학원에서 학습한 내용을 개인정리한 글입니다.
오늘의 진도
수업
for문
증감식을 생략하기
- 무한 루프가 됨
- i를 { } 안에서 증감하는 식이 있다면 중단할 수 있음
- 이렇게 쓰는것보다 while문을 씀
//증감식을생략 -> 무한루프
for(; i < 10;) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
};;만 하기
- 진짜 무한루프가 됨
- 분기문으로 빠져나옴
for (;;) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
if (i++ > 10) break;
}
초기식, 증감식 변형
- 변수 추가 선언, 증감식 추가 세팅 가능!
- 초기식 같은 경우( j, su) for문 내 { } 구문처럼 계속해서 초기화되지 않는다.
- 처음 실행할 때만 초기화함
for (int j = 0, su = 10; i < 10; j++, su += 10) {
System.out.print(j + " " + su);
}동적으로 반복문 횟수 설정
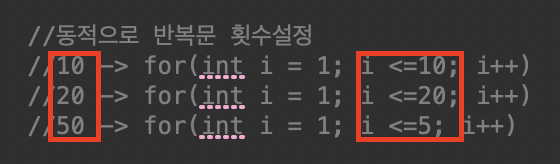
- j와 비교하는 값 (바뀌는 값)만 변수로 빼서 조건식 변경
System.out.print("input num: ");
int inputNum =sc.nextInt();
for(int j = 1; j <= inputNum; j++) {
System.out.println(j);
}실습
사용자에게 숫자 5개를 입력받고 숫자의 총합을 출력
public void sumNumberA() {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.print("insert num: ");
result += sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("result: "+ result);
}[버전 업] 원하는 만큼 입력받고 합계 출력
public void sumNumberB() {
int result = 0, repeatNum = 0;
System.out.print("insert repeatNum: ");
repeatNum = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= repeatNum; i++) {
System.out.print("insert num: ");
result += sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("result: "+ result);
}사용자에게 메세지를 5개 입력받고 출력
public void sumStringA() {
String result = "";
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.print("["+ i +"] insert string: ");
String temp = sc.next();
result += (temp + " ");
}
System.out.println("result: "+ result);
}사용자가 exit 입력할때까지 반복 입력받고 출력
//실습 버전
public void sumStringB() {
String result = "";
int fornum = 0;
for (;;) {
fornum ++;
System.out.print("["+ fornum +"] insert string \n(Enter exit if you want to stop): ");
String temp = sc.next();
// exit 일 때 break
if (temp.equals("exit")) {
System.out.println("* EXIT! ");
break;
// exit 아닐때 계속 반복
} else if (!temp.equals("exit")){
result += (temp + " ");
}
}
System.out.println("result: "+ result);
}
//강사님 버전
//for 문안에 boolean을 넣을 수 있는게 신기해서 추가로 넣어둠
public void sumStringB() {
String result = "";
int fornum = 0;
System.out.println("Enter exit if you want to stop");
for (String temp = ""; !temp.equals("exit");) {
fornum ++;
System.out.print("["+ fornum +"] insert string: ");
temp = sc.nextLine();
if (!temp.equals("exit")) result += temp + " ";
}
System.out.println("* EXIT! ");
System.out.println("result: "+ result);
}입력받은 문자열에 공백이 있는지 확인
public void checkEmptyString() {
System.out.print("insert string: ");
String stringLength = sc.nextLine();
int spcaeNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < stringLength.length(); i++) {
if (stringLength.charAt(i) == ' ') {
spcaeNum += 1;
}
}
if (spcaeNum > 0) {
System.out.println("checkEmpty!: ["+ stringLength +"]: " + spcaeNum );
} else {
System.out.println("no spaces: ["+ stringLength + "]");
}
}입력받은 문자열에 대문자 확인
public void checkUpperCaseString() {
System.out.print("insert string: ");
String stringLength = sc.nextLine();
int upperCaseNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < stringLength.length(); i++) {
if (stringLength.charAt(i) >= 65 &&
stringLength.charAt(i) <= 90) {
upperCaseNum += 1; }
}
if (upperCaseNum > 0) {
System.out.println("check uppercase!: ["+ stringLength +"]:" + upperCaseNum);
} else {
System.out.println("no uppercaseces: [" + stringLength + "]");
}
}중첩 반복문
- for문 안에 for문이 있는 구문
- e.g. 구구단 (21, 22….) (31, 32…)
- 활용을 많이하기때문에 잘 알아두면 좋음
//구구단
for (int i = 2; i <= 9; i++) {
System.out.println(i + " 단 ");
for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++) {
System.out.println(i + " X "+ j + " = " + i * j);
}
System.out.println("------------ ");
};While문
- 반복문 구현방법중 하나
- 의도적인 무한루프 생성
- while(조건식){로직[증감식/분기문]}
int n = 1;
while ( n <= 10 ) {
n++;
