학원에서 학습한 내용을 개인정리한 글입니다.
수업
다형성
- 객체지향 프로그래밍의 3개 특징 중 하나
- 하나의 행동으로 여러 가지의 일을 수행
- 부모 타입으로 부터 파생된 여러가지 타입의 자식 객체를 부모 클래스 타입 하나로 다룰 수 있는 기술
public void basicTest() {
A_Parent parent = new A_Parent();
A_Child child = new A_Child();
A_Child2 child2 = new A_Child2();
//부모 클래스 타입의 변수는 자식 객체를 저장할 수 있다?
parent = new A_Child();
//X 상속관계가 아님!
// parent = new_A_Child();
//X 자식클래스 타입의 변수에 부모 객체를 저장할 수 있다?
// child = new A_Parnet();
}
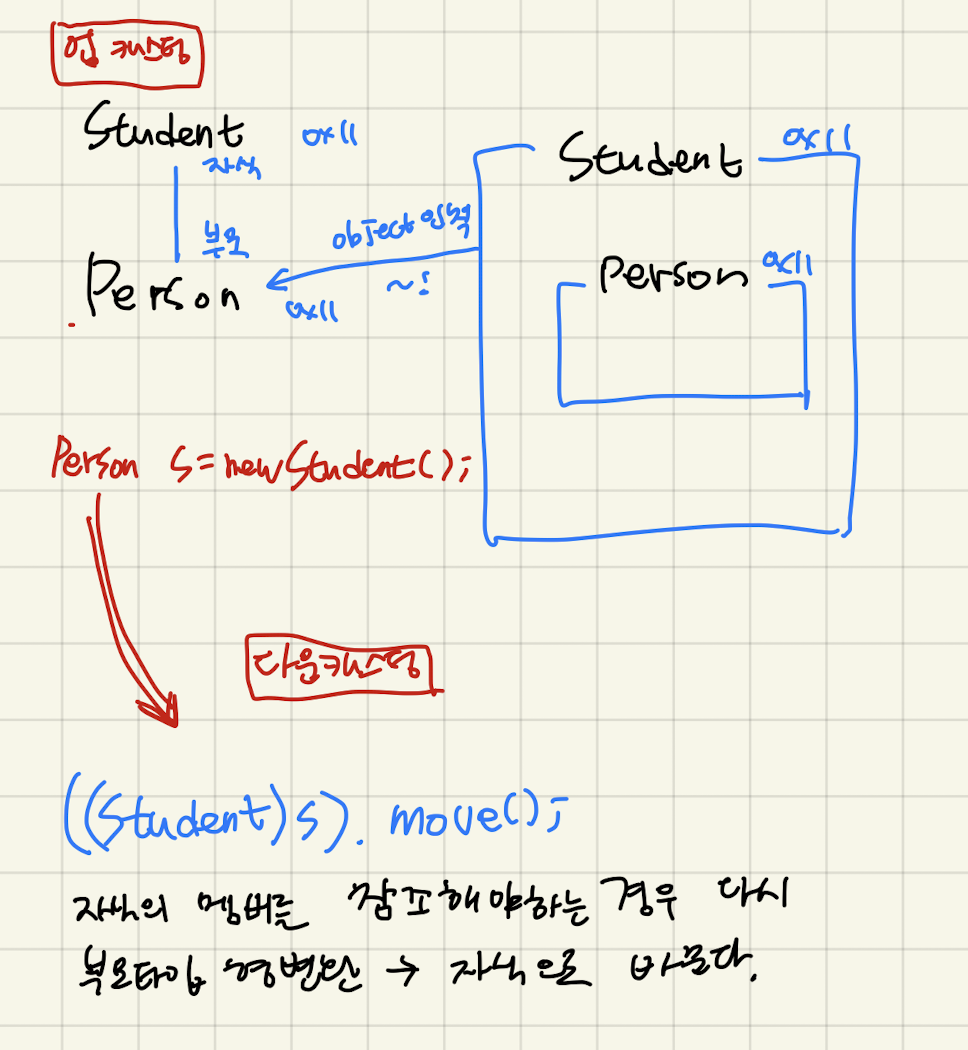
업캐스팅
- 상속 관계에 있는 부모, 자식 클래스 간에 “부모 타입의 참조형 변수”가 모든 자식 타입의 객체 주소를 받을 수 있음.
