Q. How to develop your own Internet application?
A. You should write programs(in C, Python, ...) on host using socket interface.
Socket interface : An API for correct delivery through the Internet.
There are two types for interfaces(TCP, UDP), which one to use depends on user selection according to app feature.
Internet Protocol Suite at the Transport Layer ( TCP, UDP )
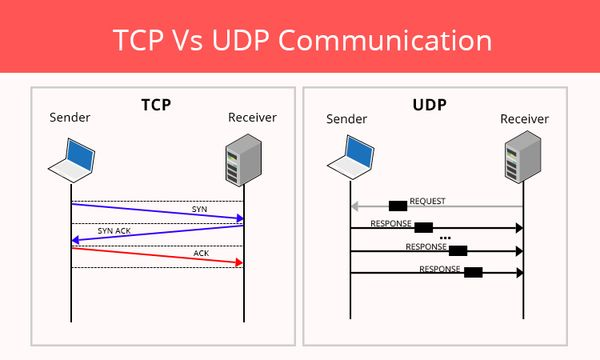
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is an important network protocol that allows two hosts to connect and exchange data streams. TCP ensures that data and packets are delivered in the order they are sent.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a communication protocol used over the Internet, especially for time-sensitive transfers such as video playback or DNS lookups. With this protocol, a connection is not formally established until data is sent, which speeds up communication.
TCP versus UDP
| Feature | TCP | UDP |
|---|---|---|
| Connection status | Requires an established connection to transmit data | Connectionless protocol with no requirements |
| Data sequencing | Able to sequence | Unable to sequence |
| Guaranteed delivery | Can guarantee delivery of data to the destination router | Cannot guarantee delivery of data to the destination |
| Retransmission of data | Retransmission of lost packets is possible | No retransmission of lost packets |
| Error checking | Extensive error checking and acknowledgment of data | Basic error checking mechanism using checksums |
| Method of transfer | Data is read as a byte stream | UDP packets with defined boundaries |
| Speed | Slower than UDP | Faster than TCP |
| Broadcasting | Does not support Broadcasting | Does support Broadcasting |
| Optimal use | Used by HTTPS, HTTP, etc | Video conferencing, streaming, DNS, etc |
Reference
https://www.lifesize.com/blog/tcp-vs-udp/
https://www.colocationamerica.com/blog/tcp-ip-vs-udp
