[백준][20365] 블로그2
그리디 알고리즘 (Greedy algorithm)
import sys
# sys.setrecursionlimit(10**7)
# sys.stdin = open("sample_input.txt", "r")
n = int(sys.stdin.readline())
text = sys.stdin.readline()
color = {"B": 0, "R": 0}
color[text[0]] += 1
for i in range(1, n):
if text[i] != text[i-1]:
color[text[i]] += 1
min_col = min(color["B"], color["R"]) + 1
print(min_col)[백준][1916] 최소비용 구하기
다익스트라 알고리즘 (Dijkstra's algorithm)
import sys
n = int(sys.stdin.readline()) # 도시의 개수 n
m = int(sys.stdin.readline()) # 버스의 개수 m
graph = {}
for i in range(1, n+1):
graph[i] = {}
for _ in range(m):
start, end, cost = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
if end in graph[start]:
graph[start][end] = min(graph[start][end], cost)
else:
graph[start][end] = cost
city1, city2 = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
def dijkstra(graph, start):
# 모든 도시까지의 요금을 무한대로 초기화
costs = {vertex: float('infinity') for vertex in graph}
# 각 도시를 방문했을 때, 이전에 방문한 도시를 기록
previous_nodes = {vertex: None for vertex in graph}
# 시작 도시 요금 0으로 초기화
costs[start] = 0
# 아직 방문하지 않은 모든 도시의 목록을 생성
vertices_to_visit = list(graph.keys())
# 방문하지 않은 도시가 남아있는 동안 계속 반복
while vertices_to_visit:
# 방문하지 않은 도시 중 요금이 가장 낮은 도시 선택
current_vertex = min(
vertices_to_visit, key=lambda vertex: costs[vertex])
# 선택된 도시의 요금이 무한대라면, 나머지 도시는 모두 도달할 수 없는 것이므로 반복 종료
if costs[current_vertex] == float('infinity'):
break
# 선택된 도시에 인접한 모든 도시에 대해 요금 갱신
for neighbor, weight in graph[current_vertex].items():
# 선택된 도시를 거쳐 인접한 도시로 이동하는 요금 계산
alternative_route = costs[current_vertex] + weight
# 계산된 요금이 현재 알려진 요금보다 저렴하면 갱신
if alternative_route < costs[neighbor]:
costs[neighbor] = alternative_route
previous_nodes[neighbor] = current_vertex
# 선택된 도시를 방문했으므로 목록 제거
vertices_to_visit.remove(current_vertex)
# 모든 도시까지의 최소 요금 정보 반환
return costs
print(dijkstra(graph, city1)[city2])[백준][1753] 최단경로
import sys
# sys.setrecursionlimit(10**7)
import heapq
sys.stdin = open("sample_input.txt", "r")
# 정점의 개수 v, 간선의 개수 e
v, e = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
# 시작 정점 k
k = int(sys.stdin.readline())
graph = {}
for i in range(1, v+1):