//Sonata 클래스는 Car 클래스의 후손
Car c = new Sonata();
//Sonata클래스형에서 Car클래스형으로 바뀜
다운캐스팅
- 자식의 멤버를 다시 참조해야하는 경우 업캐스팅 된 부모타입 형변환을 자식으로 바꾼다.
//Sonata 클래스는 Car 클래스의 후손
Car c = new Sonata();
((Sonata)c).moveSonata();
업캐스팅 다운캐스팅 예제
//Parent Class
public class A_Parent {
private String parentData;
public A_Parent() {
}
public A_Parent(String parentData) {
super();
this.parentData = parentData;
}
public String getParentData() {
return parentData;
}
public void setParentData(String parentData) {
this.parentData = parentData;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "parentData=" + parentData;
}
public void dynamicTest() {
System.out.println("부모 메소드");
}
}
//Child Class
public class A_Child extends A_Parent {
private int childAge;
public A_Child() {
}
public A_Child(String parentData, int childAge) {
super(parentData);
this.childAge = childAge;
}
public int getChildAge() {
return childAge;
}
public void setChildAge(int childAge) {
this.childAge = childAge;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "child=" + childAge;
}
public void dynamicTest() {
System.out.println("자식 메소드");
}
}
//Controller
//부모 클래스 타입의 변수에 자식 객체가 저장됐을 때,
//부모에 설정된 내용만 접근이 가능
System.out.println(parent);
parent.setParentData("부모");
System.out.println(parent.getParentData());
//원본 자식객체로 변경하려면 강제형변환을 해야한다
child = (A_Child)parent;
System.out.println(child.getParentData());
((A_Child)parent).setChildAge(100);;
System.out.println(((A_Child)parent).getChildAge());
Object 클래스
//Object 클래스 타입의 변수는 자바에서 사용하는 모든 객체를 저장할 수 있다
Object o;
o = new String("test");
o = new Scanner(System.in);
o = new A_Parent();
o = new A_Child();
객체 배열
//객체배열 이용하기
Employee[] employee = new Employee[5];