System.out.println("n: " + n);
}
//무한루프
int su = 1;
while(true) {
System.out.println("while");
if (su++ > 10) break;
}
//do~whiol구문
int num = 1;
do {
System.out.println ("=================");
num ++;
} while( num < 10 );실습
3의 배수만 입력
int su = 1;
while (su % 3 != 0) {
System.out.print("수 입력: ");
su = sc.nextInt();
if(su%3 != 0) {
System.out.println("3의 배수를 입력하세요");
}
}특정 문자열 받을 때까지 계속 입력
String msg = "", totalMsg = "";
while ( !msg.equals("END") ) {
System.out.print("메세지: ");
msg=sc.nextLine();
totalMsg += msg.equals("END") ? " " : msg ;
}간단 메뉴판 입력
//메뉴 프로그램 작동
int choice = 0;
while (choice !=9) {
System.out.println ("===== 점심 =====");
System.out.println ("1. 마라");
System.out.println ("2.돈까스");
System.out.println ("3.구내식당");
System.out.println ("4.일본라멘");
System.out.println ("5.");
System.out.println ("9. 종료");
System.out.println ("=================");
choice = sc.nextInt();
}실습
카페 주문받는 프로그램 만들어보기
-
원하는 메뉴를 모두 주문받고(음료갯수포함) 주문받은 결과(메뉴, 갯수)와 총 금액을 출력해주는 기능을 구현
-
다음엔 포맷 이용해보기
-
변경전
public void myMenu() {
//String menuformat = "%d. %s %d"
String allOrderString = "";
int allOrderPrice = 0;
int order1Price = 3000, order1Num = 0;
int order2Price = 4500, order2Num = 0;
int order3Price = 6000, order3Num = 0;
int order4Price = 6000, order4Num = 0;
int order5Price = 5000, order5Num = 0;
int selectNum = 404;
while (selectNum != 0) {
System.out.println("========주문==========");
System.out.println("1. 아메리카노 ₩3000");
System.out.println("2. 카페라떼 ₩4500");
System.out.println("3. 자바칩프라프치노 ₩6000");
System.out.println("4. 자몽허니블랙티 ₩6000");
System.out.println("5. 아이스티 ₩5000");
System.out.println("0. 주문종료");
System.out.println("=====================");
System.out.print("input order number: ");
selectNum = sc.nextInt();
switch (selectNum) {
case 1:
order1Num += 1;
System.out.println("1. 아메리카노 3000: " + order1Num);
break;
case 2:
order2Num += 1;
System.out.println("2. 카페라떼 4500: " + order2Num);
break;
case 3:
order3Num += 1;
System.out.println("3. 자바칩프라프치노 6000: " + order3Num);
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("4. 자몽허니블랙티 6000: " + order4Num);
order4Num += 1;
break;
case 5:
order5Num += 1;
System.out.println("5. 아이스티 5000: " + order5Num);
break;
case 0:
order5Num += 1;
System.out.println("주문 종료!");
System.out.println("=====================");
break;
default:
System.out.println("wrong number");
break;
}
}
if (order1Num > 0) {
allOrderPrice += (order1Price * order1Num);
allOrderString += ("아메리카노 " + order1Num + "잔, " + (order1Price * order1Num) + "원" + "\n");
}
if (order2Num > 0) {
allOrderPrice += (order2Price * order2Num);
allOrderString += ("카페라떼 " + order2Num + "잔, " + (order2Price * order2Num) + "원" + "\n");
}
if (order3Num > 0) {
allOrderPrice += (order3Price * order3Num);
allOrderString += ("자바칩프라푸치노 " + order3Num + "잔, " + (order3Price * order3Num) + "원" + "\n");
}
if (order4Num > 0) {
allOrderPrice += (order4Price * order4Num);
allOrderString += ("자몽허니블랙티 " + order4Num + "잔, " + (order4Price * order4Num) + "원" + "\n");
}
if (order5Num > 0) {
allOrderPrice += (order5Price * order5Num);
allOrderString += ("아이스티 " + order5Num + "잔, " + (order5Price * order5Num) + "원" + "\n");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(allOrderString);
System.out.println("=====================");
System.out.println("총 금액: " + allOrderPrice + "원");
System.out.println("=====================");
}- 변경 후
- 변수가 너무 많아서 count로 통일. 배열 사용하면 될 문제라 우선 패스하기로 함
- if문 반복 삭제
public void myMenu() {
//String menuformat = "%d. %s %d"
String allOrderString = "";
int allOrderPrice = 0;
int order1Price = 3000;
int order2Price = 4500;
int order3Price = 6000;
int order4Price = 6000;
int order5Price = 5000;
int selectNum = 404, count = 0;
while (selectNum != 0) {
System.out.println("========주문==========");
