
객체지향 프로그래밍
(자바스크립트에서 객체지향을 하는 게 맞나요? | 요즘IT)[https://yozm.wishket.com/magazine/detail/1396/]을 참고하여 작성
절차적(구조적)으로 덩치가 큰 프로그래밍을 하다가 변수명 관리가 복잡해졌다.
-> 데이터를 묶어서 관리하자 = 구조체 (변수들의 집합)
-> 구조체에 항상 쓰이는 함수들도 하나로 합치자 = 클래스 (변수와 함수까지 포함하는 개념)
데이터와 처리 방식이 하나의 모듈과 관리되면서 마치 작은 프로그램이 독립적으로 돌아가는 형태를 띄게 되어 덩치가 큰 프로그래밍을 작성하더라도 작은 부품을 미리 만들어두고 이를 조립하고 결합하는 방식으로 개발할 수 있게 되었다.
구조체와 함수를 합쳐서 선언하는 것을 Class, Class를 통해 만들어질 실체를 Object, 구현된 구체적인 실체를 instance라고 한다.
/* 클래스 */
public class Animal {
...
}
/* 객체와 인스턴스 */
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal cat, dog; // '객체'
// 인스턴스화
cat = new Animal(); // cat은 Animal 클래스의 '인스턴스'(객체를 메모리에 할당)
dog = new Animal(); // dog은 Animal 클래스의 '인스턴스'(객체를 메모리에 할당)
}
}
https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/09/17/class-object-instance.html객체지향 프로그래밍의 특징
캡슐화
외부로 노출해야 하는 값과 내부에서만 사용하는 값을 구분한다.
내부 데이터에 바로 접근을 하지 못하게 하고 필요한 메소드만 열어두는 특성을 캡슐화라고 한다.
상속
객체의 일부분만 재사용하는 방식. 객체의 공통된 부분만 따로 만들어서 그 코드를 같이 상속받아서 활용을 하고 나머지 달라지는 것들만 각자 코드를 작성한다.
추상화
공통적인 부분을 모아서 상위의 개념으로 새롭게 이름을 붙이는 것을 추상화라고 한다.
ex) 사과, 바나나를 모아서 과일이라고 부름.
다형성
상속과 추상화를 통해서 객체를 만들면, 하위 타입인 여러가지 타입으로 참조할 수 있다는 것이 다형성이다.
객체지향을 더 잘하기 위한 원칙: SOLID 원칙
SRP 단일책임원칙
- 클래스는 단 한개의 책임을 가져야 한다.
- 클래스를 변경하는 이유는 단 하나여야 한다.
- 이를 지키지 않으면, 한 책임의 변경에 의해 다른 책임과 관련된 코드에 영향을 미칠 수 있다.