Teacher[] teacher = new Teacher[5];
A_Person[] person = new A_Person[10];
person[0] = new Employee("ㅇㅇㅇ", 28, '여', 100, "개발");
person[1] = new Teacher("ㅁㅁㅁ", 28, '여', "영어", 3);
person[2] = new Employee("ㅅㅅㅅ", 28, '여', 100, "개발");
person[3] = new Student("ㅁㅁㅁ", 28, '여', new String[] {"자바"}, 3);
instanceof 연산자
- 참조형 변수가 어떤 클래스 형의 객체 주소를 참조하고 있는지 확인할 때 사용
- 맞으면 true, 틀리면 false
int sCount = 0, eCount = 0, tCount = 0;
int addResult = 0, totalCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <person.length; i++) {
//각 타입에 맞춰서 데이터 출력
//instanceof 연산자 이용
if(person[i] == null) {
continue;
}
if(person[i] instanceof Employee) {
Employee e = (Employee)person[i];
System.out.println(e.toString());
eCount++;
} else if (person[i] instanceof Teacher){
Teacher t = (Teacher)person[i];
System.out.println(t.toString());
tCount++;
if(t.getMajor().equals("영어")) {
System.out.println("선생이고 영어과목: " + t.toString());
}
} else if (person[i] instanceof Student) {
Student s = (Student)person[i];
System.out.println(s.toString());
sCount++;
}
addResult += person[i].getAge();
totalCount ++;
}
바인딩
- 이 함수는 코드랑 연결된다 라고 정해주는 것
- 형변환 하지 않고 그냥 가져와서 쓸 수 있다
동적 바인딩
- 그때그때 바뀌는 약속
- 상속 & 오버라이딩 된 메서드
- 실행 중에 어떤 메소드를 사용할지 정하는 것
public A_Person makePerson(String title) {
switch(title) {
case "student":
return new Student();
case "teacher":
return new Teacher();
case "employee":
return new Employee();
default:
return null;
}
}
정적 바인딩
- 미리 정해진 약속
- 일반 메서드 호출
- 실행되기 전에 메소드가 어떤 객체와 연결될 지 정함
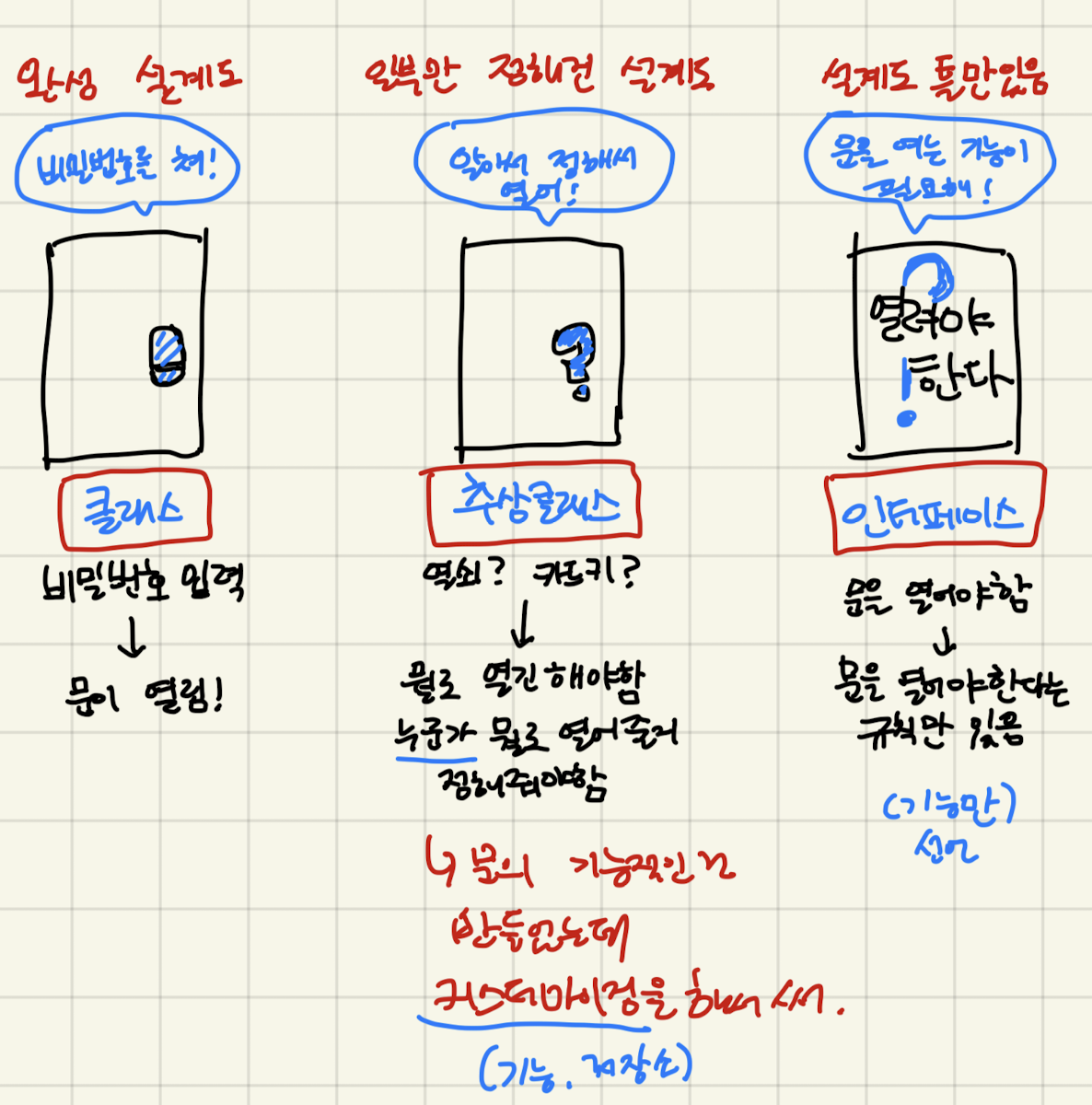
abstract 추상
추상 클래스
- 몸체 없는 메소드를 포함한 클래스
- 미완성인 클래스
- 자체적인 객체 생성 불가
- 반드시 상속하여 객체 생서앻야함
- 참조형 변수 타입으로는 사용 가능
- 구현부가 없음
- 일관된 인터페이스 제공
- 꼭 필요한 기능 강제화?
