문제
7569 - 토마토
풀이
알고리즘
-
토마토 창고를 3차원 좌표계로 생각하고 입력값 M(가로), N(세로), H(높이)를 3차원 배열을 선언한다.
int box[MAX][MAX][MAX]; -
이 때 우리는 익어있는 토마토(1)의 좌표과 익지 않은 토마토(0)의 갯수를 입력과 동시에 받아준다.
익어있는 토마토의 좌표는 BFS를 시작할 지점을 알기 위해서 필요하다.
익지 않은 토마토의 갯수는 '토마토가 모두 익지는 못하는 상황'을 알기 위해 필요하다.
그럼 아래와 같이 입력을 받을 수 있다.
// Tomato => {h, y, x}
vector<Tomato> targets;
// 높이만큼 반복
for (int i = 0; i < H; i++)
{
// 세로(행)만큼 반복
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
// 가로(열)만큼 반복
for (int k = 0; k < M; k++)
{
// box[높이][세로][가로]
cin >> box[i][j][k];
// 익어있는 토마토의 좌표
if (box[i][j][k] == 1)
targets.push_back({i, j, k});
// 익지 않은 토마토의 갯수
else if (box[i][j][k] == 0)
zero++;
}
}
}- 3차원 좌표계를 사용하여 BFS를 수행해야하니 다음 좌표 이동을 위한
dh[], dy[], dx[]배열을 만들고 값을 넣어주자.
아래 그림을 보면 h,y,x를 축으로 사용한 3차원 좌표계를 볼 수 있다.(좌표축의 순서나 이름은 다르지만 x,y,z 좌표계와 다를 것은 없고 자기 입맛에 맞게 편하게 만들면 된다. 수학시간 같고 참 좋다.)
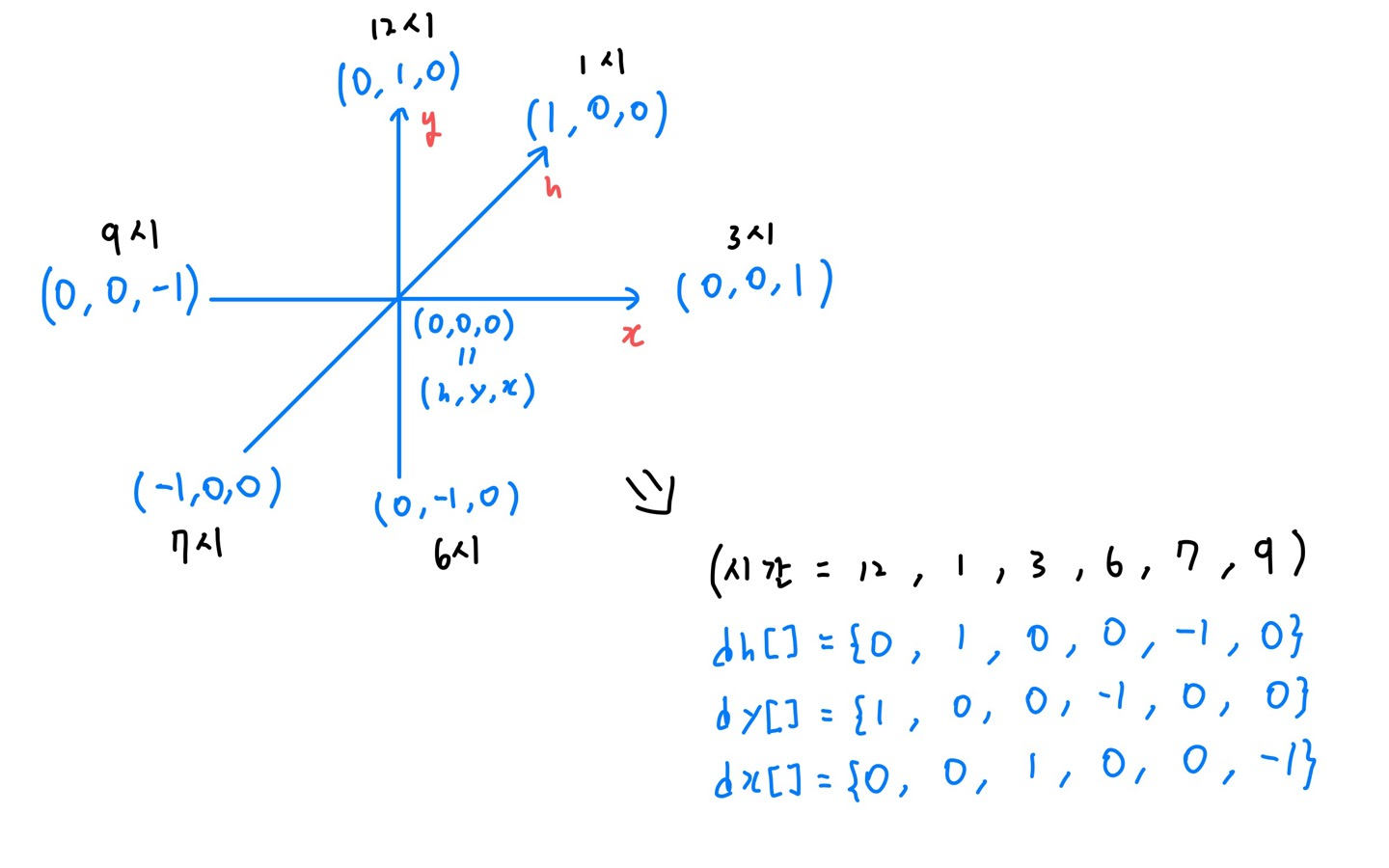
// 12시, 1시, 3시, 6시, 7시, 9시
int dh[] = {0, 1, 0, 0, -1, 0};
int dy[] = {1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0};
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, 0, 0, -1};- 이제 밑작업은 모두 마쳤으니 일반적인 BFS를 수행하자.
3차원 좌표계라 겁날 수도 있으나 그냥 2차원 좌표계로 수행해왔던 BFS의 단계마다 코드 한 줄씩 늘어난 버전이라고 생각하면 편하다.
int Solve(vector<Tomato> &targets)