System.out.println("1. 아메리카노 ₩3000");
System.out.println("2. 카페라떼 ₩4500");
System.out.println("3. 자바칩프라프치노 ₩6000");
System.out.println("4. 자몽허니블랙티 ₩6000");
System.out.println("5. 아이스티 ₩5000");
System.out.println("0. 주문종료");
System.out.println("=====================");
System.out.print("input order menu: ");
selectNum = sc.nextInt();
if (selectNum != 0) {
System.out.printf("input count: ");
count = sc.nextInt();
}
switch (selectNum) {
case 1:
allOrderPrice += (order1Price * count);
allOrderString += ("아메리카노 " + count + "잔 " + (order1Price * count) + "원" + "\n");
break;
case 2:
allOrderPrice += (order2Price * count);
allOrderString += ("카페라떼 " + count + "잔 " + (order2Price * count) + "원" + "\n");
break;
case 3:
allOrderPrice += (order3Price * count);
allOrderString += ("자바칩프라푸치노 " + count + "잔 " + (order3Price * count) + "원" + "\n");
break;
case 4:
allOrderPrice += (order4Price * count);
allOrderString += ("자몽허니블랙티 " + count + "잔 " + (order4Price * count) + "원" + "\n");
break;
case 5:
allOrderPrice += (order5Price * count);
allOrderString += ("아이스티 " + count + "잔 " + (order5Price * count) + "원" + "\n");
break;
case 0:
System.out.println("주문 종료!");
System.out.println("=====================");
break;
default:
System.out.println("wrong number");
break;
}
System.out.println(allOrderString);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(allOrderString);
System.out.println("=====================");
System.out.println("총 금액: " + allOrderPrice + "원");
System.out.println("=====================");
}QNA
Temi: 변수를 여러개 만들어서 따로 관리하는 것이 나은지, 하나 만들어서 돌려쓰지만 가끔 예외처리가 필요한게 나은지
Teacher: 고객에 따라 다르겠지만, 변수가 여러개 생기면 유지보수가 힘들어져서 웬만해선 많이 만들진않음
분기문
break
- 실행되는 로직 중단
- 특정코드 생략하고 진행하는 로직 구성할 때 사용
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
if(i > 5) {
break;
}
}- 중첩 반복문 break 활용
//중첩 반복문에서 break문 활용
//t: 해당 블럭만 해당
t:
for (int i = 2; i <= 9; i++) {
System.out.println(i + " 단 ");
for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++) {
//t 멈추게함
if(j == 5) break t;
System.out.println(i + " X "+ j + " = " + i * j);
}
System.out.println("------------ ");
};continue
- 실행하는 로직 생략
//짝수는 생략
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if(i%2 == 0) {
continue;
}
System.out.println(i);
}실습
입력받은 숫자만큼 정방향 절반 피라미드 쌓기
public void practice13(){
System.out.print("input floor number: ");
int inputNum = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= inputNum; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print("#");
}
System.out.print("*");
System.out.println();
}
}입력받은 숫자만큼 역방향 절반 피라미드 쌓기
System.out.print("input floor number: ");
int inputNum = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = inputNum; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print("#");
}
System.out.print("*");
System.out.println();
}랜덤
자바에서 랜덤값 가져오기
- Math.random() 메소드 사용
- Random 클래스에서 제공하는 기능을 이용
- 0~1 사이 임의의 수를 출력
public void randomTest() {
System.out.println("Math.random(): " + Math.random());
//정수형으로 출력
System.out.println("Math.random(): " + (int)(Math.random() * 10));
//0~4까지
System.out.println("Math.random(): " + (int)(Math.random() * 5));
//1~5까지
System.out.println("Math.random(): " + (int)(Math.random() * 5) + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
int random = (int)(Math.random() * 45) + 1;
System.out.print(random + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//random class
Random rnd = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
System.out.print(rnd.nextInt(45)+1 + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}미리 준비
- 주말에 실습과제하기
- 다음 주에 배열이랑 2차원한다던데 잘 따라가면 좋겠다..
- 리프레쉬하기
하지만 실습과제도 끝내주게 하기
느낀점
- 생각보다 진도 따라가기 급급해서 실습시간에 이전보다 시간을 쏟기가 어렵당
- 그래도 집가서 복습하고 실습다시하면 괜찮긴한데 체력이 조금 모자란거같기도..
- 피라미드 손파일러로 성공해서 뿌듯하다
- 반에 전공자나 경력자들이 있어서 더 열심히해야겠다 생각한다ㅏ~!! !화이팅!