추상 메소드
- 몸에 없는 메소드
- 구현부를 만듬 (오버라이드)
//추상 클래스 이용
//생성이 불가능함
// _AbstractParent ap = new B_AbstractParent();
//타입으로 선언은 가능
//자기 자신은 생성이 불가능
//자식은 선언 가능
B_AbstractParent ap;
//추상 클래스는 자식클래스가 상속해서 이용하는 클래스
ap = new B_AbstractParentChild();
System.out.println(ap.getTest());
//클래스에 선언된 메소드 중 추상메소드가 있으면
//반드시 추상클래스로 선언해야한다
추상 메소드 예시
package com.poly.model.vo;
public abstract class B_AbstractIncludeAbstractMethod {
public abstract void test();
}
- abstract를 상속받았을 때 abstract가 선언한 메소드를 무조건 포함해야한다.
- 상속 강제?
public class B_AbstractImplement2 extends B_AbstractIncludeAbstractMethod{
@Override
public void test() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("2에서 구현!");
}
}
package com.poly.model.vo;
public class B_AbstractImplement extends B_AbstractIncludeAbstractMethod{
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("구현내용~");
}
- 아래처럼 쓸 수 있다.
B_AbstractIncludeAbstractMethod aiam;
aiam = new B_AbstractImplement();
aiam.test();
aiam = new B_AbstractImplement2();
aiam.test();
public void testCheck(B_AbstractIncludeAbstractMethod param) {
