디지털 신호 처리(DSP) Study
Source
- https://www.kaggle.com/code/faressayah/signal-processing-with-python
- https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/technical-articles/an-introduction-to-digital-signal-processing/
- http://preview.hanbit.co.kr/4030/sample.pdf
Signal Processing
- Signal Processing is the field of science which involves the manipulation of signal from time domain to frequency and vice versa, smoothing the signal, separating the noise from signal i.e filtering, extracting information from the signal.
- Signals which exist in nature are continuous signal. Continuous-time(or analog) signals exist for the continuous interval (t1, t2) can range from to
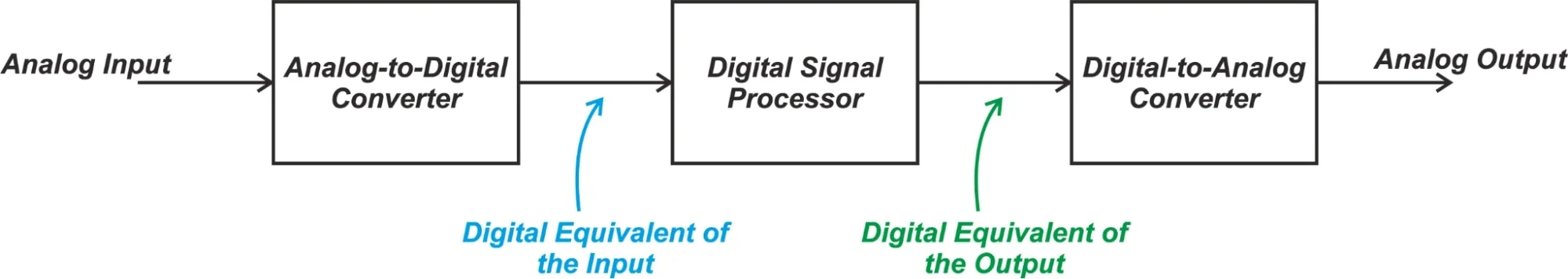
Basics of Signal Processing System
- Since computer needs digital signals for processing, therefore, in order to use an analog signal on a computer it must be digitized with an analog-to-digital converter.
- Thus, there is a need for an interface between the analog signal and the digital signal processor.
Core Components of Signal Processing
-
1) Sampling: sampling is the reduction of a continuous-time signal to a discrete-time signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave, a continuous signal, to a sequence of samples, a discrete-time signal.
-
2) Quantization: quantization is the proces of mapping input values from large set(often continuous set) to output values in a (countable) smaller set, often with a finite number of elements. Rouding and Truncation are typical examples of quantization processes.
-
3) Encoding : After each sample is quantized and the number of bits per smaple is decided, each sample can be changed to an nb-bit code word. The number of bits for each sample is determined from the number of quantization levels. If the number of quantization level is
L, the number of bits isnb=log2.L