LSP 리스코프
- 하위 타입 객체는 상위 타입 객체에서 가능한 행위를 수행할 수 있어야 한다.
- 즉, 상위 타입 객체를 하위 타입 객체로 치환해도 정상적으로 동작해야 한다. - 상속관계에서는 일반화 관계가 성립해야 한다는 것 (일관성있는 관계인지)
- 상속 관계가 아닌 클래스를 상속 관계로 설정하면, 이 원칙이 위배된다 (재사용 목적으로 사용하는 경우)
Class와 Prototype
prototype 사용법
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 프로토타입 객체에 메소드 정의
Person.prototype.setName = function (name) {
this.name = name;
};
// 프로토타입 객체에 메소드 정의
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
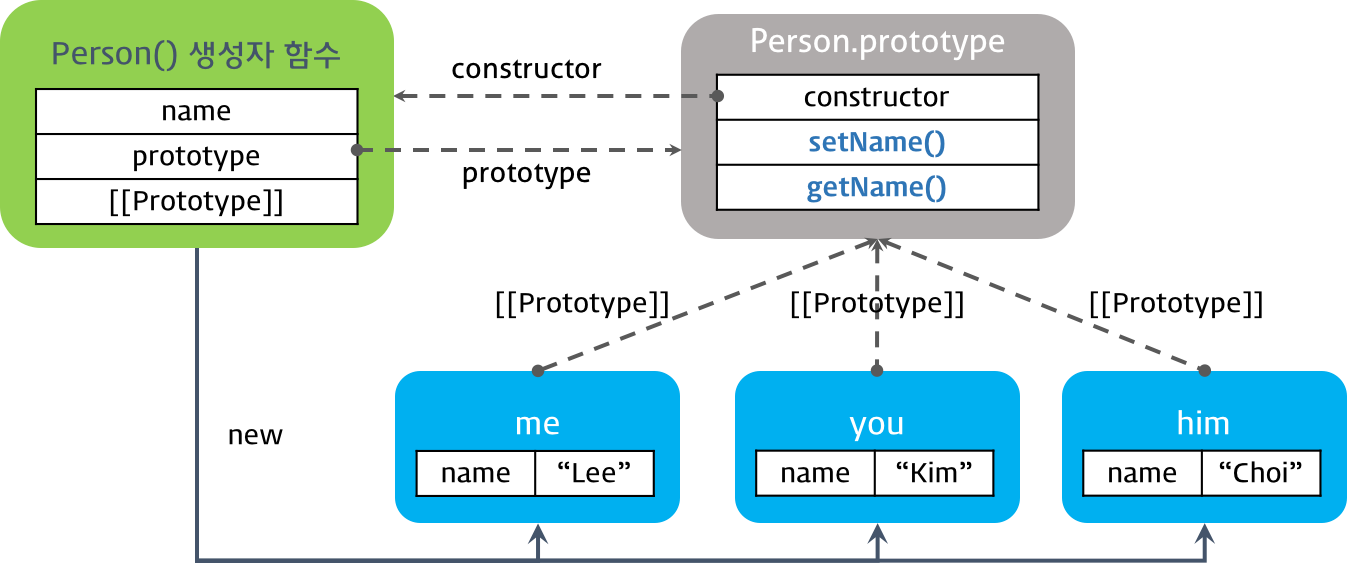
var me = new Person('Lee');
var you = new Person('Kim');
var him = new Person('choi');
console.log(Person.prototype);
// Person { setName: [Function], getName: [Function] }
console.log(me); // Person { name: 'Lee' }
console.log(you); // Person { name: 'Kim' }
console.log(him); // Person { name: 'choi' }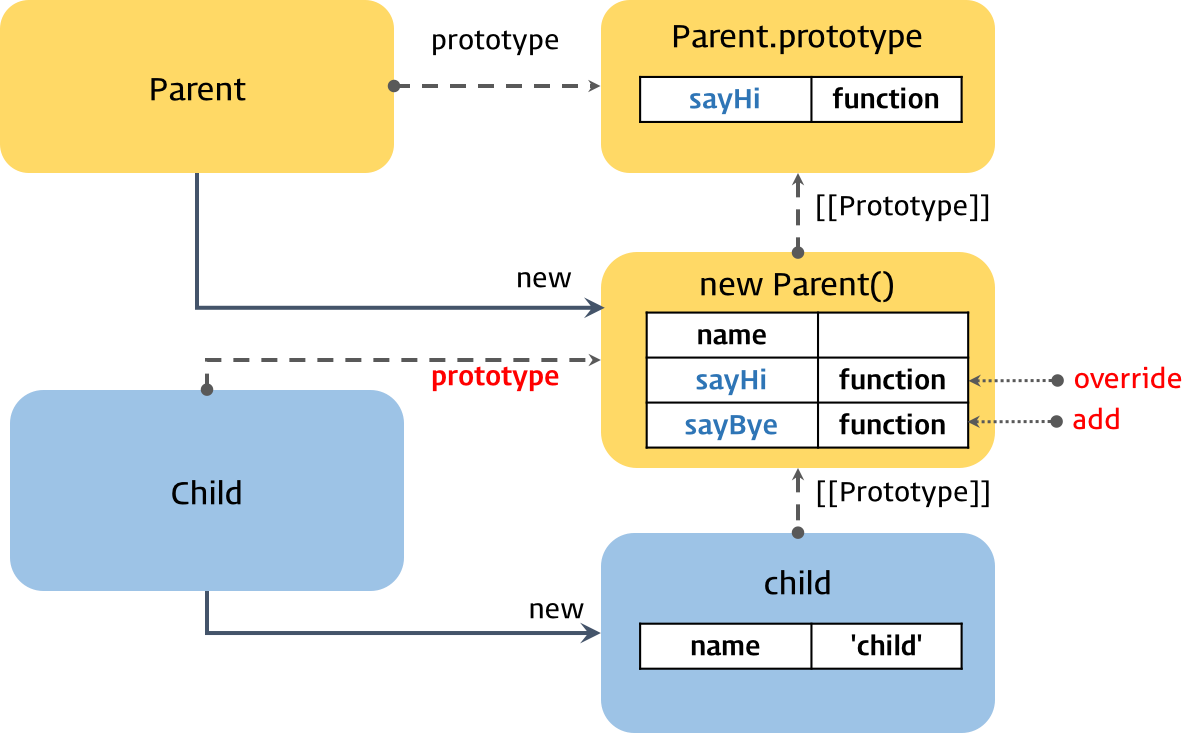
// 부모 생성자 함수
var Parent = (function () {
// Constructor
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// method
Parent.prototype.sayHi = function () {
console.log('Hi! ' + this.name);
};
// return constructor
return Parent;
}());
// 자식 생성자 함수
var Child = (function () {
// Constructor
function Child(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 자식 생성자 함수의 프로토타입 객체를 부모 생성자 함수의 인스턴스로 교체.