param.test();
}
Interface 인터페이스
- 추상화와 비슷함
- 상수형 필드와 추상 메소드만을 작성할 수 있는 추상 클래스의 변형체
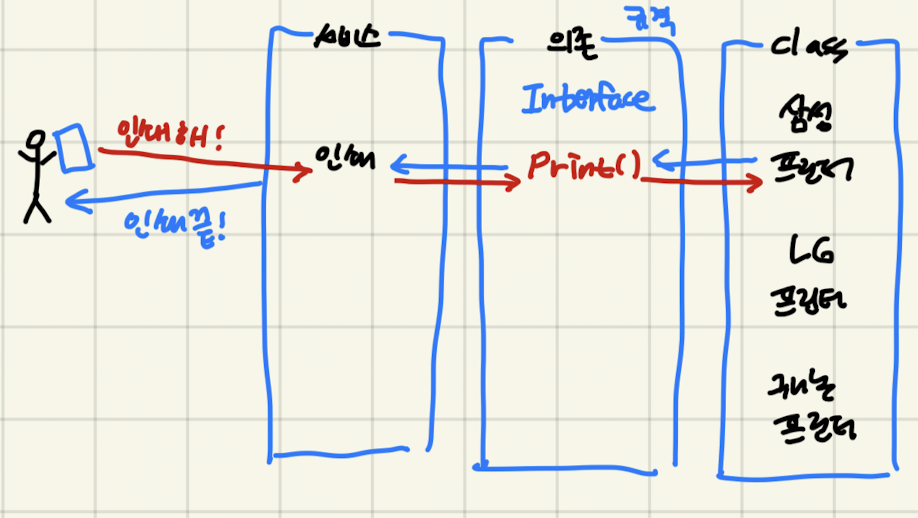
- 인터페이스 다중 상속이 가능
- 인터페이스 구현 클래스는 다수의 인터페이스 구현이 가능
익명 클래스
- 이름 없이 즉석에서 정의하여 사용하는 클래스
- 일회용 객체를 만들때 사용하고, 인터페이스나 추상 클래스를 구현할 때 유용함
Functional Interface
- 인터페이스에 선언된 추상메소드가 한개인 경우 람다 표현식으로 처리가 가능
() -> {} ==> public void ooo(){}
() -> {return 10} ==> public int ooo{}
Data()-> {} ==> public void ooo(paran){}
MyFunctionalInter test = new MyFunctionalInter() {
@Override
public boolean test(String a) {
return a.length()>5;
}
};
test = (msg) -> {return msg.charAt(0) == '자';};
testString((s) -> s.charAt(0) == 't');
public void testString(MyFunctionalInter func) {
if(func.test("test")) {
System.out.println("yes");
}else {
System.out.println("no");
}
}
기본 API
String
- 기본 자료형처럼 사용하는 클래스
- 대입연산 가능, 불변
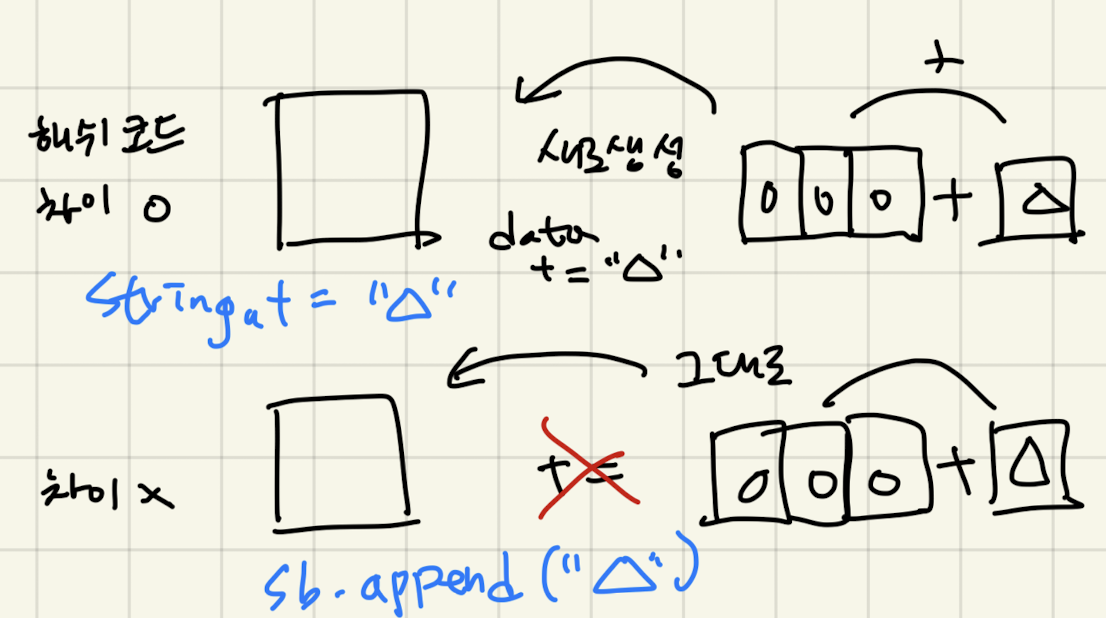
StringBuffer StringBuilder
- 대입연산자를 이용해서 문자열을 저장할 수 없다
- 클래스가 제공하는 메소드를 이용해서 문자열을 저장, 관리

미리 준비
- 다음거 정리.. string, date
- 실습과제, 학생관리프로그램 업그레이드
느낀점
- 계속 프로젝트를 빨리하고싶다는 생각만 하고있다.......ㅠㅠ