graph[i] = {}
for _ in range(e):
start, end, w = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
if end in graph[start]:
graph[start][end] = min(graph[start][end], w)
else:
graph[start][end] = w
# 모든 정점까지의 소요시간을 무한대로 초기화
weights = {vertex: float('infinity') for vertex in graph}
heap = []
def dijkstra_heap(graph, start):
# 시작 정점의 가중치는 0으로 초기화
weights[start] = 0
# (가중치, 현재 정점)
heapq.heappush(heap, (0, start))
while heap:
w, n = heapq.heappop(heap)
# 현재 정점과 연결된 다른 정점 확인
for i, j in graph[n].items():
nw = w + j
if nw < weights[i]:
weights[i] = nw
heapq.heappush(heap, (nw, i))
return weights
weights = dijkstra_heap(graph, k)
for w in weights.values():
if w == float('infinity'):
print("INF")
else:
print(w)[백준][14501] 퇴사
DP (동적 프로그래밍)
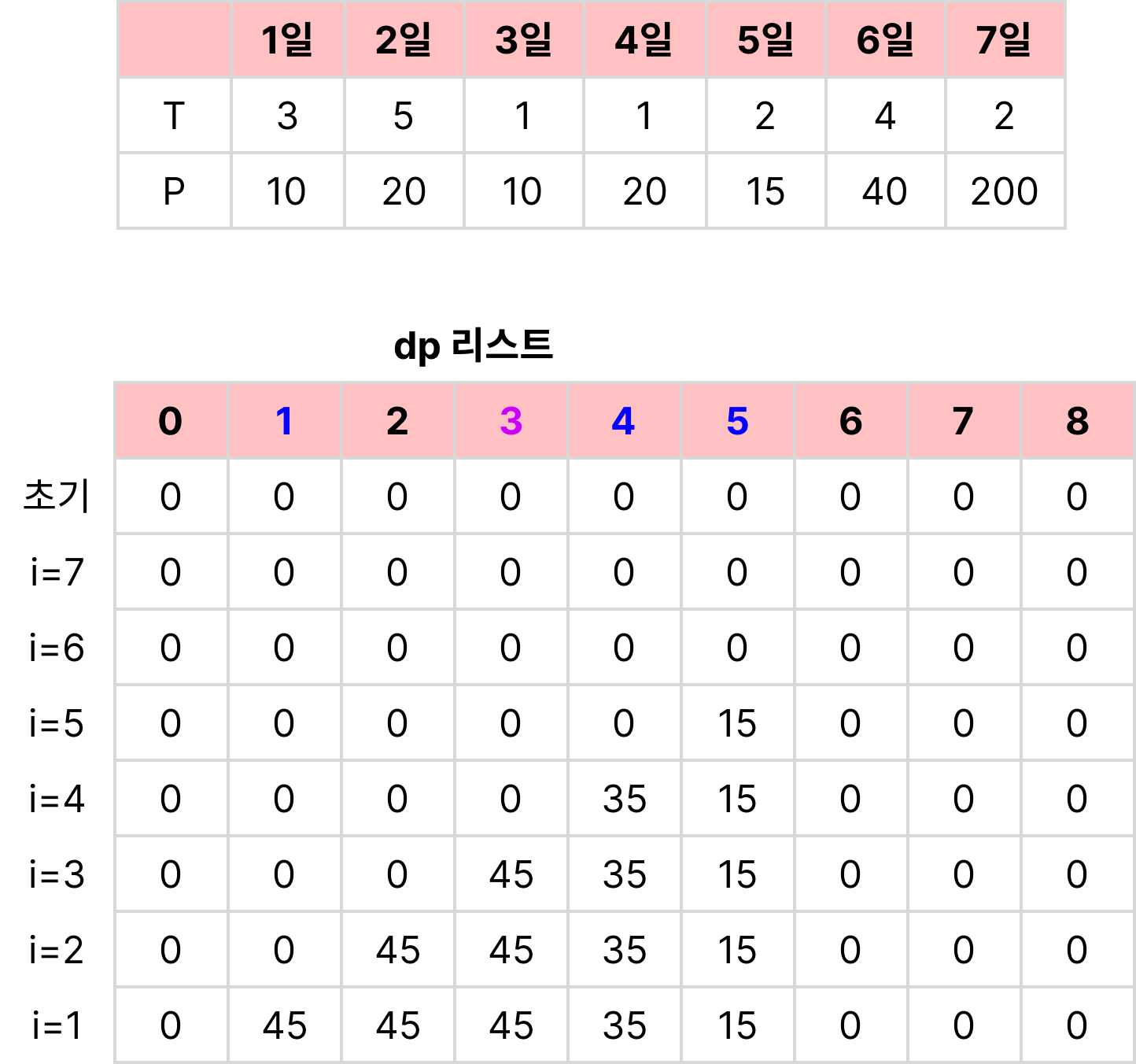
import sys
sys.stdin = open("sample_input.txt", "r")
# 상담이 가능한 기간 n (n+1일에 퇴사)
n = int(sys.stdin.readline())
schedules = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
for i in range(1, n+1):
schedules[i] = list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split()))
# [[], [3, 10], [5, 20], [1, 10], [1, 20], [2, 15], [4, 40], [2, 200]]
print(schedules)
dp = [0 for i in range(n+2)]
# 거꾸로 접근
for i in range(n, 0, -1):
if i + schedules[i][0] - 1 > n: # 퇴사일보다 오래 걸리면
dp[i] = dp[i+1]
else: # 퇴사일보다 짧게 걸리면
dp[i] = max(schedules[i][1] + dp[i + schedules[i][0]], dp[i+1])
print(i)
print(dp)
print(dp[1])[백준][2309] 일곱 난쟁이
완전 탐색 (Brute Force)
import sys
sys.stdin = open("sample_input.txt", "r")
# 일곱 난쟁이의 키 입력 받기
heights = []
for _ in range(9):
heights.append(int(sys.stdin.readline()))
# 키 정렬
heights.sort()
found = False
for i in range(9):
for j in range(i+1, 9):
if sum(heights) - heights[i] - heights[j] == 100:
del1, del2 = i, j # 삭제할 난쟁이 인덱스
found = True
break
if found:
# 두 난쟁이를 리스트에서 제거
heights.pop(del2)
heights.pop(del1)
break
for height in heights:
print(height)[백준][23971] ZOAC 4
이 문제는 for문 돌리면서 완전 탐색처럼 짰더니, 메모리 초과가 떴다.
도저히 해법이 안 보여서 찾아봤더니.. 너무 간단하게 끝났다. 🤯 으악!
import math
import sys
sys.stdin = open("sample_input.txt", "r")
# 행의 개수 h, 열의 개수 w, 세로 n칸, 가로 m칸 이상 비워서 앉기
h, w, n, m = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