Child.prototype = new Parent(); // ②
// 메소드 오버라이드
Child.prototype.sayHi = function () {
console.log('안녕하세요! ' + this.name);
};
// sayBye 메소드는 Parent 생성자함수의 인스턴스에 위치된다
Child.prototype.sayBye = function () {
console.log('안녕히가세요! ' + this.name);
};
// return constructor
return Child;
}());
var child = new Child('child'); // ①
console.log(child); // Parent { name: 'child' }
console.log(Child.prototype); // Parent { name: undefined, sayHi: [Function], sayBye: [Function] }
child.sayHi(); // 안녕하세요! child
child.sayBye(); // 안녕히가세요! child
console.log(child instanceof Parent); // true
console.log(child instanceof Child); // trueClass
ES6에서 도입된 문법이다.
사실 Javascript 객체 지향의 근간인 prototype 방식을 문법적으로 class처럼 보이게 만들어준 도구에 불과하다.
this와 super
this
this | mdn을 참고
this의 값은 함수를 어떻게 호출했는지에 따라 결정된다.
- ES5에서는 this값을 설정할 수 있는 bind() 메서드가 도입됨.
- ES2015에서는 bind()을 제공하지 않는 화살표 함수가 도입됨.
(렉시컬 컨텍스트 안의 this 값을 유지함)
+) prototye에 메서드를 추가할 때 화살표 함수와 this를 쓰면 찾지 못한다.
function Tmp {
this.name = "tmp"
}
Tmp.prototype.method1 = () => {
console.log(this.name); // 참조 오류
}- this는 자신이 속한 객체 또는 자신이 생성할 인스턴스를 가리키는 자기 참조 변수이다.
- this를 통해 자신이 속한 객체 또는 자신이 생성할 인스턴스의 프로퍼티나 메서드를 참조할 수 있다.
- 일반적으로 객체의 매서드 내부 또는 생성자 함수 내부에서만 의미가 있다.
super
super | mdn을 참고
super 키워드는 부모 오브젝트의 함수를 호출할 때 사용한다.
class Polygon {
constructor(height, width) {
this.name = 'Polygon';
this.height = height;
this.width = width;
}
sayName() {
console.log('Hi, I am a ', this.name + '.');
}
}
class Square extends Polygon {
constructor(length) {
this.height; // 참조 오류
super(length, length);
this.name = 'Square';
}
get area() {
return this.height * this.width;
}
set area(value) {
this.area = value;
}
}- prototype에서도 / 생성자 외 다른 메서드도 사용 가능
var obj1 = {
method1() {
console.log("method 1");
}
}
var obj2 = {
method2() {
super.method1();
}
}
Object.setPrototypeOf(obj2, obj1);
obj2.method2(); // logs "method 1"객체의 인스턴스 비교하기
- 객체 내부의 값 비교하기
- 키를 통해 객체를 순회하면서 값을 체크하기
- JSON.stringify 사용하기
JSNO.stringify(obj1) === JSON.stringify(obj2)

너무 좋은 글이네요. 공유해주셔서 감사합니다.