{
// 익을 수 있는 토마토가 모두 익는데 걸리는 일 수
int day = 0;
// Tomato => {h, y, x}
queue<Tomato> q;
// targets => 시작 시 익어있는 토마토들의 좌표
// queue에 targets를 모두 넣어두고 한 번에 BFS를 수행한다.
for (auto target : targets)
q.push(target);
// BFS
while (!q.empty())
{
int h = q.front().h;
int y = q.front().y;
int x = q.front().x;
q.pop();
// 일 수 업데이트
// 시작 시 day = 1 이다.
// 익은 토마토의 좌표부터 탐색하기 때문에(익은 토마토 = 1)
day = max(day, box[h][y][x]);
// dh[], dy[], dx[] 배열 원소 갯수 = 6
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
int nextH = h + dh[i];
int nextY = y + dy[i];
int nextX = x + dx[i];
if (nextH < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX < 0 ||
nextH >= H || nextY >= N || nextX >= M)
continue;
// 다음 좌표에 토마토가 없거나 || 이미 익은 토마토라면 => 건너뛴다.
if (box[nextH][nextY][nextX] == -1 || box[nextH][nextY][nextX] >= 1)
continue;
// 다음 좌표 = 현재 날짜 + 1
// BFS를 사용한 최단 경로 탐색 알고리즘과 같다.
box[nextH][nextY][nextX] = box[h][y][x] + 1;
q.push({nextH, nextY, nextX});
// zero => 익지 않은 토마토의 갯수
// 토마토가 익었으니 익지 않은 토마토의 갯수를 하나 줄여준다.
zero--;
}
}
// day에 -1 한 값을 return 해준다.
// 문제에서 시작 시 일 수 = 0 인데 우리는 위에서 day = 1부터 BFS를 시작했으므로
return day - 1;
}- 문제에서 요구하는 출력 값
1) 익지 않은 토마토가 있을 때 => -1
2) 모두 익었을 때 => 걸린 일 수
이므로 아래처럼 출력하면 되겠다.