print(math.ceil(h/(n+1)) * math.ceil(w/(m+1)))[백준][2667] 단지번호붙이기
import sys
from collections import deque
sys.stdin = open("sample_input.txt", "r")
n = int(sys.stdin.readline())
graph = list(list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().strip())) for _ in range(n))
dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
dy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
blocks = []
def bfs(x, y):
queue = deque([(x, y)])
graph[x][y] = "V"
count = 1
while queue:
x, y = queue.popleft()
for i in range(4):
nx, ny = x + dx[i], y + dy[i]
if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < n:
if graph[nx][ny] == 1:
graph[nx][ny] = "V"
queue.append((nx, ny))
count += 1
return count
for r in range(n):
for c in range(n):
if graph[r][c] == 1:
blocks.append(bfs(r, c))
blocks.sort()
print(len(blocks))
for b in blocks:
print(b)[백준][9184] 신나는 함수 실행
DP (동적 프로그래밍)
import sys
sys.stdin = open("sample_input.txt", "r")
dp = [[[0 for _ in range(21)] for _ in range(21)] for _ in range(21)]
def w(a, b, c):
if a <= 0 or b <= 0 or c <= 0:
return 1
if a > 20 or b > 20 or c > 20:
return w(20, 20, 20)
if dp[a][b][c]:
return dp[a][b][c]
if a < b < c:
dp[a][b][c] = w(a, b, c-1) + w(a, b-1, c-1) - w(a, b-1, c)
return dp[a][b][c]
dp[a][b][c] = w(a-1, b, c) + w(a-1, b-1, c) + \
w(a-1, b, c-1) - w(a-1, b-1, c-1)
return dp[a][b][c]
while True:
a, b, c = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
if a == -1 and b == -1 and c == -1:
break
print(f"w({a}, {b}, {c}) = {w(a, b, c)}")[백준][2565] 전깃줄
DP - LIS 알고리즘
import sys
sys.stdin = open("sample_input.txt", "r")
n = int(sys.stdin.readline())
wires = []
for _ in range(n):
wires.append(list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())))
# [[1, 8], [3, 9], [2, 2], [4, 1], [6, 4], [10, 10], [9, 7], [7, 6]]
wires.sort()
# [[1, 8], [2, 2], [3, 9], [4, 1], [6, 4], [7, 6], [9, 7], [10, 10]]
dp = [1] * n
for i in range(1, n):
for j in range(i):
if wires[i][1] > wires[j][1]:
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1)
#print("i", i, "j", j, dp)
print(n-max(dp))