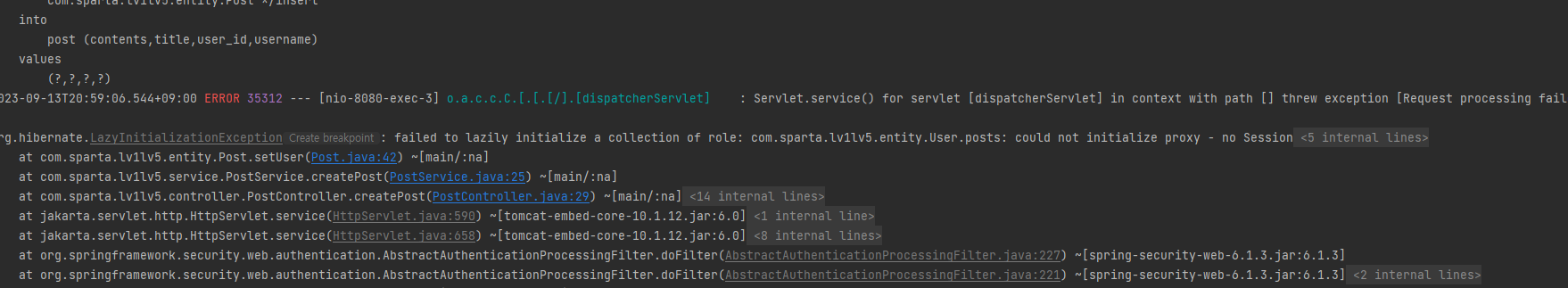
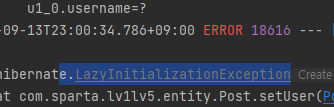
LazyInitializationException 예외
📟컨트롤러
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PostController {
private final PostService postService;
// jwt초기 검증 성공 -> 식별 정보 -> SecurityContext에 저장
// @AuthenticationPrincipal -> 2차적으로 저장된 식별 정보를 불러올 수 있다.
// 게시글 작성
@PostMapping("/post")
public ResponseEntity<PostResponseDto> createPost(@RequestBody PostRequestDto postRequestDto, @AuthenticationPrincipal UserDetailsImpl userDetails){
return postService.createPost(postRequestDto, userDetails.getUser());
}
// 게시글 조회
}📟서비스
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class PostService {
private final PostRepository postRepository;
// 게시글 작성
@Transactional
public ResponseEntity<PostResponseDto> createPost(PostRequestDto postRequestDto, User user) {
Post post = new Post(postRequestDto, user);
postRepository.save(post);
post.setUser(user);
return new ResponseEntity<>(new PostResponseDto(post), HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
- post.setUser(user); -> 이 부분에서 오류가 발생
📟엔티티
@Entity
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Post {
// ----------------------- 필드
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String title;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String username;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String contents;
// ------------------------연관관계 맵핑
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
private User user;
public Post(PostRequestDto postRequestDto, User user) {
this.title = postRequestDto.getTitle();
this.username = postRequestDto.getUsername();
this.contents = postRequestDto.getContents();
this.user = user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
user.getPosts().add(this);
}
}@Entity @Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
// 기본 생성자를 사용하지 않더라도 JPA 구현체가 필요로함 (리플렉션,프록시)
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String username;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String password;
@Column(nullable = false)
@Enumerated(value = EnumType.STRING)
// type = ordinal -> 숫자로 순서대로 저장(id)
// type = string -> 필드 이름명 그대로 저장
private UserRoleEnum role;
// ------------------------연관관계 맵핑
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "user", orphanRemoval = true)
private List<Post> posts = new ArrayList<>();
// 회원가입 로직 -> 사용자 등록
public User(String username, String password, UserRoleEnum role) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.role = role;
}
}📟시도1. Lazy가 원인?
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
private User user;
FetchType.Lazy , .Eager-> 지연, 즉시 로딩의 차이
도서관에서 심리와 관련된 하나의 책을 조회할 때,즉시 = 주제와 관련 없는 모든 책을 조회/지연 = 주제와 과련이 있는 것들만 조회할 때 데이터에 접근정보의 초기화 = 데이터를 로딩할 때
- 그래서 기존에 쓰던 Lazy가 문제인가?
- Eager로 바꾸었으나 똑같은 문제 발생
- 다른 문제
📟시도2. 영속성 컨텍스트 문제
Post post = new Post(postRequestDto, user);
postRepository.save(post);
post.setUser(user);이미 유저 정보를 위에서 넣었기 때문에, 영속성 컨텍스트 깨졌다?
- 트랜젝션이 활성화 되어있고, 영속성 컨텍스트가 활성화되어 있는 동안 먼저
user의 정보를 초기화 - 그래서 이미 로딩된 데이터를 다시 한 번 로딩 하려고 했기 때문에
"could not initialize proxy - no session"과 같은 오류가 발생
트랜잭션은 보장해야 하는 ACID라는 원칙
Atomicity(원자성): 모든 작업이 전부 성공하거나 전부 실패해야 한다는 원칙입니다.
Consistency(일관성): 트랜잭션이 실행되기 전과 실행된 후의 데이터베이스 상태가 일관되어야 합니다.
Isolation(격리성): 동시에 여러 개의 트랜잭션이 실행될 때 각각 독립적으로 실행되는 것처럼 보장되어야 합니다.
Durability(지속성): 성공적으로 완료된 트랜잭션은 영구적으로 반영되어야 합니다.
-일반적으로 영속성 컨텍스트에서는 변경 감지(Dirty Checking) 기능을 통해 엔티티의 상태 변화를 추적하고, 트랜잭션이 커밋될 때 변경된 내용을 데이터베이스에 자동으로 반영. 그러나 위의 코드에서는 post.setUser(user) 호출로 인해 연관된 엔티티인 user 객체가 수정되었음에도 불구하고, 해당 변경 사항은 영속성 컨텍스트가 알지 못하는 상태
🤷♂️🤷♂️🤷♂️ = 트랜젝션이 종료가 된 시점에 데이터에 접근했다.
-따라서 다음과 같은 상황에서 컨텍스트가 종료되었을 수 있습니다:
- @Transactional 어노테이션이 부적절하게 설정되어 트랜잭션이 시작되지 않았거나, 제대로 동작하지 않았을 경우.
- 예외 발생 등의 이유로 롤백이 발생하여 트랜잭션이 강제로 종료된 경우.
- 다른 코드에서 명시적으로 영속성 컨텍스트를 닫거나 초기화한 경우.
💻해결
- 영속성 컨텍스트(Session)가 종료되어 세션이 없는 상태에서 지연 로딩된 엔티티나 컬렉션에 접근하는 경우.
- 트랜잭션이 종료되어 데이터베이스 연결이 끊긴 상태에서 지연 로딩된 엔티티나 컬렉션에 접근하는 경우.
- 즉, 해당 오류의 원인은 지연 로딩된 User 엔티티의 posts 컬렉션을 사용하려고 할 때 영속성 컨텍스트가 이미 종료되거나 세션이 없는 상태여서 초기화할 수 없기 때문
- 결국에는 user를 다루기 때문에 필요 없는 메서드 = setUser
->원인은 추측하기에 이미 처리된 데이터를 로딩하면서 예외가 발생했고, 그로 인해서 영속성 컨텍스트가 종료, 그 종료된 시점에 엔티티 객체를 로딩하려고 했기 때문에 발생