if (zero > 0)
cout << "-1";
else
cout << day;코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 101
int M, N, H;
int box[MAX][MAX][MAX];
int zero = 0;
// 12시, 1시, 3시, 6시, 7시, 9시
int dh[] = {0, 1, 0, 0, -1, 0};
int dy[] = {1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0};
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, 0, 0, -1};
struct Tomato
{
int h = 0;
int y = 0;
int x = 0;
};
int Solve(vector<Tomato> &targets)
{
int day = 0;
queue<Tomato> q;
for (auto target : targets)
q.push(target);
while (!q.empty())
{
int h = q.front().h;
int y = q.front().y;
int x = q.front().x;
q.pop();
day = max(day, box[h][y][x]);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
int nextH = h + dh[i];
int nextY = y + dy[i];
int nextX = x + dx[i];
if (nextH < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX < 0 ||
nextH >= H || nextY >= N || nextX >= M)
continue;
if (box[nextH][nextY][nextX] == -1 || box[nextH][nextY][nextX] >= 1)
continue;
box[nextH][nextY][nextX] = box[h][y][x] + 1;
q.push({nextH, nextY, nextX});
zero--;
}
}
return day - 1;
}
int main()
{
// 가로 >> 세로 >> 높이
cin >> M >> N >> H;
vector<Tomato> targets;
for (int i = 0; i < H; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < M; k++)
{
cin >> box[i][j][k];
if (box[i][j][k] == 1)
targets.push_back({i, j, k});
else if (box[i][j][k] == 0)
zero++;
}
int day = Solve(targets);
if (zero > 0)
cout << "-1";
else
cout << day;
}주석코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 101
int M, N, H;
int box[MAX][MAX][MAX];
int zero = 0;
// 12시, 1시, 3시, 6시, 7시, 9시
int dh[] = {0, 1, 0, 0, -1, 0};
int dy[] = {1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0};
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, 0, 0, -1};
struct Tomato
{
int h = 0;
int y = 0;
int x = 0;
};
int Solve(vector<Tomato> &targets)
{
// 익을 수 있는 토마토가 모두 익는데 걸리는 일 수
int day = 0;
// Tomato => {h, y, x}
queue<Tomato> q;
// targets => 시작 시 익어있는 토마토들의 좌표
// queue에 targets를 모두 넣어두고 한 번에 BFS를 수행한다.
for (auto target : targets)
q.push(target);
// BFS
while (!q.empty())
{
int h = q.front().h;
int y = q.front().y;
int x = q.front().x;
q.pop();
// 일 수 업데이트
// 시작 시 day = 1 이다.
// 익은 토마토의 좌표부터 탐색하기 때문에(익은 토마토 = 1)
day = max(day, box[h][y][x]);
// dh[], dy[], dx[] 배열 원소 갯수 = 6
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
int nextH = h + dh[i];
int nextY = y + dy[i];
int nextX = x + dx[i];
if (nextH < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX < 0 ||
nextH >= H || nextY >= N || nextX >= M)
continue;
// 다음 좌표에 토마토가 없거나 || 이미 익은 토마토라면 => 건너뛴다.
if (box[nextH][nextY][nextX] == -1 || box[nextH][nextY][nextX] >= 1)
continue;
// 다음 좌표 = 현재 날짜 + 1
// BFS를 사용한 최단 경로 탐색 알고리즘과 같다.
box[nextH][nextY][nextX] = box[h][y][x] + 1;
q.push({nextH, nextY, nextX});
// zero => 익지 않은 토마토의 갯수
// 토마토가 익었으니 익지 않은 토마토의 갯수를 하나 줄여준다.
zero--;
}
}
// day에 -1 한 값을 return 해준다.
// 문제에서 시작 시 일 수 = 0 인데 우리는 위에서 day = 1부터 BFS를 시작했으므로
return day - 1;
}
int main()
{
// 가로 >> 세로 >> 높이
cin >> M >> N >> H;
// Tomato => {h, y, x}
vector<Tomato> targets;
// 높이만큼 반복
for (int i = 0; i < H; i++)
{
// 세로(행)만큼 반복
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
// 가로(열)만큼 반복
for (int k = 0; k < M; k++)
{
// box[높이][세로][가로]
cin >> box[i][j][k];
// 익어있는 토마토의 좌표
if (box[i][j][k] == 1)
targets.push_back({i, j, k});
// 익지 않은 토마토의 갯수
else if (box[i][j][k] == 0)
zero++;
}
}
}
int day = Solve(targets);
if (zero > 0)
cout << "-1";
else
cout << day;
}